Abstract
A nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) protocol was developed for rapid genotyping of hepatitis B virus (HBV). During the first PCR round, a universal HBV primer pair was used to amplify the entire pre-S region of the HBV genome. Within the pre-S region, many nucleotide exchanges are observed. These are partly correlated to the serological hepatitis B surface antigen subtypes. Five additional subtype-specific primers were selected from that region which, together with two universal non-group-specific primers, generated specific combinations of two to four DNA fragments of defined sizes. By this approach, 55 hepatitis B surface antigen-positive patients from a pediatric oncology unit in Germany were analyzed. Fifty-four patients who had been infected within 2 years had an identical pattern in the multiplex PCR, suggesting a common source of infection and person-to-person transmission within the unit. One child who was infected 5 years later had a different PCR pattern and, therefore, must have been infected from a different source. Furthermore, 109 serum samples taken from pregnant Cameroonian women and 25 serum samples from their babies taken 6 months after birth were analyzed. In one case, mother-to-infant transmission of the virus was demonstrated. Apart from its role in epidemiological studies on HBV, multiplex PCR may also be a useful tool for rapid genetic analysis in other fields if there is a moderate degree of sequence variation which enables the design of specific primers.
Full text
PDF

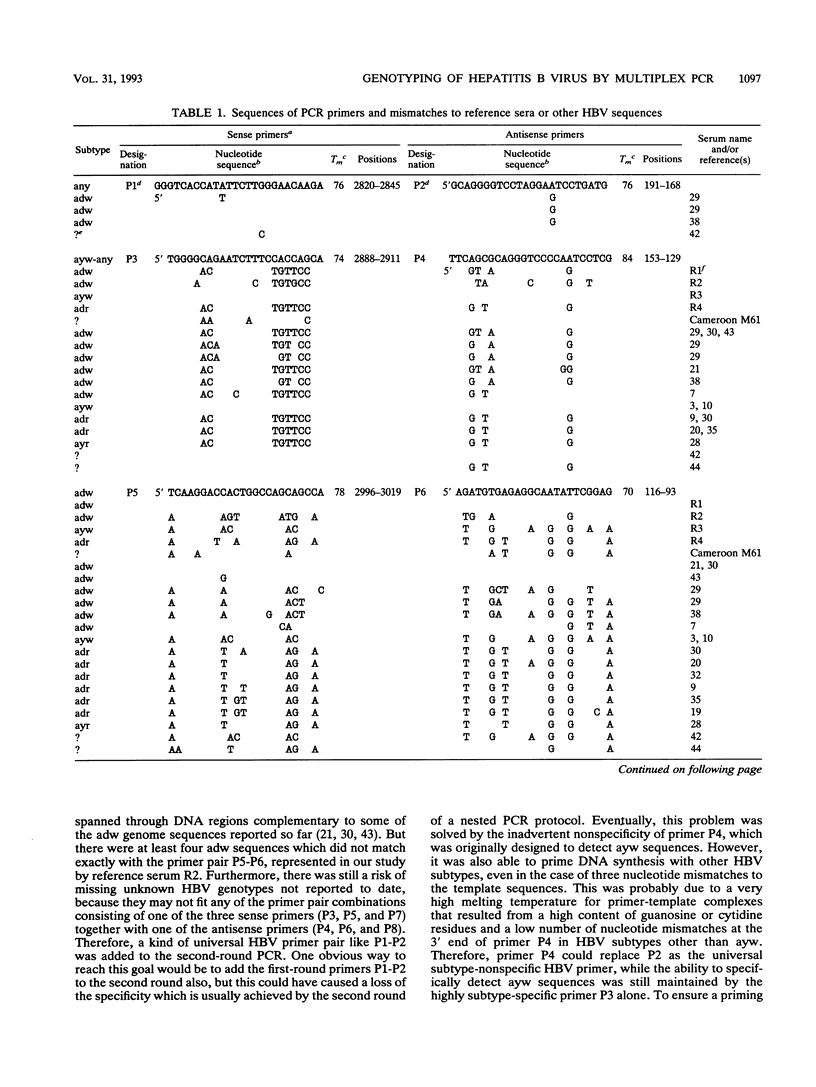

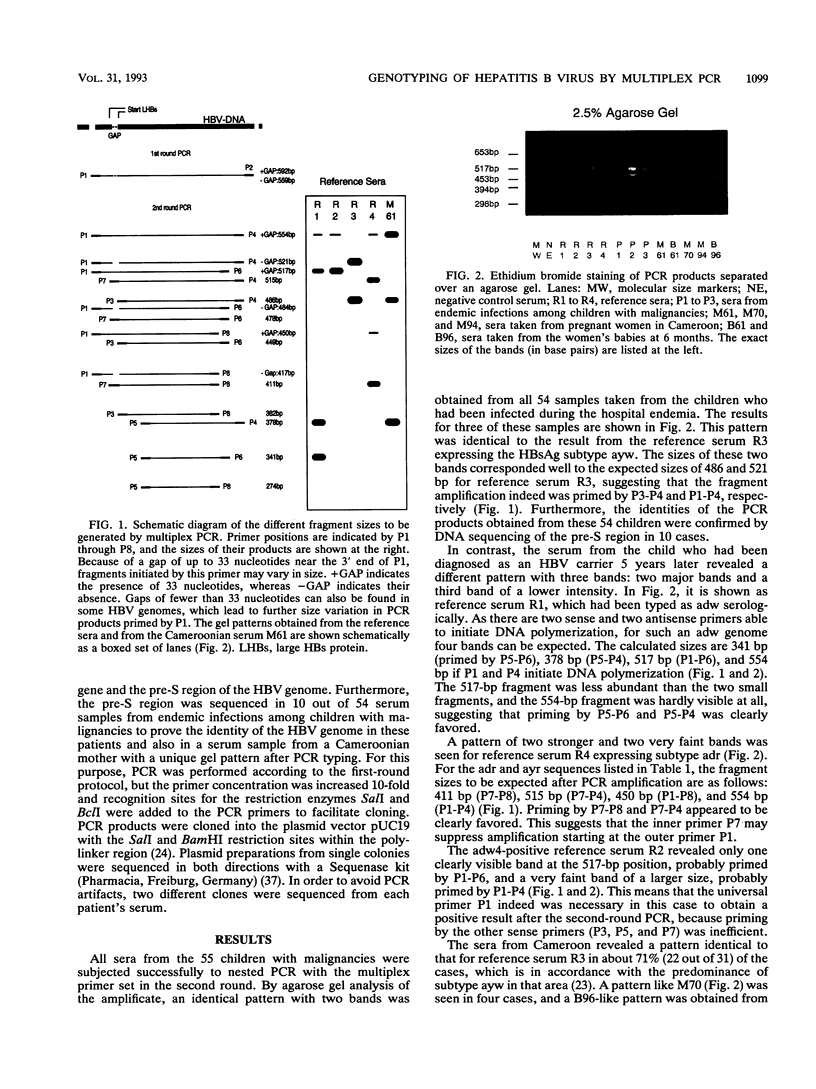



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert J., Fenyö E. M. Simple, sensitive, and specific detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in clinical specimens by polymerase chain reaction with nested primers. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1560–1564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1560-1564.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram U., Repp R., Lampert F., Fischer H. P., Willems W. R. Hepatitis-B-Endemie bei zytostatisch behandelten Kindern. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1990 Aug 17;115(33):1253–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichko V., Pushko P., Dreilina D., Pumpen P., Gren E. Subtype ayw variant of hepatitis B virus. DNA primary structure analysis. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80771-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Penna A., Bertoletti A., Valli A., Antoni A. D., Giuberti T., Cavalli A., Petit M. A., Fiaccadori F. Cellular immune response to hepatitis B virus-encoded antigens in acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3442–3449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Miyanohara A., Nozaki C., Yoneyama T., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Cloning and structural analyses of hepatitis B virus DNAs, subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4601–4610. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson J. A., Tedder R. S., Briggs M., Tuke P., Glazebrook J. A., Trute A., Parker D., Barbara J. A., Contreras M., Aloysius S. Detection of hepatitis C viral sequences in blood donations by "nested" polymerase chain reaction and prediction of infectivity. Lancet. 