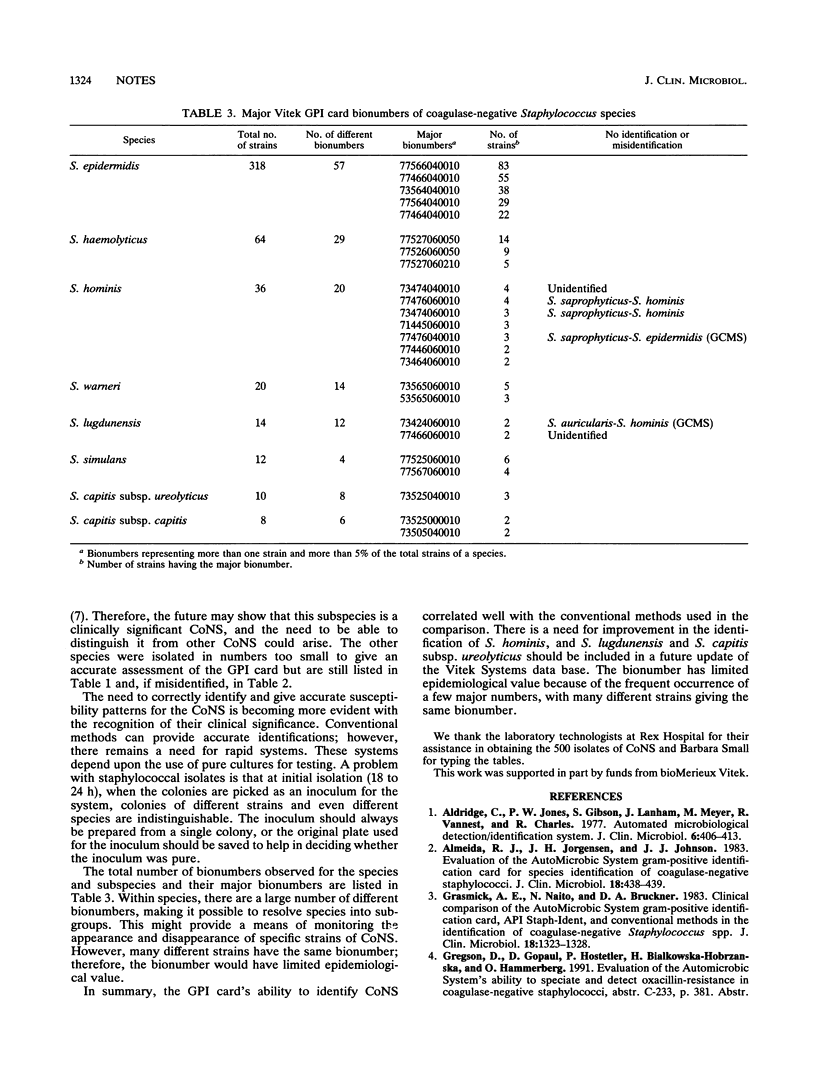
Abstract
Vitek Systems' Gram-Positive Identification test (GPI) card was evaluated for the ability to identify 12 coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species and subspecies. The bionumber generated from the GPI card was examined for its potential use in epidemiological studies. Results indicated that the GPI card had a high degree of correlation with the conventional methods of identification. The species identified with the greatest accuracy were Staphylococcus epidermidis (92%), S. haemolyticus (95%), S. capitis subsp. capitis (88%), and S. saprophyticus (100%). S. hominis (63%) was identified with the least accuracy. The bionumber was found to have limited epidemiological value because of the frequent occurrence of a few major bionumbers.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge C., Jones P. W., Gibson S., Lanham J., Meyer M., Vannest R., Charles R. Automated microbiological detection/identification system. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):406–413. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.406-413.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida R. J., Jorgensen J. H., Johnson J. E. Evaluation of the automicrobic system gram-positive identification card for species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):438–439. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.438-439.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasmick A. E., Naito N., Bruckner D. A. Clinical comparison of the AutoMicrobic system gram-positive identification card, API Staph-Ident, and conventional methods in the identification of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1323–1328. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1323-1328.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamory B. H., Parisi J. T., Hutton J. P. Staphylococcus epidermidis: a significant nosocomial pathogen. Am J Infect Control. 1987 Apr;15(2):59–74. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(87)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleeman K. T., Bannerman T. L., Kloos W. E. Species distribution of coagulase-negative staphylococcal isolates at a community hospital and implications for selection of staphylococcal identification procedures. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1318–1321. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1318-1321.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Pfaller M. A., Wenzel R. P. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteremia. Mortality and hospital stay. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Jan 1;110(1):9–16. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews K. R., Oliver S. P., King S. H. Comparison of Vitek Gram-Positive Identification system with API Staph-Trac system for species identification of staphylococci of bovine origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1649–1651. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1649-1651.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Herwaldt L. A. Laboratory, clinical, and epidemiological aspects of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jul;1(3):281–299. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Ferraro M. J., Jerz M. E., Kissling J. Automated identification of gram-positive bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1091–1095. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1091-1095.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell C. M., Clarridge J. E., Young E. J., Guthrie R. K. Clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):236–239. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.236-239.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stager C. E., Davis J. R. Automated systems for identification of microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jul;5(3):302–327. doi: 10.1128/cmr.5.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


