Abstract
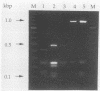
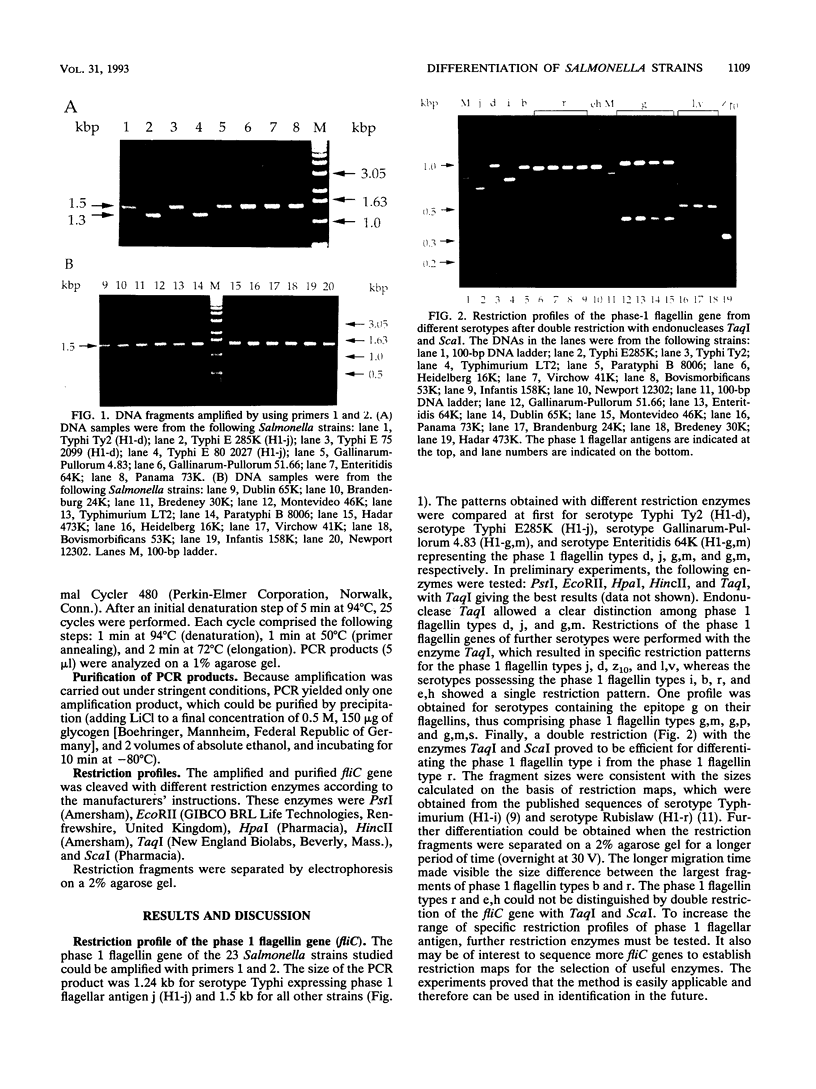
The large antigenic diversity (over 2,300 serotypes) expressed by Salmonella strains can probably be observed at the genetic level. The phase 1 flagellin gene fliC was amplified, and the amplified fragment was cleaved with a mixture of both endonucleases TaqI and ScaI. The restriction patterns observed allowed differentiation of flagellar types b, i, d, j, l,v, and z10. Flagellar group g (g,m, g,p, or g,m,s) could be differentiated from the other flagellar types. Flagellar types r and e,h could not be separated, although they could be distinguished from the other flagellar types studied. Practical applications of flagellar gene restriction are the distinction between serotype Gallinarum-Pullorum, which carries a cryptic gene for flagellar type g,m, and nonmotile Vi-negative variants of serotype Typhi, and the tentative assignation of nonmotile variants of Salmonella serotypes to a flagellar type.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The covalent structure of the phase-1 flagellar filament protein of Salmonella typhimurium and its comparison with other flagellins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M. Y., Bockemühl J., McWhorter-Murlin A. Supplement 1991 (no. 35) to the Kauffmann-White scheme. Res Microbiol. 1992 Oct;143(8):807–811. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Smith N. H., Li J., Beltran P., Ferris K. E., Kopecko D. J., Rubin F. A. Molecular evolutionary genetics of the cattle-adapted serovar Salmonella dublin. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3587–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3587-3592.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. H., Beltran P., Selander R. K. Recombination of Salmonella phase 1 flagellin genes generates new serovars. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2209–2216. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2209-2216.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. H., Selander R. K. Sequence invariance of the antigen-coding central region of the phase 1 flagellar filament gene (fliC) among strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):603–609. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.603-609.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. Covalent structure of three phase-1 flagellar filament proteins of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. The nucleotide sequence of the H-1r gene of Salmonella rubislaw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8227–8227. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINDER N. D., LEDERBERG J. Genetic exchange in Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1952 Nov;64(5):679–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.5.679-699.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]