Abstract
The ABCB1-type multi-drug resistance efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) has been hypothesized to regulate hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis activity by limiting the access of glucocorticoids to the brain. In vivo systemic administration studies using P-gp-deficient mice have shown increased glucocorticoid entry to the brain compared with wild-type controls. However, these studies did not control for the presence of radiolabeled drug in the capillaries, verify an intact blood-brain barrier, or confirm stability of the glucocorticoids used. In the present study, an in situ brain perfusion method, coupled with capillary depletion and HPLC analyses, was used to quantify brain uptake of [3H]dexamethasone, [3H]cortisol, and [3H]corticosterone in P-gp-deficient and control mice. A vascular marker was included in these experiments. The results show that brain uptake of [3H]dexamethasone was increased in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and cerebellum, of P-gp-deficient mice compared with wild-type controls. Brain uptake of [3H]cortisol was increased in the hypothalamus of P-gp-deficient mice compared with wild-type controls, but no differences were detected in other regions. Brain uptake of [3H]corticosterone was not increased in P-gp-deficient mice compared with wild-type controls in any brain areas. Following our systemic administration of the same radiolabeled glucocorticoids, HPLC analysis of plasma samples identified additional radiolabeled components, likely to be metabolites. This could explain previous findings from systemic administration studies, showing an effect of P-gp not only for dexamethasone and cortisol, but also for corticosterone. This in situ study highlights the different affinities of dexamethasone, cortisol and corticosterone for P-gp, and suggests that the entry of the endogenous glucocorticoids into the mice brain is not tightly regulated by P-gp. Therefore, our current understanding of the role of P-gp in HPA regulation in mice requires revision.
Keywords: Antidepressants, Blood-brain barrier, Glucocorticoids, Multi-drug resistance P-glycoprotein, Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
INTRODUCTION
Transport of glucocorticoids across the blood-brain-barrier (BBB) is regulated by efflux membrane transporters, such as the ABCB1-type multi-drug resistance efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp), and this seems to have an effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis (1). Specifically, decreased HPA axis activity in P-gp-deficient mice compared with wild-type controls has been described, as measured by lower plasma corticosterone and adrenocorticotrophin-releasing hormone (ACTH), as well as lower hypothalamic expression of corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH). This has been explained as evidence of increased entry of corticosterone into the brains of P-gp-deficient mice, consequently increasing negative feedback (2, 3). Moreover, antidepressants have also been shown to inhibit P-gp in vitro, and to decrease HPA axis activity in vivo, leading to the hypothesis that antidepressants inhibit P-gp on the BBB and increase glucocorticoid access to the brain (4, 5, 6, 7).
Small (<400-500 Da) and lipophilic (log P>0.8) molecules are able to diffuse across the BBB; glucocorticoids possess these features and quickly enter the parenchyma (8), but the presence of efflux transporters complicate the process. P-gp, coded by the multi-drug resistance gene ABCB1, is a membrane-bound ABC class efflux transporter that has been localized on the luminal membrane of cerebral capillary endothelium (9). P-gp transports substrates against a diffusion gradient, from the cytoplasmic side to the blood side of the cell, and is believed to protect the brain from xenobiotic compounds (9, 10, 11). In vitro data indicate that mouse, rat and human P-gp can all transport cortisol (the main endogenous glucocorticoid in humans), as shown by experiments in mouse fibroblasts (6), primary rat neuronal cultures (6), as well as porcine kidney (LLC-PK1) cells transfected with the human ABCB1 (12, 13). Two mouse isoforms of ABCB1 exist, abcb1a and abcb1b, which share 90% homology with one another and 80% homology with ABCB1. Abcb1a is localized in the cerebral capillary endothelium, as well as in the liver, lung, kidney, and intestinal epithelium (11, 14, 15, 16). Abcb1b has been found in brain parenchyma, adrenal gland, and liver (15, 17), but its presence at the BBB is in doubt (18).
Meijer et al (19) and Karssen et al (13) administered a subcutaneous injection of [3H]dexamethasone, [3H]corticosterone, and [3H]cortisol to adrenalectomized abcb1a-deficient mice, and they found higher brain to blood concentration of [3H]dexamethasone and [3H]cortisol, but not [3H]corticosterone, in abcb1a-deficient mice compared with wild-type controls. They concluded that abcb1a plays a role in the access of dexamethasone and cortisol, but not of corticosterone, to the brain. Interestingly, this work is consistent with studies that demonstrated a lower retention of cortisol compared to corticosterone in rodent brain (8, 20). In contrast, Uhr et al (21) found that abcb1a and 1b-deficient mice subcutaneously injected with [3H]corticosterone had higher levels in their brains compared with wild-type controls, thus implicating mdr1b in the removal of corticosterone from the brain. However, examining the role of P-gp at the BBB without ensuring the physiological integrity of the barrier or confirming the presence of intact, radiolabeled drug, can create misleading data.
