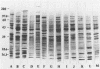
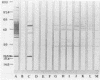
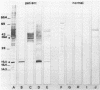
Abstract
Current methods for the diagnosis of melioidosis are based on bacteriological culture. A number of serological tests currently available lack specificity and sensitivity. This is largely due to the use of crude antigens which results in a significant cross-reactivity with sera from individuals infected with other bacteria. In this study five different antigens were prepared and evaluated for their potential usefulness in diagnosis of melioidosis. These included a 19.5-kDa antigen which was previously shown to be specific by Western blotting (immunoblotting), a crude cell extract, a veronal extract, a 39.0-kDa antigen, and an immunoaffinity-purified antigen. All antigens were used for detecting antibody in sera from patients with septicemic melioidosis by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The results were compared with those obtained with sera from patients with other bacterial infections and normal sera from areas where the infection is and is not endemic. The 19.5-kDa antigen exhibited the most satisfactory results, with 92% sensitivity, 91% specificity, 81% positive predictive value, and 96% negative predictive value based on a background obtained with normal sera from the area where the infection is nonendemic. These values were 82% sensitivity, 96% specificity, 94% positive predictive value, and 87% negative predictive value based on results with normal sera from the area where the infection is endemic. Results from this study showed that the 19.5-kDa antigen was potentially useful in the diagnosis of melioidosis and deserves further investigation.
Full text
PDF
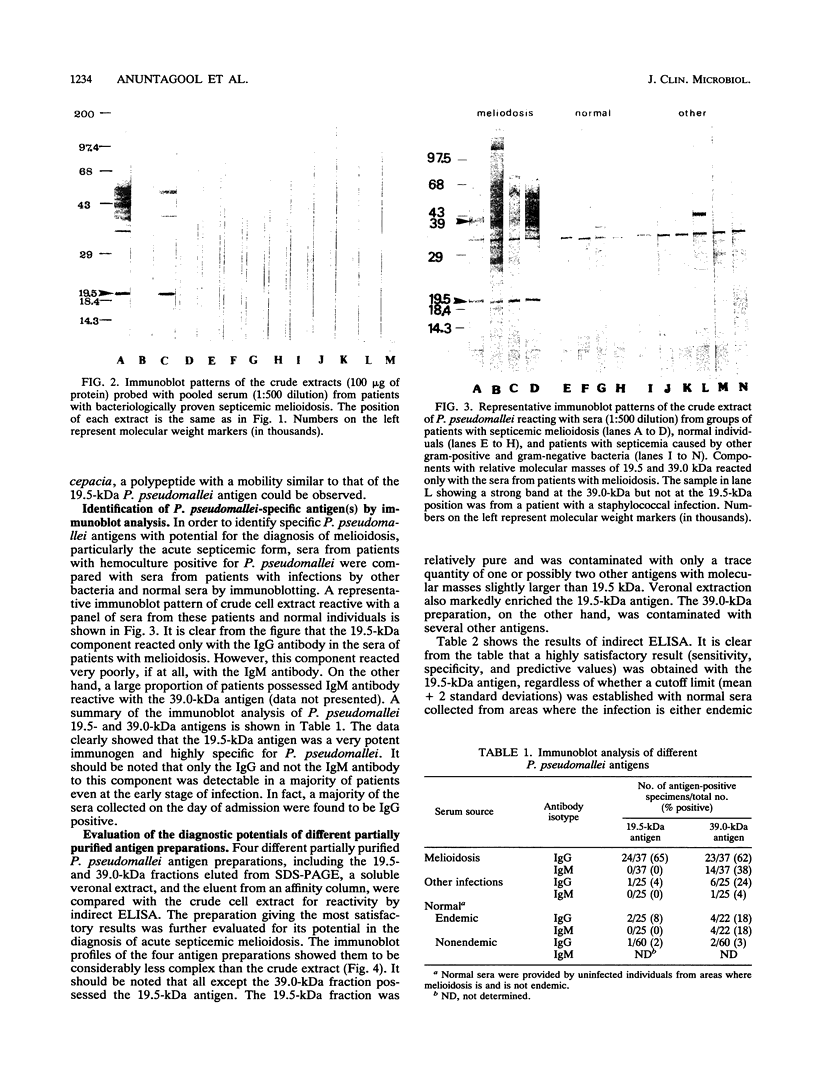
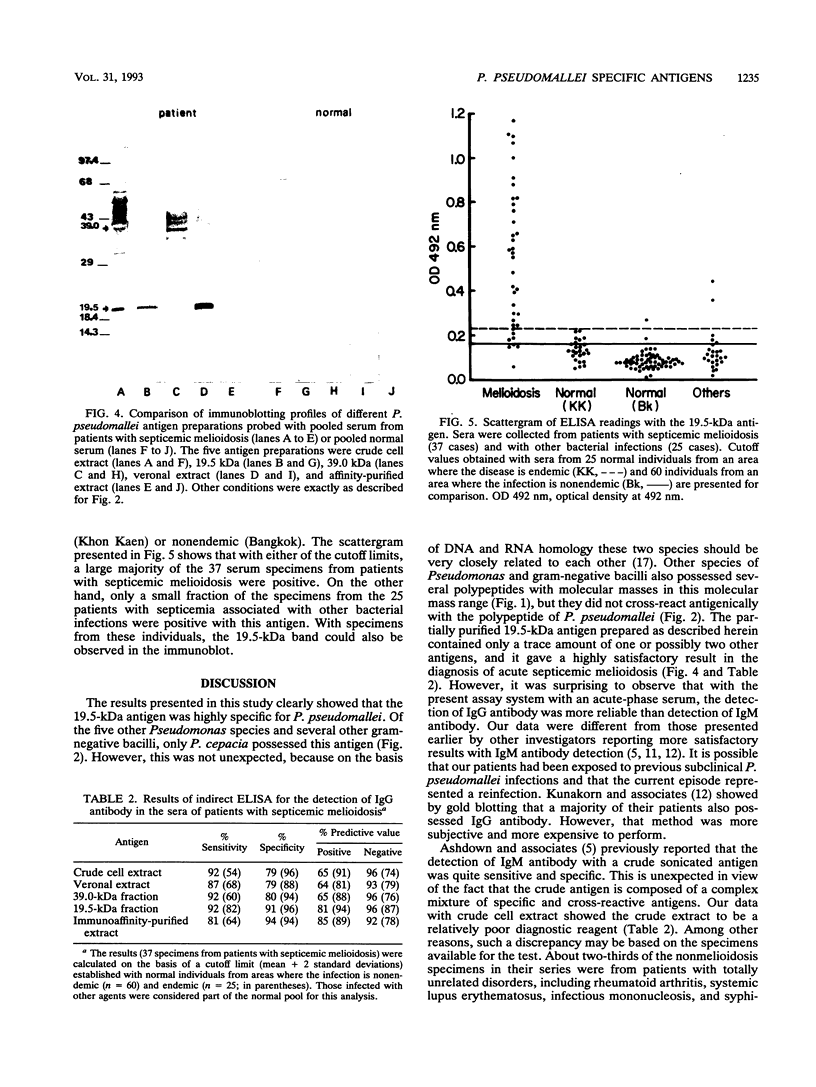

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. D., Huxsoll D. L., Warner A. R., Jr, Shepler V., Dorsey A. Serological diagnosis of human melioidosis with indirect hemagglutination and complement fixation tests. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Nov;20(5):825–833. doi: 10.1128/am.20.5.825-833.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anuntagool N., Sarasombath S., Ratanabanangkoon K. Studies on the 52 kDa antigen of Salmonella typhi: physicochemical stability, purification by affinity chromatography and immunochemical specificity. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1991 Sep;22(3):362–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appassakij H., Silpapojakul K. R., Wansit R., Pornpatkul M. Diagnostic value of the indirect hemagglutination test for melioidosis in an endemic area. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Mar;42(3):248–253. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.42.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashdown L. R., Johnson R. W., Koehler J. M., Cooney C. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of clinical and subclinical melioidosis. J Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;160(2):253–260. