Abstract
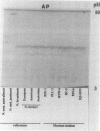
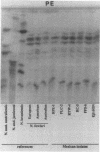
Five Naegleria strains isolated from patients with primary amebic meningoencephalitis and one strain isolated from the water of an artificial canal were investigated. All strains were pathogenic for mice when instilled intranasally and showed cytopathic effects in Vero cell cultures. Their growth characteristics (isolation and subculture at 45 degrees C), serological results, and isoenzyme patterns permitted us to identify the six strains as Naegleria fowleri. This is the first time that Naegleria fowleri has been isolated from patients with primary amebic meningoencephalitis in Mexico.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cerva L. Naegleria fowleri and N. lovaniensis: differences in sensitivity to trimethoprim and other antifolates. Z Parasitenkd. 1986;72(5):585–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00925478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. F. Isoenzyme patterns of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Naegleria spp. using agarose isoelectric focusing. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):319–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J., Van Dijck P., Van de Voorde H. The effect of thermal pollution on the distribution of Naegleria fowleri. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):7–13. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlec V., Cerva L., Skvárová J. Virulent Naegleria fowleri in an indoor swimming pool. Science. 1978 Sep 15;201(4360):1025–1025. doi: 10.1126/science.684423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Corella E., De León B., de Jonckheere J. F. Meningoencefalitis amibiana primaria por Naegleria fowleri en un adolescente de Huetamo, Michoacán, México. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 1989 Sep;46(9):619–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F. Biology of Naegleria spp. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):114–133. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.114-133.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera F., Lares F., Gallegos E., Ramirez E., Bonilla P., Calderon A., Martinez J. J., Rodriguez S., Alcocer J. Pathogenic amoebae in natural thermal waters of three resorts of Hidalgo, Mexico. Environ Res. 1989 Dec;50(2):289–295. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(89)80010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela G., López-Corella E., De Jonckheere J. F. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis in a young male from northwestern Mexico. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(4):558–559. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Balamuth W. Comparative studies on related free-living and pathogenic amebae with special reference to Acanthamoeba. J Protozool. 1975 May;22(2):245–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1975.tb05860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Healy G. R. Comparative antigenic analysis of pathogenic and free-living Naegleria species by the gel diffusion and immunoelectrophoresis techniques. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):95–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.95-108.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Peralta M. J., Brandt F. H., Wilson M., Aloisio C., Franko E. Production of monoclonal antibodies to Naegleria fowleri, agent of primary amebic meningoencephalitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1629–1634. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1629-1634.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warhurst D. C. Pathogenic free-living amoebae. Parasitol Today. 1985 Jul;1(1):24–28. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(85)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings F. M., Amuso P. T., Chang S. L., Lewis A. L. Isolation and identification of pathogenic Naegleria from Florida lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):661–667. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.661-667.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonckheere J. F. Pathogenic and nonpathogenic Acanthamoeba spp. in thermally polluted discharges and surface waters. J Protozool. 1981 Feb;28(1):56–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1981.tb02804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]