Abstract
A new method for fingerprinting Aspergillus fumigatus by random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) by using single primers with arbitrary sequences is described. Five primers were examined with 19 isolates from six patients with aspergilloma as well as with A. fumigatus NCPF 2109. Two of the primers (GCT GGT GG and GCG CAC GG, 5' to 3') gave adequate discrimination between isolates, generating five and six types, respectively. Combination of the results obtained with each of these two primers generated 12 types. This compares very favorably with immunoblot fingerprinting and XbaI-generated restriction fragment length polymorphisms on the same isolates. Typeability and reproducibility were good with RAPD, and RAPD was less labor-intensive than immunoblot fingerprinting. RAPD typing results suggested that aspergillomas sometimes contain isolates of more than one type.
Full text
PDF
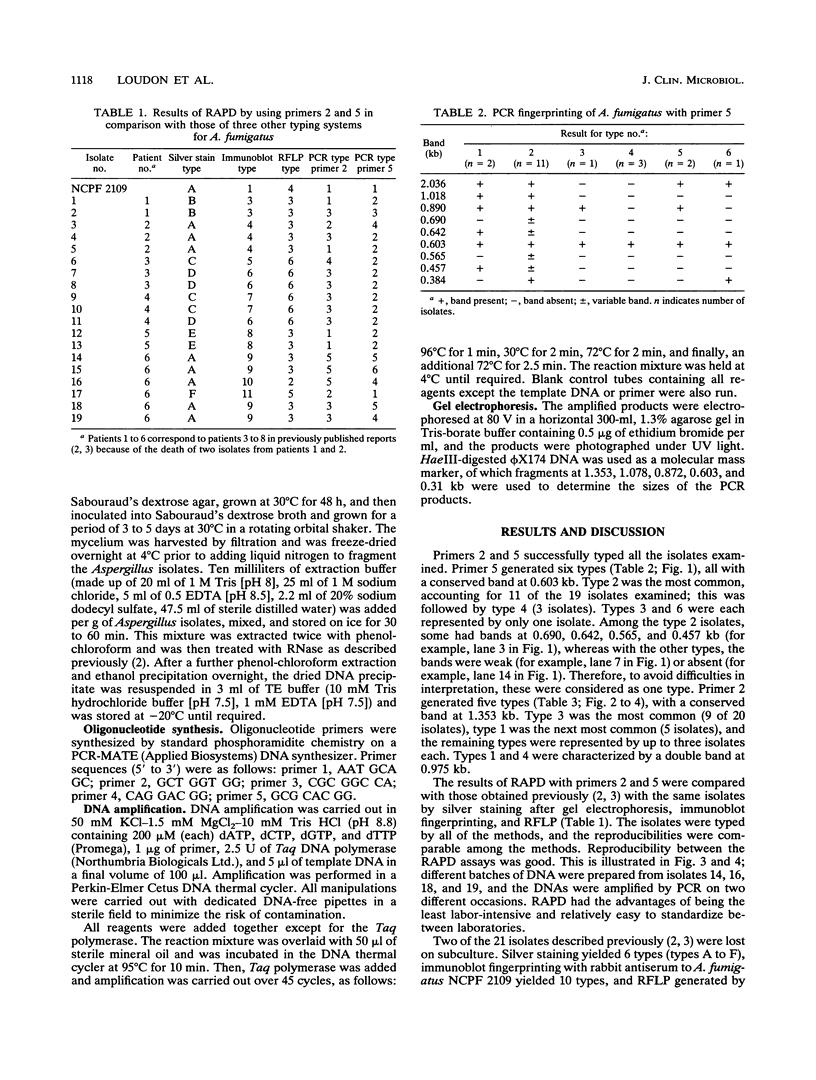
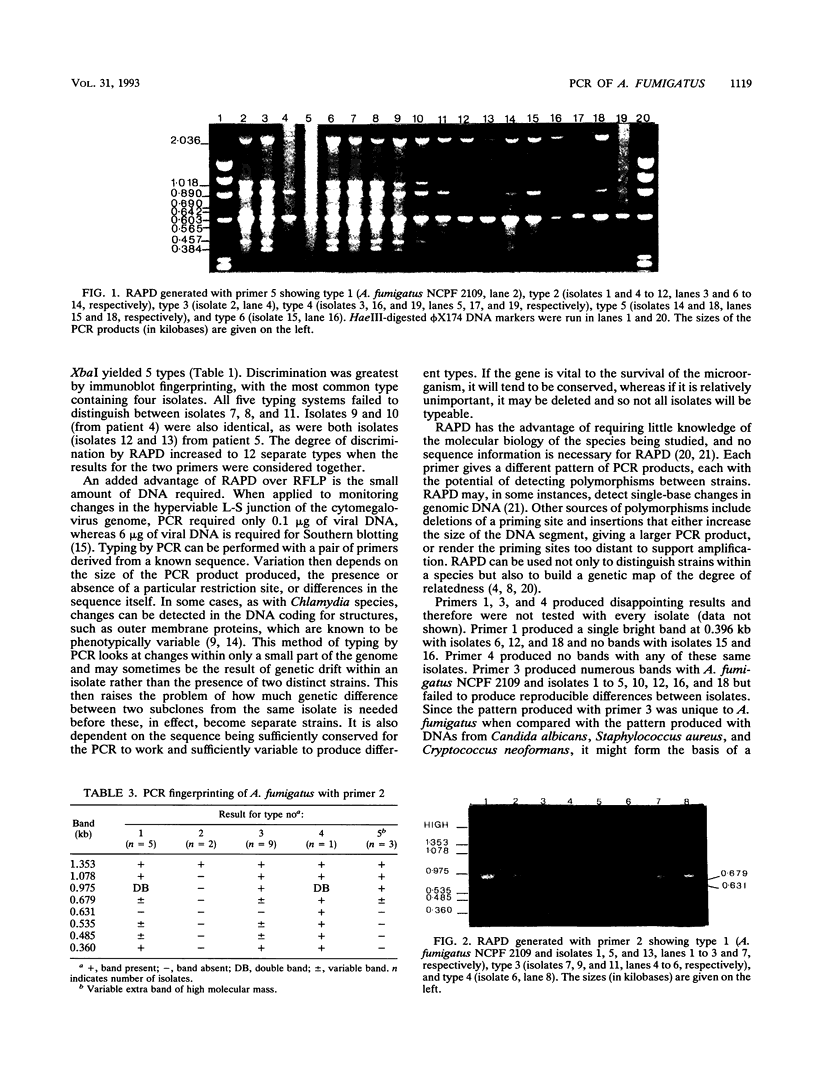


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubin J. T., Collandre H., Candotti D., Ingrand D., Rouzioux C., Burgard M., Richard S., Huraux J. M., Agut H. Several groups among human herpesvirus 6 strains can be distinguished by Southern blotting and polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):367–372. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.367-372.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Coke A., Matthews R. C. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Aspergillus fumigatus DNA. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Apr;45(4):324–327. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.4.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Matthews R. C., Clark I., Milne L. J. Immunoblot fingerprinting Aspergillus fumigatus. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Mar 31;118(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowhurst R. N., Hawthorne B. T., Rikkerink E. H., Templeton M. D. Differentiation of Fusarium solani f. sp. cucurbitae races 1 and 2 by random amplification of polymorphic DNA. Curr Genet. 1991 Nov;20(5):391–396. doi: 10.1007/BF00317067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Clemons K. V., Hanson L. H., Stevens D. A. Restriction endonuclease analysis of total cellular DNA of Aspergillus fumigatus isolates of geographically and epidemiologically diverse origin. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1151–1158. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Shankland G. S., Stevens D. A. DNA fingerprinting of Aspergillus fumigatus isolates from patients with aspergilloma. J Med Vet Mycol. 1991;29(5):339–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanti F., Conti S., Campani L., Morace G., Dettori G., Polonelli L. Studies on the epidemiology of Aspergillus fumigatus infections in a university hospital. Eur J Epidemiol. 1989 Mar;5(1):8–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00145038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin P. H., Annis S. L. Rapid identification of genetic variation and pathotype of Leptosphaeria maculans by random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2482–2486. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2482-2486.