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.2.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashdown L. R. Relationship and significance of specific immunoglobulin M antibody response in clinical and subclinical melioidosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):361–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.361-364.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber C., Vladoianu I. R., Dimache G. Contributions to the study of Salmonella. Immunological specificity of proteins separated from Salmonella typhi. Immunology. 1966 Oct;11(4):287–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaowagul W., White N. J., Dance D. A., Wattanagoon Y., Naigowit P., Davis T. M., Looareesuwan S., Pitakwatchara N. Melioidosis: a major cause of community-acquired septicemia in northeastern Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):890–899. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmkrong-at A., Migasena S., Suntharasamai P., Bunnag D., Priwan R., Sirisinha S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to Gnathostoma antigen in patients with intermittent cutaneous migratory swelling. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):847–851. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.847-851.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp O. H., Vinogradov S. N. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from proteins. Anal Biochem. 1978 Nov;91(1):230–235. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90835-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khupulsup K., Petchclai B. Application of indirect hemagglutination test and indirect fluorescent antibody test for IgM antibody for diagnosis of melioidosis in Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Mar;35(2):366–369. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunakorn M., Boonma P., Khupulsup K., Petchclai B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin M specific antibody for the diagnosis of melioidosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1249–1253. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1249-1253.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunakorn M., Petchclai B., Khupulsup K., Naigowit P. Gold blot for detection of immunoglobulin M (IgM)- and IgG-specific antibodies for rapid serodiagnosis of melioidosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2065–2067. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2065-2067.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIGG C. SEROLOGIC STUDIES ON SUBCLINICAL MELIOIDOSIS. J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:18–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Klinger J. D., Stern R. C. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization among patients with cystic fibrosis. A new opportunist. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 May;131(5):791–796. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.5.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]