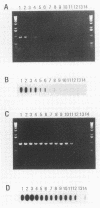
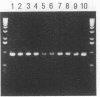
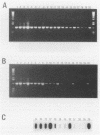
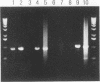
Abstract
Analysis based on comparisons of 16S rRNA sequences provides a rapid and reliable approach to identifying human pathogens. By directing oligonucleotide primers at sequences conserved throughout the eubacterial kingdom, bacterial 16S ribosomal DNA sequences of virtually any member of the eubacterial kingdom can be amplified by polymerase chain reaction and subsequently analyzed by sequence determination. Indeed, automated systems for broad-range amplification, sequencing, and data analysis are now feasible and may form the basis of the next generation of automated microbial identification systems. However, identification of pathogens by this strategy is hampered by the frequent contamination of reagents used for the amplification reaction, in particular Taq polymerase, with exogenous bacterial DNA. Here, we describe detailed investigations on the use of 8-methoxypsoralen and long-wave UV light to eliminate contaminating DNA in polymerase chain reaction reagents. The clinical utility of the developed procedure was demonstrated in a case of paucibacillary osteomyelitis, for which no specific bacterial agent had been cultured.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R. I., Krumholz L., Stahl D. A. Fluorescent-oligonucleotide probing of whole cells for determinative, phylogenetic, and environmental studies in microbiology. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):762–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.762-770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Sumner J. W., Dawson J. E., Tzianabos T., Greene C. R., Olson J. G., Fishbein D. B., Olsen-Rasmussen M., Holloway B. P., George E. H. Detection of the etiologic agent of human ehrlichiosis by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):775–780. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.775-780.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnoldi J., Schlüter C., Duchrow M., Hübner L., Ernst M., Teske A., Flad H. D., Gerdes J., Böttger E. C. Species-specific assessment of Mycobacterium leprae in skin biopsies by in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction. Lab Invest. 1992 May;66(5):618–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry T., Powell R., Gannon F. A general method to generate DNA probes for microorganisms. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Mar;8(3):233–236. doi: 10.1038/nbt0390-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard A., Gautier M., Mayau V. Detection and identification of mycoplasmas by amplification of rDNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jun 1;65(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90467-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böddinghaus B., Rogall T., Flohr T., Blöcker H., Böttger E. C. Detection and identification of mycobacteria by amplification of rRNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1751–1759. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1751-1759.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böddinghaus B., Wolters J., Heikens W., Böttger E. C. Phylogenetic analysis and identification of different serovars of Mycobacterium intracellulare at the molecular level. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jul;58(2):197–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb13978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger E. C. Frequent contamination of Taq polymerase with DNA. Clin Chem. 1990 Jun;36(6):1258–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger E. C. Rapid determination of bacterial ribosomal RNA sequences by direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger E. C., Teske A., Kirschner P., Bost S., Chang H. R., Beer V., Hirschel B. Disseminated "Mycobacterium genavense" infection in patients with AIDS. Lancet. 1992 Jul 11;340(8811):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90397-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K., Neimark H., Rumore P., Steinman C. R. Broad range DNA probes for detecting and amplifying eubacterial nucleic acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 1;48(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimino G. D., Metchette K. C., Tessman J. W., Hearst J. E., Isaacs S. T. Post-PCR sterilization: a method to control carryover contamination for the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):99–107. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards U., Rogall T., Blöcker H., Emde M., Böttger E. C. Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7843–7853. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaydos C. A., Quinn T. C., Eiden J. J. Identification of Chlamydia pneumoniae by DNA amplification of the 16S rRNA gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):796–800. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.796-800.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göbel U., Maas R., Haun G., Vinga-Martins C., Stanbridge E. J. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes complementary to rRNA for group- and species-specific detection of mycoplasmas. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 Jun;23(6):742–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshina S., Kahn S. M., Jiang W., Green P. H., Neu H. C., Chin N., Morotomi M., LoGerfo P., Weinstein I. B. Direct detection and amplification of Helicobacter pylori ribosomal 16S gene segments from gastric endoscopic biopsies. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Nov-Dec;13(6):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(90)90079-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman T., Ståhl S., Hornes E., Uhlén M. Direct solid phase sequencing of genomic and plasmid DNA using magnetic beads as solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4937–4946. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinno Y., Yoshiura K., Niikawa N. Use of psoralen as extinguisher of contaminated DNA in PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6739–6739. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner P., Böttger E. C. Microheterogeneity within rRNA of Mycobacterium gordonae. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):1049–1050. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.1049-1050.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo M. C., Berninger M. S., Hartley J. L. Use of uracil DNA glycosylase to control carry-over contamination in polymerase chain reactions. Gene. 1990 Sep 1;93(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90145-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou C. Y., Moore J. L., Schochetman G. Use of UV irradiation to reduce false positivity in polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1991 Apr;10(4):442–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H. Polymerase chain reaction: trenches to benches. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1281–1285. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1281-1285.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Telford S. R., 3rd, Rys P. N., Dodge D. E., White T. J., Malawista S. E., Spielman A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in museum specimens of Ixodes dammini ticks. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1420–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2402635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand K. H., Houck H. Taq polymerase contains bacterial DNA of unknown origin. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Dec;4(6):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90003-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Loutit J. S., Schmidt T. M., Falkow S., Tompkins L. S. The agent of bacillary angiomatosis. An approach to the identification of uncultured pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1573–1580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Schmidt T. M., MacDermott R. P., Falkow S. Identification of the uncultured bacillus of Whipple's disease. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 30;327(5):293–301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207303270501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogall T., Flohr T., Böttger E. C. Differentiation of Mycobacterium species by direct sequencing of amplified DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Sep;136(9):1915–1920. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-9-1915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogall T., Wolters J., Flohr T., Böttger E. C. Towards a phylogeny and definition of species at the molecular level within the genus Mycobacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;40(4):323–330. doi: 10.1099/00207713-40-4-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Trust T. J. Rapid identification of Campylobacter species using oligonucleotide probes to 16S ribosomal RNA. Mol Cell Probes. 1989 Jun;3(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(89)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossau R., Vanmechelen E., De Ley J., Van Heuverswijn H. Specific Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA-probes derived from ribosomal RNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jun;135(6):1735–1745. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-6-1735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Shedding light on PCR contamination. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):27–27. doi: 10.1038/343027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. M., Pace B., Pace N. R. Detection of DNA contamination in Taq polymerase. Biotechniques. 1991 Aug;11(2):176–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teske A., Wolters J., Böttger E. C. The 16S rRNA nucleotide sequence of Mycobacterium leprae: phylogenetic position and development of DNA probes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 May 15;64(2-3):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90601-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. E., Guiver L., Miller R. F., Hopkin J. M. DNA amplification on induced sputum samples for diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1991 Jun 8;337(8754):1378–1379. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93062-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., McCutchan T. F. Rapid, sensitive diagnosis of malaria based on ribosomal RNA. Lancet. 1989 Jun 17;1(8651):1343–1346. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Barns S. M., Pelletier D. A., Lane D. J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):697–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. H., Blitchington R. B., Greene R. C. Amplification of bacterial 16S ribosomal DNA with polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1942–1946. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1942-1946.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. H., Blitchington R., Frothingham R., Wilson J. A. Phylogeny of the Whipple's-disease-associated bacterium. Lancet. 1991 Aug 24;338(8765):474–475. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90545-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. H., Blitchington R., Shah P., McDonald G., Gilmore R. D., Mallavia L. P. Probe directed at a segment of Rickettsia rickettsii rRNA amplified with polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2692–2696. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2692-2696.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]