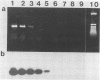
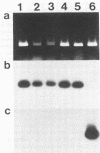
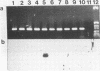
Abstract
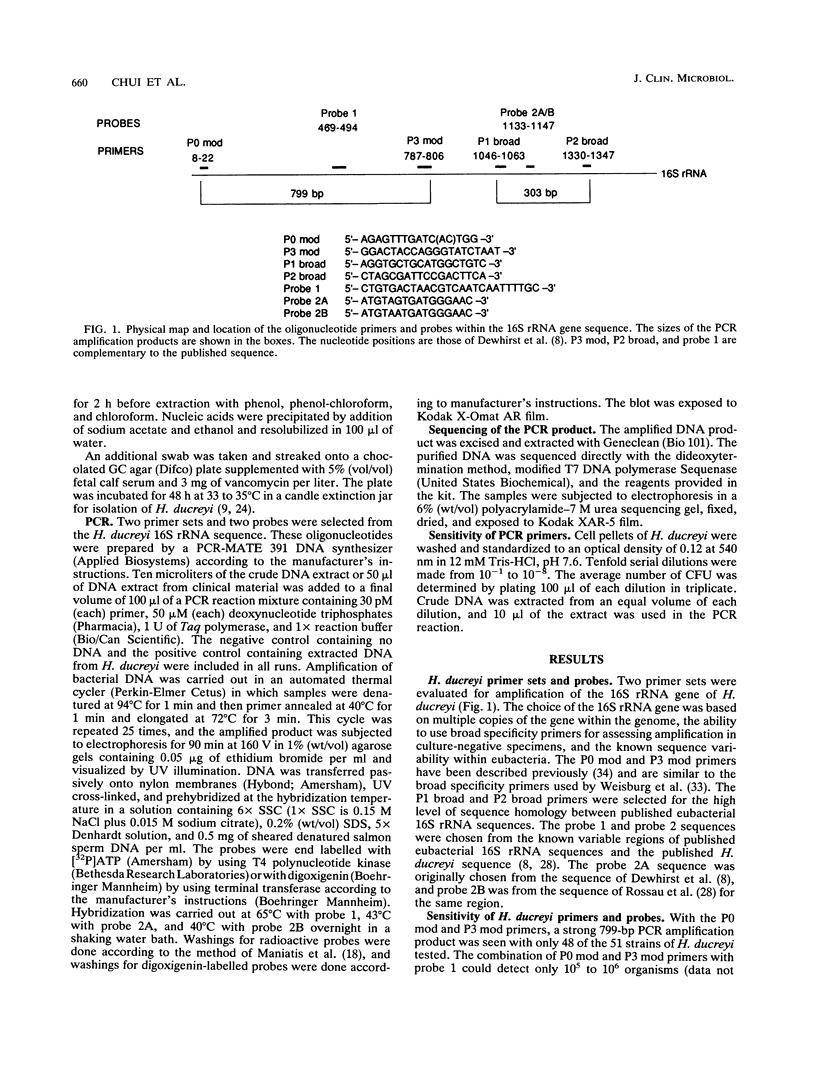
The published nucleotide sequences of the 16S rRNA gene of Haemophilus ducreyi were used to develop primer sets and probes for the diagnosis of chancroid by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) DNA amplification. One set of broad specificity primers yielded a 303-bp PCR product from all bacteria tested. Two 16-base probes internal to this sequence were species specific for H. ducreyi when tested with 12 species of the families Pasteurellaceae and Enterobacteriaceae. The two probes in combination with the broad specificity primers were 100% sensitive with 51 strains of H. ducreyi isolated from six continents over a 15-year period. The direct detection of H. ducreyi from 100 clinical specimens by PCR showed a sensitivity of 83 to 98% and a specificity of 51 to 67%, depending on the number of amplification cycles.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L. Biology of Haemophilus ducreyi. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):377–389. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.377-389.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard R. C., Abeck D., Korting H. C., Dangor Y., Braun-Falco O. Morphologische Varianten des durch Haemophilus ducreyi bedingten Genitalulkus. Hautarzt. 1989 Jul;40(7):443–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt K. A., Hoke A. W. Simplified laboratory technique for diagnosis of chancroid. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Aug;102(2):188–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapel T., Brown W. J., Jeffries C., Stewart J. A. The microbiological flora of penile ulcerations. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jan;137(1):50–56. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary B. P., Kumari S., Bhatia R., Agarwal D. S. Bacteriological study of chancroid. Indian J Med Res. 1982 Sep;76:379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangor Y., Ballard R. C., da L Exposto F., Fehler G., Miller S. D., Koornhof H. J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of genital ulcer disease. Sex Transm Dis. 1990 Oct-Dec;17(4):184–189. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199010000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denys G. A., Chapel T. A., Jeffries C. D. An indirect fluorescent antibody technique for Haemophilus ducreyi. Health Lab Sci. 1978 Jul;15(3):128–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhirst F. E., Paster B. J., Olsen I., Fraser G. J. Phylogeny of 54 representative strains of species in the family Pasteurellaceae as determined by comparison of 16S rRNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):2002–2013. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.2002-2013.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dylewski J., Nsanze H., Maitha G., Ronald A. Laboratory diagnosis of Haemophilus ducreyi: sensitivity of culture media. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;4(3):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast M. V., D'Costa L. J., Nsanze H., Piot P., Curran J., Karasira P., Mirza N., Maclean I. W., Ronald A. R. The clinical diagnosis of genital ulcer disease in men in the tropics. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Apr-Jun;11(2):72–76. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198404000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn G. Y., Karim Q. N., Easmon C. S. The production and characterisation of rabbit antiserum and murine monoclonal antibodies to Haemophilus ducreyi. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Mar;31(3):219–224. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-3-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Loftus T. A. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with all strains of Haemophilus ducreyi. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):196–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.196-198.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim Q. N., Finn G. Y., Easmon C. S., Dangor Y., Dance D. A., Ngeow Y. F., Ballard R. C. Rapid detection of Haemophilus ducreyi in clinical and experimental infections using monoclonal antibody: a preliminary evaluation. Genitourin Med. 1989 Dec;65(6):361–365. doi: 10.1136/sti.65.6.