To address these concerns, we have quantified the ability of [3H]dexamethasone, [3H]cortisol, and [3H]corticosterone to cross the BBB in P-gp-deficient [FVB-abcb1a/b (-/-)] and wild-type [FVB-abcb1a/b (+/+)] mice, with a sensitive brain perfusion technique linked with capillary depletion analysis. We have also examined the systemic administration of these radiolabeled glucocorticoids, in new experiments conducted similarly to the work by Meijer et al (19), Karssen et al (13), and Uhr et al (21). Integrity of all the radiolabeled drugs was confirmed by high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis.
METHOD
Materials
Radiolabelled Substances
[3H]cortisol (74.0 Ci/mmol), [3H]corticosterone (79.0 Ci/mmol), [3H]dexamethasone (89.0 Ci/mmol) were purchased from GE Healthcare (Buckinghamshire, UK). [14C]sucrose (0.49 Ci/mmol) was purchased from Moravek Biochemicals (Brea, CA, USA).
Animals
Adult FVB-abcb1a/b (+/+)and FVB-abcb1a/b (-/-) mice were imported from Taconic Farms, Inc. (Germantown, NY, USA) and a breeding colony was established at King’s College London under an academic breeding agreement. Genotype was confirmed by PCR analysis (Harlan UK, Ltd. Hillcrest, Belton, Loughborough, UK) and it is recognized that Dr.Alfred Schinkel of the Netherlands Cancer Institute is the creator of the abcb1a/b-deficient mice. All animals were maintained under standard conditions of temperature and lighting and given food and water ad libitum.
Procedures
All procedures are within the guidelines of the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act, 1986.
In-Situ Brain Perfusion Technique
The brain perfusion technique is a very well established method for examining the movement of endogenous and exogenous molecules across the BBB in several species including the rat, guinea-pig and mouse, and it has been used by several groups to examine the influence of P-gp on the distribution of molecules, both by inclusion of specific inhibitors in the artificial plasma and by the use of knockout animals (16, 22, 23). Adult male mice (25-40 weeks and 25g-46g) were anaesthetised with a medetomidine hydrochloride (2 mg/kg, i.p.) and ketamine hydrochloride solution (150 mg/kg, i.p.) and heparinised (100 Units, i.p.). The body cavity was opened and the left ventricle cannulated with a fine needle (25 gauge) connected to a perfusion circuit. A Watson-Marlow peristaltic pump (323S/RL, Cornwall, UK) was used to perfuse the heart in situ with a modified Krebs-Henseleit mammalian Ringer solution (117.0 mM NaCl, 4.7 mM KCl, 1.2 mM MgSO4(7H2O), 24.8 mM NaHCO3, 1.2 mM KH2PO4, 2.5 mM CaCl2 ·6H2O, 39.0 g L-1 dextran (MW 60 000-90 000), 10 mM g L-1 glucose and 1 g L-1 bovine serum albumin), which was warmed (37°C) and oxygenated (95% O2; 5% CO2). With the start of perfusion (5.0 ml/min), the right atrium was sectioned to create an open circuit and allow drainage of the artificial plasma. In all experiments, a 2.5 min pre-drug perfusion of artificial plasma ensured removal of endogenous glucocorticoids from the brain vasculature. [3H]dexamethasone (3.9nM), [3H]cortisol (3.6 nM) or [3H]corticosterone (3.8 nM) along with [14C]sucrose (vascular space marker; 0.5-1.0 nM), was then administered by a slow-drive syringe pump (model 22; Harvard Apparatus; Kent, UK) into the artificial plasma. Following the desired isotope perfusion time period up to 20 minutes, the mouse was decapitated. The brain was removed. Samples (frontal cortex, hypothalamus, hippocampus, cerebellum, and pituitary gland - including anterior and posterior) were dissected and weighed. All brain samples, together with 100 μl artificial plasma samples, were prepared for liquid scintillation counting as described below.
Capillary Depletion Step
In order to assess how much of drug has actually entered the brain tissue, rather than accumulated within the cerebral capillary endothelial cells, the capillary depletion method was performed (24). The remaining brain was weighed and homogenized with five strokes in the presence of a capillary depletion buffer [10 mM HEPES, 140 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2.8 mM CaCl2(6H2O), 1 mM MgSO4(7H2O), 1 mM NaH2PO4(2H20), 10 mM g L -1 glucose; (volume × 3 brain weight composition)]. A 26% dextran solution [MW 60 000-90 000; (volume × 4 brain weight)] was then added to the homogenizer and combined with five strokes. Two 100μl aliquots of brain homogenate were taken and weighed, and the rest of the homogenate was centrifuged at 5,400 × g for 15 minutes at 4°C. The endothelial cell-enriched pellet and the supernatant containing brain parenchyma and interstitial fluid were then separated and weighed. Homogenate, supernatant, and pellet samples were prepared for radioactive analysis as described below.
Liquid Scintillation Counting
All samples were solubilized over approximately 48 hours in 0.5 ml of Solvable (PerkinElmer Life and Analytical Sciences, Boston, MA, USA). All samples were vortexed, 3 mls of scintillation counting fluid (Lumasafe; PerkinElmer Life and Analytical Sciences) was then added and the samples vortexed again. The samples were then placed in a Packard TriCarb 2100 or 2900TR (PerkinElmer, Beaconsfield, UK) liquid scintillation counter for estimation of [3H] and [14C] radioactivities. All results were corrected for background radioactivity.
