Abstract
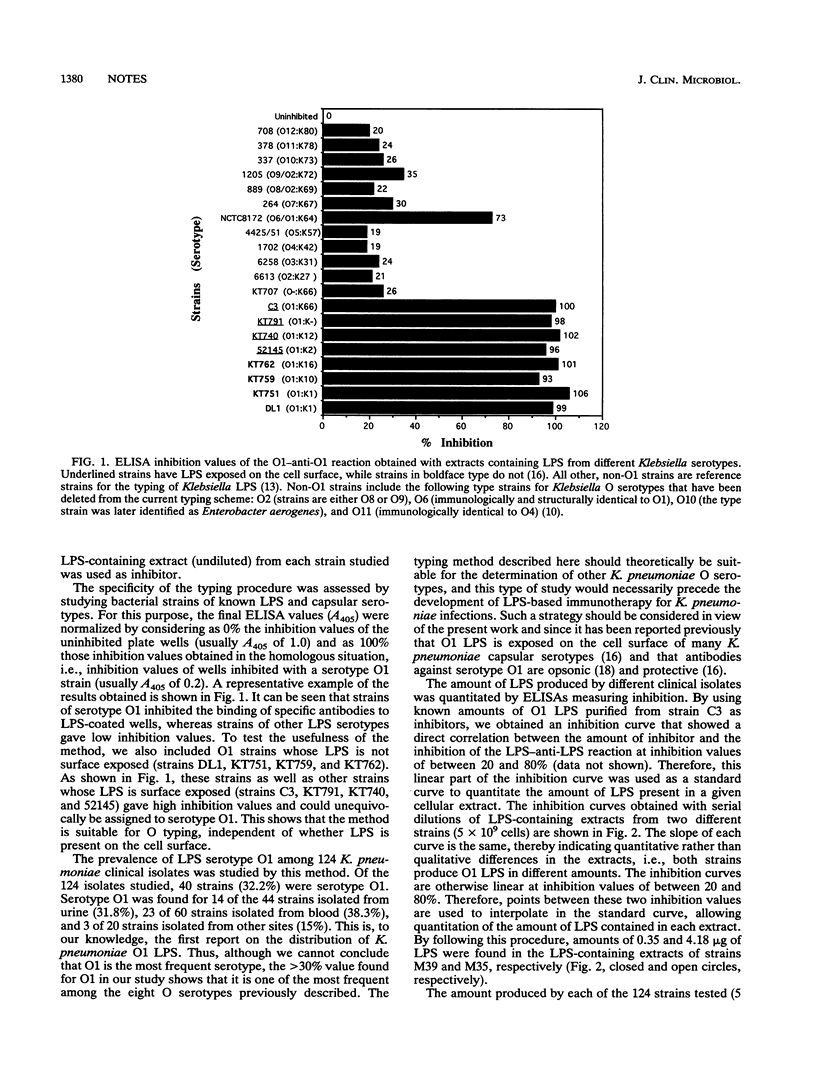
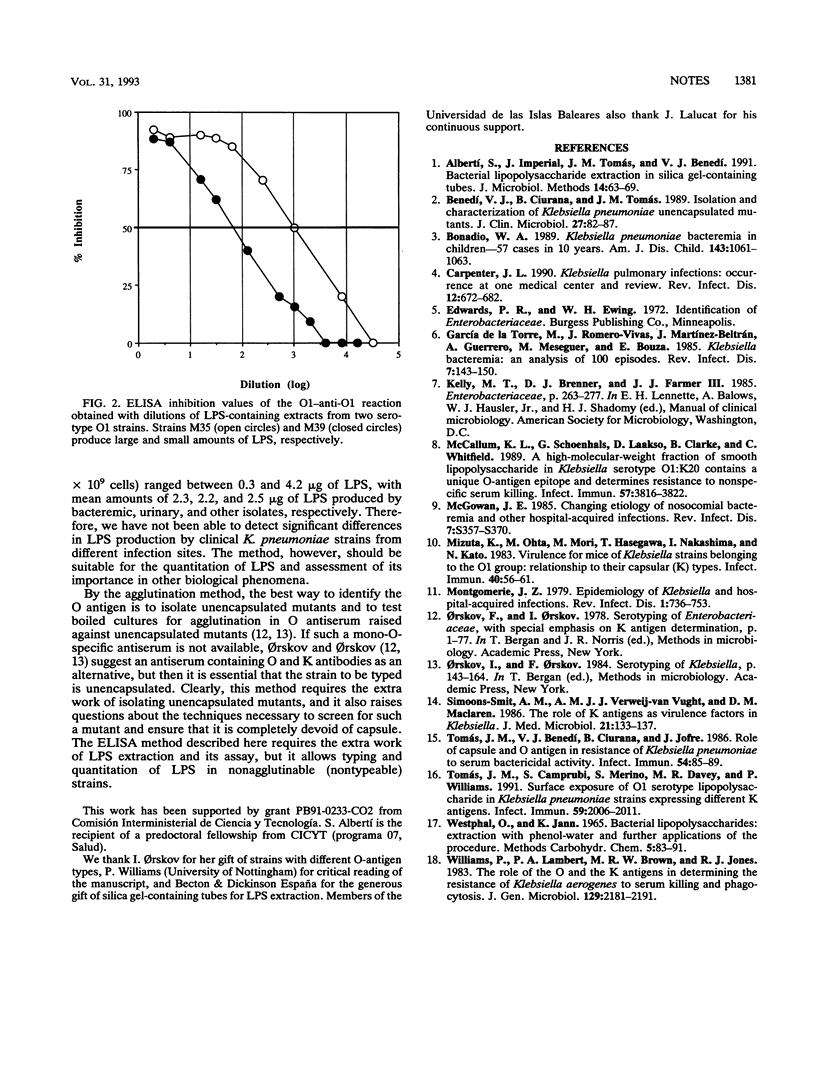
We describe a method for the typing and quantitation of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype O1 lipopolysaccharide (LPS) based on inhibition in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of a reaction of known O1 LPS antigen and anti-O1 antibody by unknown LPS extracts. Serotype O1 was found in 32% of the 124 K. pneumoniae clinical isolates tested, showing that this serotype is frequent among the eight O serotypes which have been described previously.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benedí V. J., Ciurana B., Tomás J. M. Isolation and characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae unencapsulated mutants. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.82-87.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonadio W. A. Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia in children. Fifty-seven cases in 10 years. Am J Dis Child. 1989 Sep;143(9):1061–1063. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1989.02150210095025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter J. L. Klebsiella pulmonary infections: occurrence at one medical center and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jul-Aug;12(4):672–682. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.4.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García de la Torre M., Romero-Vivas J., Martínez-Beltrán J., Guerrero A., Meseguer M., Bouza E. Klebsiella bacteremia: an analysis of 100 episodes. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):143–150. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum K. L., Schoenhals G., Laakso D., Clarke B., Whitfield C. A high-molecular-weight fraction of smooth lipopolysaccharide in Klebsiella serotype O1:K20 contains a unique O-antigen epitope and determines resistance to nonspecific serum killing. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3816–3822. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3816-3822.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr Changing etiology of nosocomial bacteremia and fungemia and other hospital-acquired infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7 (Suppl 3):S357–S370. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.supplement_3.s357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuta K., Ohta M., Mori M., Hasegawa T., Nakashima I., Kato N. Virulence for mice of Klebsiella strains belonging to the O1 group: relationship to their capsular (K) types. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):56–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.56-61.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomerie J. Z. Epidemiology of Klebsiella and hospital-associated infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Sep-Oct;1(5):736–753. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.5.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoons-Smit A. M., Verweij-van Vught A. M., MacLaren D. M. The role of K antigens as virulence factors in Klebsiella. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Mar;21(2):133–137. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-2-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomás J. M., Benedí V. J., Ciurana B., Jofre J. Role of capsule and O antigen in resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae to serum bactericidal activity. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):85–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.85-89.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomás J. M., Camprubi S., Merino S., Davey M. R., Williams P. Surface exposure of O1 serotype lipopolysaccharide in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains expressing different K antigens. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2006–2011. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2006-2011.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P., Lambert P. A., Brown M. R., Jones R. J. The role of the O and K antigens in determining the resistance of Klebsiella aerogenes to serum killing and phagocytosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2181–2191. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


