Abstract
Screening for Chlamydia trachomatis infection in men has traditionally been limited to men who present with urethral symptoms, thereby limiting the detection of asymptomatic chlamydia infection in men. In order to effectively screen both symptomatic and asymptomatic men, we evaluated a newly developed polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay, Amplicor C. trachomatis, from Roche Molecular Systems for the detection of C. trachomatis in urine specimens in comparison with urethral culture. A total of 530 male urine specimens were collected from 322 symptomatic and 208 asymptomatic men attending two sexually transmitted disease clinics in Baltimore, Md. The prevalence of C. trachomatis by culture was 9.8% (10.6% in symptomatic men and 8.2% in asymptomatic men). Compared with culture, the sensitivity of the PCR was 92.8%, the specificity was 94.7%, the positive predictive value was 68.4%, and the negative predictive value was 99.1%. Discrepant results between culture and PCR were further analyzed by direct fluorescent-antibody staining of elementary bodies in urine sediment and in culture transport vials and by major outer membrane protein PCR of transport media for specimens with negative culture. The revised sensitivity and specificity of PCR for urine were 95.0 and 99.8%, respectively, and the positive and negative predictive values were 98.7 and 99.1%, respectively. The sensitivity of culture compared with PCR and/or direct fluorescent-antibody staining was 68.4%. These results indicate that the PCR assay is a highly sensitive and specific assay for the detection of C. trachomatis in male urine specimens and provides a noninvasive technique for routine screening of chlamydia infection in both symptomatic and asymptomatic men.
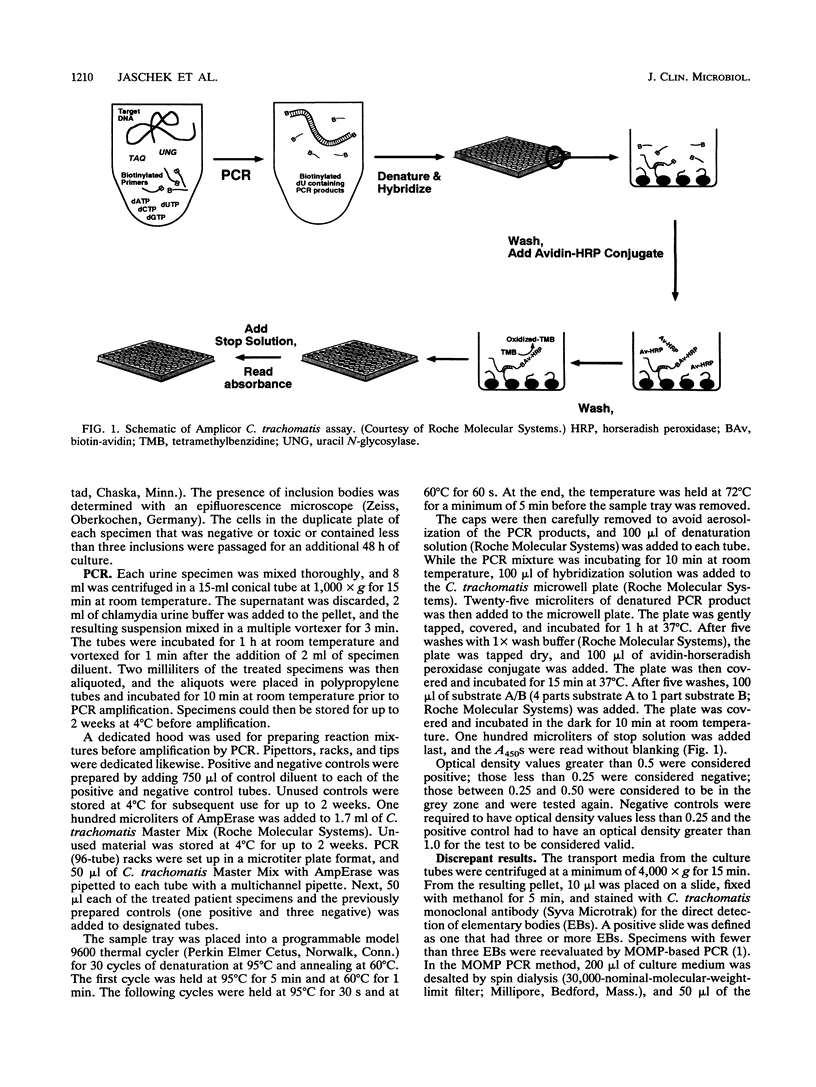
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bobo L., Coutlee F., Yolken R. H., Quinn T., Viscidi R. P. Diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis cervical infection by detection of amplified DNA with an enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1968–1973. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1968-1973.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernesky M., Castriciano S., Sellors J., Stewart I., Cunningham I., Landis S., Seidelman W., Grant L., Devlin C., Mahony J. Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis antigens in urine as an alternative to swabs and cultures. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):124–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A., Stamm W. E., Gaydos C., Welsh L., Quinn T. C., Schachter J., Moncada J. Multicenter evaluation of the AntigEnz Chlamydia enzyme immunoassay for diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis genital infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2762–2764. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2762-2764.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaydos C. A., Reichart C. A., Long J. M., Welsh L. E., Neumann T. M., Hook E. W., 3rd, Quinn T. C. Evaluation of Syva enzyme immunoassay for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in genital specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1541–1544. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1541-1544.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getts A. G. Diagnosing Chlamydia trachomatis urethritis by first-catch urine enzyme immunoassay in adolescent males. J Adolesc Health Care. 1989 May;10(3):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0197-0070(89)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen I. P. A comparison of urine sample to urethral swab for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in asymptomatic young men using two enzyme immunoassays. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 May-Jun;19(3):165–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judson F. N. Assessing the number of genital chlamydial infections in the United States. J Reprod Med. 1985 Mar;30(3 Suppl):269–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi G. P., Seitz M., Edstrom R., Cruz J., Costello P., Szabo K. Evaluation of three immunoassays for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in urine specimens from asymptomatic males. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2793–2796. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2793-2796.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeffelholz M. J., Lewinski C. A., Silver S. R., Purohit A. P., Herman S. A., Buonagurio D. A., Dragon E. A. Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in endocervical specimens by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2847–2851. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2847-2851.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer H. M., Gilroy C. B., Thomas B. J., Hay P. E., Gilchrist C., Taylor-Robinson D. Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis by the polymerase chain reaction in swabs and urine from men with non-gonococcal urethritis. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Apr;44(4):321–325. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.4.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul I. D., Caul E. O. Evaluation of three Chlamydia trachomatis immunoassays with an unbiased, noninvasive clinical sample. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):220–222. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.220-222.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellors J., Mahony J., Jang D., Pickard L., Castriciano S., Landis S., Stewart I., Seidelman W., Cunningham I., Chernesky M. Rapid, on-site diagnosis of chlamydial urethritis in men by detection of antigens in urethral swabs and urine. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):407–409. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.407-409.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer M. A., Prager V., Shalwitz J., Vaughan E., Moscicki B., Brown R., Wibbelsman C., Schachter J. Prevalence of urethral Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae among asymptomatic, sexually active adolescent boys. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):223–224. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E., Cole B. Asymptomatic Chlamydia trachomatis urethritis in men. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Jul-Sep;13(3):163–165. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198607000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E. Diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis genitourinary infections. Ann Intern Med. 1988 May;108(5):710–717. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-5-710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Lee M. F., Yin S. C., Yang D. M., Cheng S. F. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction, monoclonal antibody based enzyme immunoassay, and cell culture for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in genital specimens. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 Jul-Aug;19(4):193–197. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199207000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