1990 Jun 16;335(8703):1419–1422. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91446-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermann K. H., Goldmann U., Schwartz W., Seyffarth T., Baumgarten H., Gerlich W. H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):396–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.396-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Gerety R. J., Smallwood L. A., Barker L. F. Subtyping of hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody by radioimmunoassay. Gastroenterology. 1977 Feb;72(2):290–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Rossi J. J., Wallace R. B. Synthesis and use of synthetic oligonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:323–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izraeli S., Pfleiderer C., Lion T. Detection of gene expression by PCR amplification of RNA derived from frozen heparinized whole blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):6051–6051. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.6051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Miller R. H. Characterization of primers for optimal amplification of hepatitis B virus DNA in the polymerase chain reaction assay. J Virol Methods. 1990 Aug;29(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90115-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Koike K. Complete nucleotide sequence of hepatitis B virus DNA of subtype adr and its conserved gene organization. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert F., Willems W. R., Bertram U., Berthold F. No adverse prognostic influence of hepatitis B virus infection in acute childhood lymphoblastic leukemia. Blut. 1987 Aug;55(2):115–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00631782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzur S., Burgert S., Blumberg B. S. Geographical distribution of Australia antigen determinants d, y and w. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):38–40. doi: 10.1038/247038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimms L. T., Floreani M., Tyner J., Whitters E., Rosenlof R., Wray L., Goetze A., Sarin V., Eble K. Discrimination of hepatitis B virus (HBV) subtypes using monoclonal antibodies to the PreS1 and PreS2 domains of the viral envelope. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):604–619. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90031-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norder H., Hammas B., Löfdahl S., Couroucé A. M., Magnius L. O. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of nine different serotypes of hepatitis B surface antigen and genomic classification of the corresponding hepatitis B virus strains. J Gen Virol. 1992 May;73(Pt 5):1201–1208. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-5-1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norder H., Hammas B., Magnius L. O. Typing of hepatitis B virus genomes by a simplified polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1990 Jul;31(3):215–221. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890310308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Imai M., Shimozaki M., Hoshi Y., Iizuka H., Gotanda T., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned hepatitis B virus genome, subtype ayr: comparison with genomes of the other three subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2305–2314. