Abstract
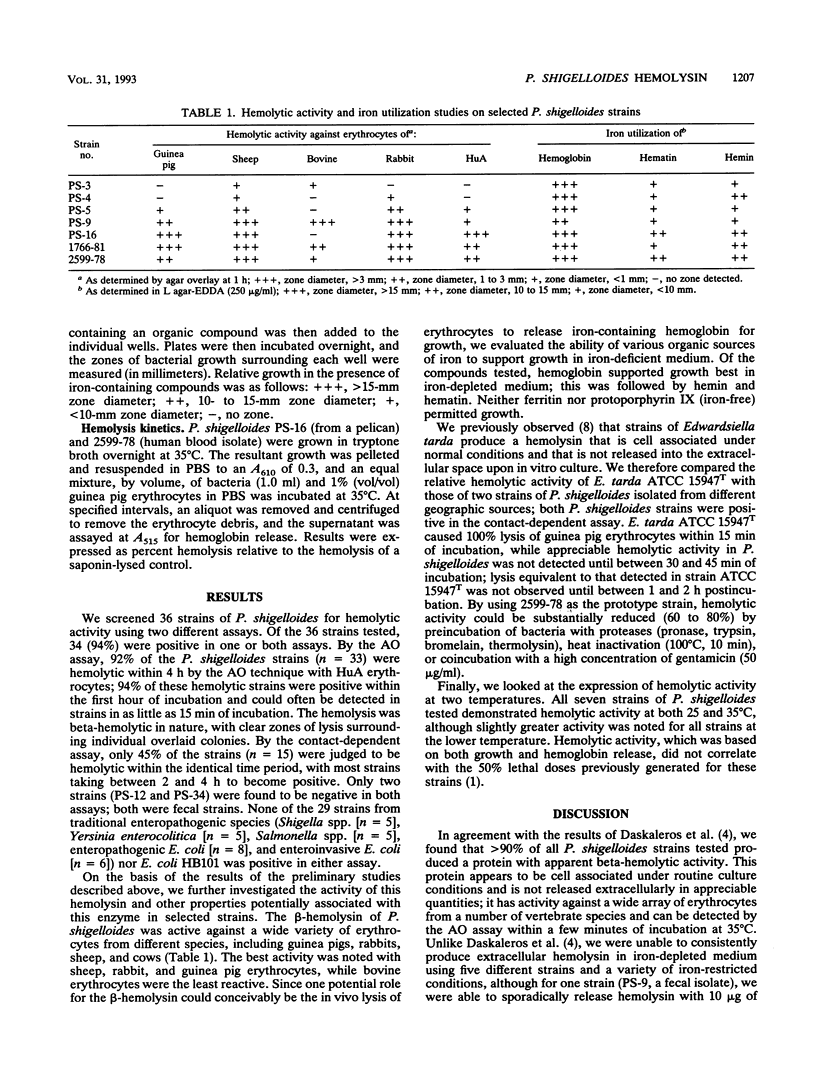
More than 90% of the Plesiomonas shigelloides strains that we tested produced a beta-hemolysin, as judged by the results of agar overlay and contact-dependent hemolysis assays. The hemolysin was cell associated, was active against the erythrocytes of various animal species, and was synthesized at both 25 and 35 degrees C. Activity was lost after thermal or proteolytic treatments or after preincubation in the presence of gentamicin; hemolytic activity did not appear to correlate with the previously established 50% lethal doses for seven of these strains. The hemolysin may play a role in iron acquisition in vivo via the lysis of erythrocytes, liberating hemoglobin, or, alternatively, may be involved in gastrointestinal disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott S. L., Kokka R. P., Janda J. M. Laboratory investigations on the low pathogenic potential of Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):148–153. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.148-153.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenden R. A., Miller M. A., Janda J. M. Clinical disease spectrum and pathogenic factors associated with Plesiomonas shigelloides infections in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Mar-Apr;10(2):303–316. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskaleros P. A., Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M. Iron uptake in Plesiomonas shigelloides: cloning of the genes for the heme-iron uptake system. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2706–2711. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2706-2711.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner S. E., Fowlston S. E., George W. L. In vitro production of cholera toxin-like activity by Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):720–722. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Tzipori S., Robins-Browne R. M., Tall B. D., Levine M. M. In vitro and in vivo pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):979–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.979-985.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Blake P. A., Farmer J. J., 3rd Plesiomonas enteric infections in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):690–694. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Abbott S. L., Oshiro L. S. Penetration and replication of Edwardsiella spp. in HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):154–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.154-161.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Z. D., Nelson A. C., Mathewson J. J., Ericsson C. D., DuPont H. L. Intestinal secretory immune response to infection with Aeromonas species and Plesiomonas shigelloides among students from the United States in Mexico. J Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;164(5):979–982. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.5.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kain K. C., Kelly M. T. Clinical features, epidemiology, and treatment of Plesiomonas shigelloides diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):998–1001. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.998-1001.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto T., Kinoshita Y., Shimada T., Sakazaki R. Two epidemics of diarrhoeal disease possibly caused by Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Apr;80(2):275–280. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