Expression of Results
The concentration of [3H] or [14C] radioactivity in the brain tissue (dpm g-1) is expressed as a percentage of that in artificial plasma (dpm ml-1) and is referred to as Percentage Uptake. Uptake values of the radioactive glucocorticoids were corrected with the uptake values of [14C]sucrose, termed “vascular-space corrected”, and is used when comparing glucocorticoid values between strains.
Systemic Administration Studies
[3H]dexamethasone (8.9μCi/ml; 3.9 pM), [3H]cortisol (1.6 ng/g; 58.0μM), or [3H]corticosterone (1.7 ng/g; 58.9μM) were prepared in 0.9% saline solution (injection volume: 10μl/g) as previously described in Meijer et al (19) and Uhr et al (21). Mice were subcutaneously injected with radiolabeled drugs, allowed to rest for 2 hours, then decapitated and trunk blood collected in heparinised syringes. Blood was centrifuged at 1,268 × g for 5 min at 20°C and plasma samples were collected. The pituitary gland (including anterior and posterior), cerebellum, and remaining brain matter were separated and individually weighed. Samples were then prepared for liquid scintillation counting as described above. The concentration of radioactivity in the brain tissue (dpm g-1) is expressed as a percentage of that in the injectate (dpm ml-1) and is referred to as Percentage Distribution.
Data Analysis
The data from all the experiments are presented at mean ± standard error of the mean. The Sigma Stat 2.0 statistical program (SPSS Science Software UK Ltd., Birmingham, UK) was used for all determinations. The level of significance was set at P<0.05. In the multiple-time uptake studies, Two-Way ANOVA was used to compare strains. Data from the systemic administration studies were compared using Student’s t-tests.
High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
To determine the integrity of the radiolabeled drugs during in situ cerebral perfusion, samples of arterial inflow (i.e., radiolabeled drugs in artificial plasma), the venous (jugular) outflow and pooled whole brains (n=5) were taken after 20 min perfusion of each of the radiolabeled drugs. To establish the integrity of the radiolabeled drugs after the systemic injections, samples of plasma taken after decapitation were analyzed. All samples were extracted by the procedure previously cited by Gibbs and Thomas (25) and separated using a method modified from Hay and Mormede (28). Radioactive samples were compared with standards of radiolabeled drug in determined concentrations and standards of extracted plasma and brain not containing any drug.
Octanol-Saline Partition Coefficient
Octanol-saline partition coefficients were determined by using 0.0112 mM of [3H]dexamethasone, 0.0135 mM of [3H]cortisol, 0.0127 mM of [3H]corticosterone, or 0.2 mM of [14C]sucrose, by the method cited in Gibbs and Thomas (25). The partition coefficient was calculated as the ratio of labeled concentration in the octanol phase to the concentration in the aqueous phase.
Protein Binding Analysis
Protein binding of each drug in saline, artificial plasma, murine plasma or human plasma was determined by the ultrafiltration centrifugal dialysis method cited in Gibbs and Thomas (25). To confirm that the majority of protein present was limited by the micropartition filter, protein concentrations in the ultrafiltrates were determined by the method of Lowry et al (28) using standards of bovine serum albumin. As expected, the ultrafiltrates from the saline samples produced no detectable protein, those from the artificial plasma samples produced 0.9% ± 1.3% detectable protein, those from the murine plasma samples produced 8.2% ± 1.2% detectable protein, and 2.9% ± 1.1% of total protein was detected from the human plasma samples. Overall these results confirm the integrity of the filters.
RESULTS
[14C]sucrose Comparisons
Data concerning the uptake of [14C]sucrose (and [3H]glucocorticoid values) are presented in Figures 1-3 to confirm integrity of the BBB during brain perfusion experiments. As expected, because sucrose does not cross the BBB and is not transported by P-gp, uptake was similar (ranging from 1-3.5%) in the frontal cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum, and was not influenced by differences in strain or the co-infused glucocorticoid. The [14C]sucrose values in the hypothalamus (ranged from 1.2-4.2%) and the pituitary (ranged from 6.8-25%) were higher than in the other sampled regions. This was expected in the pituitary gland, which is outside the BBB and thus molecules are able to pass more freely between blood and tissue. However, data in the hypothalamus were unexpected and may represent greater vascularity. All further experiments were analyzed by correcting the uptake values of the radioactive glucocorticoids with the uptake values of [14C]sucrose (“vascular-space corrected”).
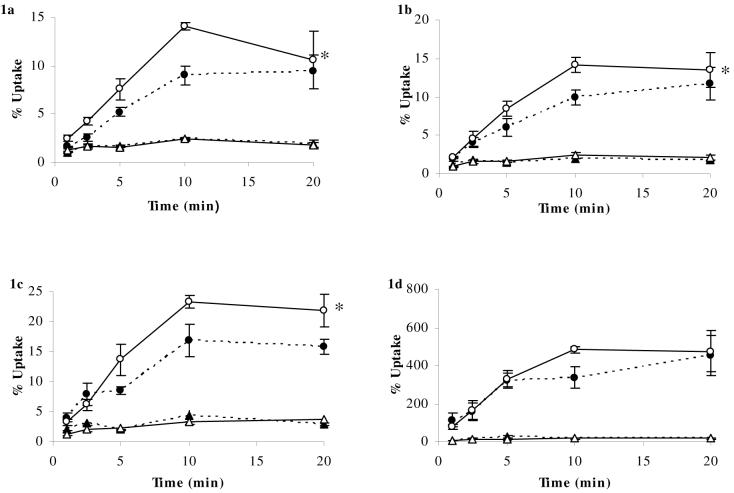
Figure 1a-d. Percentage Uptake of [3H]dexamethasone and [14C]sucrose in abcb1a/b (+/+) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice using in-situ brain perfusion.