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus S. J., Werman B. S., Biddle J. W., Sottnek F. O., Ewing E. P., Jr Pseudogranuloma inguinale caused by haemophilus ducreyi. Arch Dermatol. 1982 Jul;118(7):494–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegren U., Kaiser R., Caskey C. T., Hood L. DNA diagnostics--molecular techniques and automation. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):229–237. doi: 10.1126/science.3051381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsch W. C., Haas N., Stüttgen G. Ultrastructural detection of Haemophilus ducreyi in biopsies of chancroid. Arch Dermatol Res. 1978 Nov 10;263(2):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00446436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarley M. E., Cruz P. D., Jr, Sontheimer R. D. Chancroid: clinical variants and other findings from an epidemic in Dallas County, 1986-1987. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988 Aug;19(2 Pt 1):330–337. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(88)70180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A. Chancroid and Haemophilus ducreyi. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):137–157. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Museyi K., Van Dyck E., Vervoort T., Taylor D., Hoge C., Piot P. Use of an enzyme immunoassay to detect serum IgG antibodies to Haemophilus ducreyi. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1039–1043. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nsanze H., Fast M. V., D'Costa L. J., Tukei P., Curran J., Ronald A. Genital ulcers in Kenya. Clinical and laboratory study. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Dec;57(6):378–381. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.6.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nsanze H., Plummer F. A., Maggwa A. B., Maitha G., Dylewski J., Piot P., Ronald A. R. Comparison of media for the primary isolation of Haemophilus ducreyi. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Jan-Mar;11(1):6–9. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198401000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons L. M., Shayegani M., Waring A. L., Bopp L. H. DNA probes for the identification of Haemophilus ducreyi. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1441–1445. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1441-1445.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossau R., Duhamel M., Jannes G., Decourt J. L., Van Heuverswyn H. The development of specific rRNA-derived oligonucleotide probes for Haemophilus ducreyi, the causative agent of chancroid. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Feb;137(2):277–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman R. S., Kraus S. J., Miller R. G., Sottnek F. O., Kleris G. S. Chancroidal ulcers that are not chancroid. Cause and epidemiology. Arch Dermatol. 1984 May;120(5):636–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Sanders L. L., Schmid G. P., Tam M. R., Morse S. A. Use of dot-immunobinding and immunofluorescence assays to investigate clinically suspected cases of chancroid. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):879–887. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P., Sanders L. L., Jr, Blount J. H., Alexander E. R. Chancroid in the United States. Reestablishment of an old disease. JAMA. 1987 Dec 11;258(22):3265–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm A. W., Stolting G. J., Cormane R. H., Zanen H. C. Clinical and microbiological evaluation of 46 episodes of genital ulceration. Genitourin Med. 1987 Apr;63(2):98–101. doi: 10.1136/sti.63.2.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Barns S. M., Pelletier D. A., Lane D. J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):697–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. H., Blitchington R. B., Greene R. C. Amplification of bacterial 16S ribosomal DNA with polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1942–1946. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1942-1946.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]