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltenboeck B., Kousoulas K. G., Storz J. Two-step polymerase chain reactions and restriction endonuclease analyses detect and differentiate ompA DNA of Chlamydia spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1098–1104. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1098-1104.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulik M. M., Brooks A. G. Electrophoretic studies of soluble proteins from Aspergillus spp. Mycologia. 1970 Mar-Apr;62(2):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie C. E., Flannigan B., Milne L. J. Morphological studies on clinical isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus. J Med Vet Mycol. 1988;26(6):335–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Kohno S., Maesaki S., Yamada H., Koga H., Tamura M., Kuraishi H., Sugiyama J. Application of ubiquinone systems and electrophoretic comparison of enzymes to identification of clinical isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus and several other species of Aspergillus. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):1999–2005. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.1999-2005.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D. E., Samadpour M., Krieger J. N. Detection of variable DNA repeats in diverse eukaryotic microorganisms by a single set of polymerase chain reaction primers. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2746–2751. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2746-2751.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez P., Vekris A., de Barbeyrac B., Dutilh B., Bonnet J., Bebear C. Typing of Chlamydia trachomatis by restriction endonuclease analysis of the amplified major outer membrane protein gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1132–1136. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1132-1136.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol D. M., Demmler G. J., Buffone G. J. Rapid epidemiologic analysis of cytomegalovirus by using polymerase chain reaction amplification of the L-S junction region. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):839–844. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.839-844.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Burchard G. D. Differentiation of pathogenic from nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica by restriction fragment analysis of a single gene amplified in vitro. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):250–255. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.250-255.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys R., Hester M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4238–4246. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4238-4246.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. W., Lambden P. R., Clarke I. N. Genetic diversity and identification of human infection by amplification of the chlamydial 60-kilodalton cysteine-rich outer membrane protein gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1188–1193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1188-1193.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. C., Bennett J. E., Vogel C. L., Carbone P. P., DeVita V. T. Aspergillosis. The spectrum of the disease in 98 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1970 Mar;49(2):147–173. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197003000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]