[3H]dexamethasone (3.9nM) along with [14C]sucrose (vascular space marker; 0.5-1.0 nM), was administered by a slow-drive syringe pump into the artificial plasma. Following the desired isotope perfusion time period up to 20 minutes, the mouse was decapitated, and selected areas of the brain were dissected. The concentration of [3H] or [14C] radioactivity in the brain tissue (dpm g-1) is expressed as a percentage of that in artificial plasma (dpm ml-1). The uptake of [3H]dexamethasone (n=11-26/strain) was significantly higher (Two-Way ANOVA) in the frontal cortex (Fig. 1a), hippocampus (Fig. 1b), and hypothalamus (Fig. 1c), but was not significantly different in the pituitary gland of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared to abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (Fig. 1d). [14C]Sucrose uptake was not influenced by the mouse strain.
● (dotted line) [3H]dexamethasone (abcb1a/b (+/+) mice); ○ (solid line) [3H]dexamethasone (abcb1a/b (-/-) mice); ▲ (dotted line) [14C]sucrose (abcb1a/b (+/+) mice); ∆ (solid line) [14C]sucrose (abcb1a/b (-/-) mice). * denotes significance of P<0.05, Two-Way ANOVA.
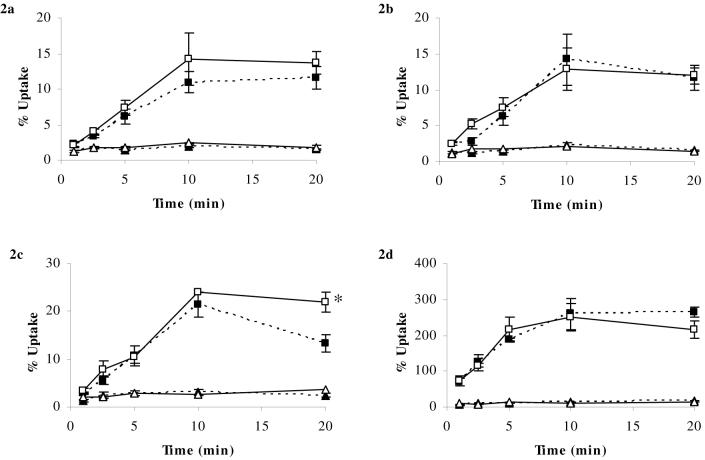
Figure 3a-d. Percentage Uptake of [3H]corticosterone and [14C]sucrose in abcb1a/b (+/+) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice using in-situ brain perfusion.
[3H]corticosterone (3.8 nM) along with [14C]sucrose (vascular space marker; 0.5-1.0 nM), was administered by a slow-drive syringe pump into the artificial plasma. Following the desired isotope perfusion time period up to 20 minutes, the mouse was decapitated, and selected areas of the brain were dissected. The concentration of [3H] or [14C] radioactivity in the brain tissue (dpm g-1) is expressed as a percentage of that in artificial plasma (dpm ml-1). The uptake of [3H]corticosterone (n=28-51/strain) in abcb1a/b (-/-) mice was not significantly different compared to abcb1a/b (+/+) mice in the frontal cortex (Fig. 3a), hippocampus (Fig. 3b), hypothalamus (Fig. 3c), or pituitary gland (Fig. 3d). [14C]Sucrose uptake was not influenced by the mouse strain.
♦ (dotted line) [3H]cortiscosterone (abcb1a/b (+/+) mice); ◊ (solid line) [3H]corticosterone (abcb1a/b (-/-) mice); ▲ (dotted line) [14C]sucrose (abcb1a/b (+/+) mice); ∆ (solid line) [14C]sucrose (abcb1a/b (-/-) mice)
Brain Perfusion of [3H]dexamethasone
The uptake of [3H]dexamethasone and [14C]sucrose in abcb1a/b (+/+) mice is illustrated in Figure 1. The uptake of [3H]dexamethasone was significantly higher in the frontal cortex (P=0.008, Fig. 1a), hippocampus (P=0.025, Fig. 1b), hypothalamus (P<0.001, Fig. 1c), and cerebellum (P<0.001, data not shown) of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice. The uptake of [3H]dexamethasone, however, was not significantly different in the pituitary gland of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (P=0.4, Fig. 1d). Capillary depletion analysis of the brains of abcb1a/mdr1b (-/-) mice indicated that [3H]dexamethasone was present in both the capillary endothelial-enriched pellet and supernatant fractions of the brains of abcb1a/b (+/+) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice (data not shown).