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Sakugawa H., Sastrosoewignjo R. I., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Typing hepatitis B virus by homology in nucleotide sequence: comparison of surface antigen subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2575–2583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter-Jordan K., Rosenberg E. I., Keiser J. F., Gross J. D., Ross A. M., Nasim S., Garrett C. T. Nested polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of cytomegalovirus overcomes false positives caused by contamination with fragmented DNA. J Med Virol. 1990 Feb;30(2):85–91. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890300202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repp R., Keller C., Borkhardt A., Csecke A., Schaefer S., Gerlich W. H., Lampert F. Detection of a hepatitis B virus variant with a truncated X gene and enhancer II. Arch Virol. 1992;125(1-4):299–304. doi: 10.1007/BF01309646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rho H. M., Kim K., Hyun S. W., Kim Y. S. The nucleotide sequence and reading frames of a mutant hepatitis B virus subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2124–2124. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih J. W., Cheung L. C., Alter H. J., Lee L. M., Gu J. R. Strain analysis of hepatitis B virus on the basis of restriction endonuclease analysis of polymerase chain reaction products. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1640–1644. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1640-1644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson P. D., Riess J. T., Krueger L. E. Determination of HBsAg subtypes in different high risk populations using monoclonal antibodies. J Virol Methods. 1991 Jun;33(1-2):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90004-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiers V., Nakajima E., Kremsdorf D., Mack D., Schellekens H., Driss F., Goudeau A., Wands J., Sninsky J., Tiollais P. Transmission of hepatitis B from hepatitis-B-seronegative subjects. Lancet. 1988 Dec 3;2(8623):1273–1276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92891-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Li J. S., Vitvitski L., Trépo C. Active hepatitis B virus replication in the presence of anti-HBe is associated with viral variants containing an inactive pre-C region. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):596–603. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90030-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotsumoto S., Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Subtyping hepatitis B virus DNA in free or integrated forms by amplification of the S-gene sequences by the polymerase chain reaction and single-track sequencing for adenine. J Virol Methods. 1990 May;28(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90024-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyzik E., Gerlich W. H., Uy A., Köchel H., Thomssen R. Assay of hepatitis B virus genome titers in sera of infected subjects. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;5(3):330–335. doi: 10.1007/BF02017791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