Brain Perfusion of [3H]cortisol
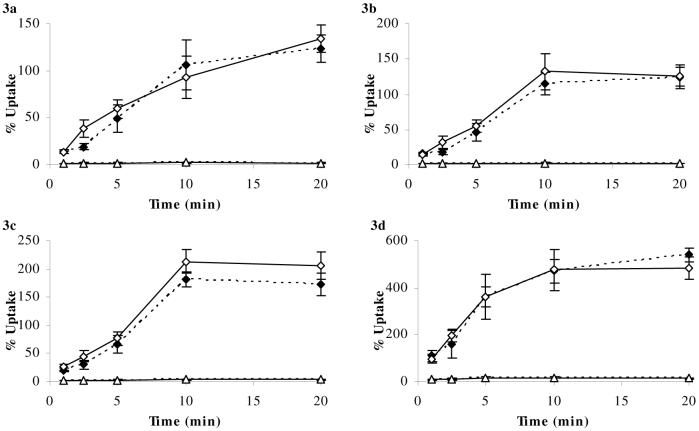
The uptake of [3H]cortisol and [14C]sucrose in abcb1a/b (+/+) mice is illustrated in Figure 2. The uptake of [3H]cortisol was significantly higher in the hypothalamus of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (P=0.009, Fig. 2c). In the frontal cortex, although there was a tendency for the abcb1a/b (-/-) mice to have higher levels of [3H]cortisol compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice, this did not reach statistical significance (P=0.2, Fig. 2a). [3H]cortisol values were not significantly different in abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice in the hippocampus (P=0.7, Fig. 2b), pituitary gland (P=0.7, Fig. 2d), or cerebellum (P=0.5, data not shown). Capillary depletion analysis indicated that [3H]cortisol was present in both the pellet and supernatant fractions the brains of abcb1a/b (+/+) and FVB-mdr1a/b (-/-) mice (data not shown).
Figure 2a-d. Percentage Uptake of [3H] cortisol and [14C]sucrose in abcb1a/b (+/+) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice using in-situ brain perfusion.
[3H]cortisol (3.6 nM) along with [14C]sucrose (vascular space marker; 0.5-1.0 nM), was administered by a slow-drive syringe pump into the artificial plasma. Following the desired isotope perfusion time period up to 20 minutes, the mouse was decapitated, and selected areas of the brain were dissected. The concentration of [3H] or [14C] radioactivity in the brain tissue (dpm g-1) is expressed as a percentage of that in artificial plasma (dpm ml-1). The uptake of [3H]cortisol (n=11-29/strain) was significantly higher (Two-Way ANOVA) in the hypothalamus of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared to abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (Fig. 1c). Although there was a tendency for the abcb1a/b (-/-) mice to have higher levels of [3H]cortisol compared to abcb1a/b (+/+) mice in the frontal cortex, this did not reach statistical significance (Fig. 1a), while [3H]cortisol values were not significantly different in abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared to abcb1a/b (+/+) mice in the hippocampus (Fig. 1b) or pituitary gland (Fig. 1d). [14C]Sucrose uptake was not influenced by the mouse strain.
■ (dotted line) [3H]cortisol (abcb1a/b (+/+) mice); □ (solid line) [3H]cortisol (abcb1a/b (-/-) mice); ▲ (dotted line) [14C]sucrose (abcb1a/b (+/+) mice); ∆ (solid line) [14C]sucrose (abcb1a/b (-/-) mice). * denotes significance of P<0.05, Two-Way ANOVA.
Brain Perfusion of [3H]corticosterone
The uptake of [3H]corticosterone and [14C]sucrose in abcb1a/b (+/+) mice is illustrated in Figure 3. The uptake of [3H]corticosterone in abcb1a/b (-/-) mice was not significantly different compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice in the frontal cortex (P=0.7, Fig. 3a), hippocampus (P=0.5, Fig. 3b), hypothalamus (P=0.2, Fig. 3c), cerebellum (P=0.8, data not shown), or pituitary gland (P=0.9, Fig. 3d). Capillary depletion analysis of the brain tissue revealed [3H]corticosterone present in both pellet and supernatant fractions of the brains of abcb1a/b (+/+) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice (data not shown).
Systemic Administration Studies
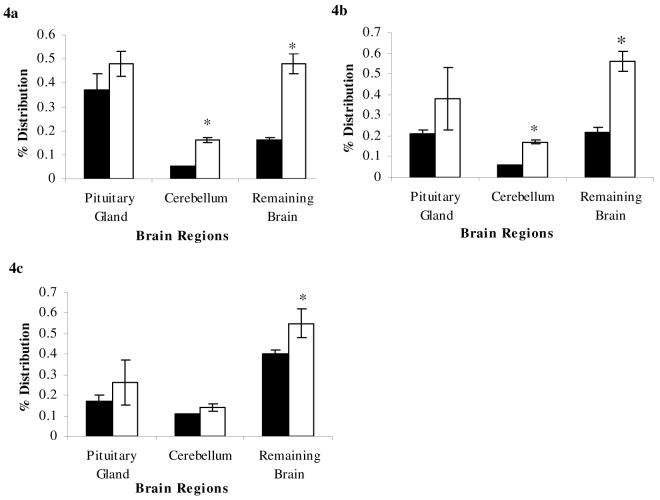
Consistent with the work by Meijer et al (23), the uptake of [3H]dexamethasone into the cerebellum and remaining brain was significantly increased in abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (P<0.001; Fig. 4a), while there was no difference in the uptake of [3H]dexamethasone in the pituitary gland (P=0.2, Fig. 4a). The uptake of [3H]cortisol was also significantly increased in the cerebellum and remainder brain of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (P<0.001, Fig. 4b); again, there was no difference in the uptake of [3H]cortisol in the pituitary (P=0.5, Fig. 4b). Moreover, in contrast with our brain perfusion experiments described above, but consistent with the work by Uhr et al (24), the uptake of [3H]corticosterone into the remainder brain was significantly increased in abcb1a/b (-/-) compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (P=0.0047, Fig. 4c) and not-significantly increased in the cerebellum (P=0.1, Fig. 4c). Again, there was no difference in the pituitary gland (P=0.9, Fig. 4c). There were no significant differences between strains in the radioactive plasma concentrations for any of the glucocorticoids (data not shown).
Figure 4a-c. Percentage Distribution following systemic administration of glucocorticoids in abcb1a/b (+/+) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice.
[3H]dexamethasone (8.9μCi/ml; 3.9 pM, Fig. 4a), [3H]cortisol (1.6 ng/g; 58.0μM, Fig. 4b), or [3H]corticosterone (1.7 ng/g; 58.9μM, Fig. 4c) was prepared in 0.9% saline solution. Mice (6 or 7/strain) were subcutaneously injected with radiolabeled drugs, allowed to rest for 2 hours, then decapitated; the pituitary gland, cerebellum, and remaining brain matter were separated and individually weighed. Samples were then prepared for liquid scintillation counting. The concentration of radioactivity in the brain tissue (dpm g-1) is expressed as a percentage of that in the injectate (dpm ml-1). The uptake of [3H]dexamethasone into the cerebellum and remaining brain was significantly increased in abcb1a/b (-/-) mice (open, white bar) compared to abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (solid, black bar), and the uptake of [3H]dexamethasone was not significantly increased in the pituitary gland of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared to abc1a/b (+/+) mice. The uptake of [3H]cortisol was significantly increased in the cerebellum and remainder brain of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice (open, white bar) compared abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (solid, black bar), and uptake of [3H]cortisol was not significantly increased in the pituitary gland between abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared to abcb1a/b (+/+) mice. The uptake of [3H]corticosterone into the remainder brain was significantly increased in abcb1a/b mice (open, white bar) compared to abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (solid, black bar). There was no significant difference between strains in the uptake of [3H]corticosterone in the cerebellum or pituitary gland. * denotes significance of P<0.05, Student’s t-test.
Octanol-Saline Partition Coefficients and Protein Binding
Octanol-saline partition coefficients, a measure of lipophilicity, and determinations of protein binding can be seen in Table 1. Both cortisol and corticosterone had similar lipophilicities, while dexamethasone was the least lipophilic glucocorticoid. Binding of cortisol and corticosterone to bovine serum albumin, the only protein present in the artificial plasma, was similar, whereas the binding of dexamethasone was significantly higher. The binding of the drugs in saline, where no protein is present, is a result of the drug accumulating on the filter of the micropartition devices.
Table 1.
Octanol-Saline Partition Coefficients and Protein Binding Determinations (Mean ± Standard Error of Mean)
| Compound | Octanol-Saline Partition Coefficients | Protein Binding Determinations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saline | Artificial Plasma (1% Bovine Serum Albumin) | Murine Plasma | Human Plasma | ||
| [3H]dexamethasone | 0.557 ± 0.130 | 0% | 24.9% ± 0.7 % | 79.7% ± 0.2% | 62.0% ± 0.1% |
| [3H]cortisol | 20.663 ± 2.032 | 7.6% ± 1.1% | 11.2% ± 1.5 % | 88.4% ± 0.1% | 92.8% ± 0.5% |
| [3H]corticosterone | 18.882 ± 1.557 | 0% | 15.1% ± 2.0% | 95.0% ± 0.2% | 93.6% ± 0.1% |
| [14C]sucrose | 0.00039 ± 0.00002 | 7.3% ± 1.9% | 0% | 4.4% ± 1.5% | 5.6% ± 2.1% |
HPLC
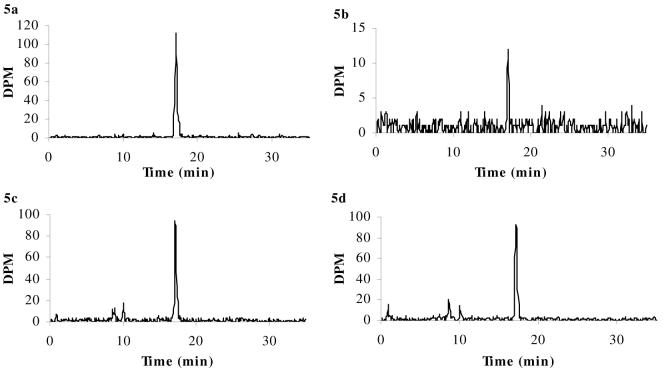
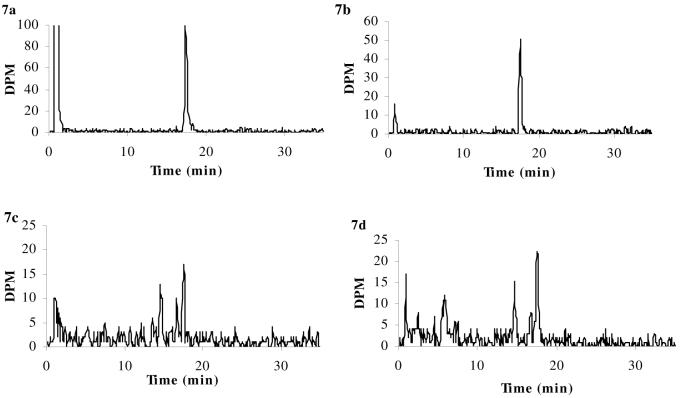
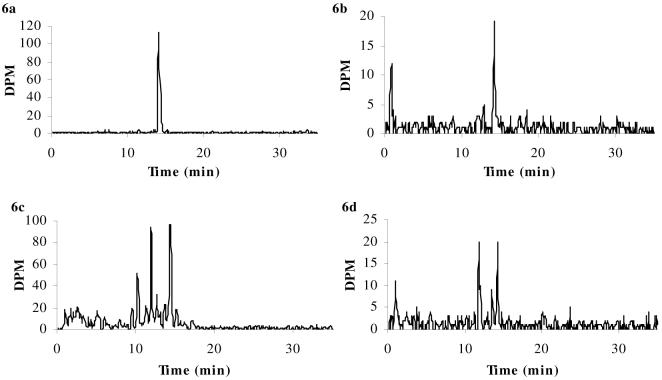
Figures 5-7 show representative chromatographs from HPLC analysis following the brain perfusion and systemic administration experiments. Our findings confirm that, following brain perfusion, intact radiolabeled drug was present in arterial inflow (Panel a in all Figures), venous outflow (data not shown) and brain samples (Panel b in all Figures) following a 20 min perfusion period. [3H]dexamethasone (Fig. 5) was eluted at 17.1 min in all samples, with approximately 100% of the total radioactivity representing intact [3H]dexamethasone in the brain samples. [3H]cortisol (Fig. 6) was eluted at 14.2 min in all samples, with approximately 64% of the total radioactivity present in the brain samples as intact [3H]cortisol. [3H]corticosterone (Fig. 7) was eluted at 17.5 min in all samples, with approximately 81% of the total radioactivity present in the brain samples present as intact [3H]corticosterone. All of these retention times matched those of the radiolabeled standards. There was an additional peak seen at 0.9 min in some of the samples, but this was determined to be [14C]sucrose that was present in the artificial plasma in some of the perfusions, and no other additional peaks were eluted.
Figure 5a-d. HPLC chromatograms of [3H]dexamethasone.
[3H]dexamethasone in samples of arterial inflow (i.e., drug in artificial plasma, Panel a) and pooled whole brains (Panel b) taken after 20 min in situ brain perfusion, and in representative samples of plasma from abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (Panel c) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice (Panel d) after the systemic injections. HPLC analysis confirms that intact radiolabeled drug was present after brain perfusion: [3H]dexamethasone was eluted at 17.1 min in all samples. This retention time matched that of the radiolabeled standard. In contrast, the HPLC chromatograms following the systemic administration experiments show that the integrity of the radiolabeled drugs was not maintained in the plasma during the 2 hours resting period preceding decapitation, as shown by the presence of additional radioactive peaks.
Figure 7a-d. HPLC chromatograms of [3H]corticosterone.
[3H]corticosterone in samples of arterial inflow (i.e., drug in artificial plasma, Panel a) and pooled whole brains (Panel b) taken after 20 min in situ brain perfusion, and in representative samples of plasma from abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (Panel c) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice (Panel d) after the systemic injections. HPLC analysis confirms that intact radiolabeled drug was present after brain perfusion: [3H]corticosterone was eluted at 17.5 min in all samples. This retention time matched that of the radiolabeled standard. In contrast, the HPLC chromatograms following the systemic administration experiments show that the integrity of the radiolabeled drugs was not maintained in the plasma during the 2 hours resting period preceding decapitation, as shown by the presence of additional radioactive peaks.
Figure 6a-d. HPLC chromatograms of [3H]cortisol.
[3H]cortisol in samples of arterial inflow (i.e., drug in artificial plasma, Panel a) and pooled whole brains (Panel b) taken after 20 min in situ brain perfusion, and in representative samples of plasma from abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (Panel c) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice (Panel d) after the systemic injections. HPLC analysis confirms that intact radiolabeled drug was present after brain perfusion: [3H]cortisol was eluted at 14.2 min in all samples. This retention time matched that of the radiolabeled standard. In contrast, the HPLC chromatograms following the systemic administration experiments show that the integrity of the radiolabeled drugs was not maintained in the plasma during the 2 hours resting period preceding decapitation, as shown by the presence of additional radioactive peaks.
In contrast, the HPLC chromatograms following the systemic administration experiments show that the integrity of the radiolabeled drugs was not maintained in the plasma during the 2 hours resting period preceding decapitation, as shown in Panels c and d of Figures 5-7. Specifically, [3H]dexamethasone was eluted at 17.1 min, and additional radioactive peaks were present at 8.6 min and 10.0 min for both strains (abcb1a/b (+/+) mice, Fig. 5c; abcb1a/b (-/-) mice, Fig. 5d); of the total radioactive signal present, approximately 75% was determined to be intact [3H]dexamethasone for both strains. [3H]cortisol was eluted at 14.4 for both strains; additional radioactive peaks were eluted at 2.6 min, 5.1 min, 10.2 min and 11.9 min for abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (Fig. 6c), with approximately 35% of total radioactivity determined to be intact [3H]cortisol. Only one additional radioactive peak was eluted at 11.8 min for abcb1a/b (-/-) mice (Fig. 6d), with approximately 48% of total radioactivity determined to be intact [3H]cortisol. [3H]corticosterone was eluted at 17.5 min with additional radioactive peaks eluting at 14.5 min and 16.7 min for abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (Fig. 7c), with approximately 44% of total radioactivity determined to be intact [3H]corticosterone, and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice (Fig. 7d), with approximately 55% of total radioactivity determined to be intact [3H]corticosterone.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, using an in situ brain perfusion model, the uptake of [3H]dexamethasone across the BBB was significantly higher in the brains of FVB mice that were deficient for both abcb1a and 1b compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) control mice. Interestingly, the brain uptake of [3H]cortisol was only higher in the hypothalamus of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with controls. Finally, there was no significant difference in the uptake of [3H]corticosterone in the brains of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice. In contrast to the brain perfusion experiments, but consistent with previous work (19, 21), the systemic administration of each radiolabeled glucocorticoid, including corticosterone, led to significantly higher brain uptake in the abcb1a/b-deficient mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice. However, radiolabeled glucocorticoid by-products were present in the peripheral circulation, which would prevent accurate interpretation of the systemic administration data.
Our findings illustrate the importance of P-gp in the efflux of dexamethasone from the brain. This confirms and expands the results obtained by Meijer et al (19) following systemic administration in abcb1a-deficient mice. There are known species differences in the kinetic parameters of substrate transport and inhibition of P-gp (28, 29), but in vitro comparison of human ABCB1 and mouse abcb1a has determined a similar efflux ratio of [3H]dexamethasone (28). Therefore, our work supports the role of P-gp in the transport of [3H]dexamethasone in humans, and thus is relevant to the use of dexamethasone in the dexamethasone suppression test and the dexamethasone/CRH test. Our data also confirms the notion that the pituitary gland is a preferential site of the HPA axis negative feedback action for dexamethasone (30, 31). In fact, our work could explain this phenomenon, as the pituitary gland was the only region investigated that had no difference in the uptake of [3H]dexamethasone between strains, following both brain perfusion and systemic administration, thus indicating that no P-gp exists at the pituitary. This lack of a P-gp effect at the pituitary gland has also been seen by Meijer et al (19) and Sanderson et al (23).
The uptake of [3H]cortisol following in situ brain perfusion tended to be higher in the frontal cortex of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice, but this was a non-statistically significant effect. Previous work by Karrsen et al (13) and Meijer et al (19) using autoradiography following systemic administration in abcb1a (-/-) mice has shown that [3H]dexamethasone is a stronger substrate for P-gp than [3H]cortisol (10-fold increase in P-gp deficient compared to wild-type mice vs. 3-to-4-fold increase), with our results consistent with these findings. Interestingly, we found no difference between abcb1a/b (-/-) mice and abcb1a/b (+/+) in the uptake of [3H]cortisol in the hippocampus, contrary to the results found by Karssen et al using autoradiography following systemic administration (13). Following the systemic administration of [3H]cortisol in our experiments, HPLC results revealed that the plasma radioactive signal was composed of several radioactive compounds. Importantly, more intact [3H]cortisol was detected in the plasma of P-gp deficient mice compared with wild-type controls. This is likely to be related to the fact that P-gp is expressed in a variety of tissues, not least of which is the liver, where it has an important role in metabolism and clearing substrates from the blood. In contrast to our brain perfusion technique, which examines the movement of molecules specifically at the BBB, any systemic administration results would be impacted by the absence of P-gp in these additional tissues. It may be that the decreased metabolism of cortisol in the P-gp deficient mice would allow more [3H]cortisol to be present in the plasma for a longer period of time and therefore produce the higher levels of [3H]cortisol binding in the hippocampus of P-gp deficient mice compared with wild-type controls. Therefore, although there is certainly an effect of P-gp on [3H]cortisol distribution after systemic administration, it is not necessarily an effect of P-gp at the BBB. Additionally, the autoradiography in Karssen et al. (13) may have shown a higher radioactive signal in the hippocampus of abcb1a (-/-) mice because of increased entry of [3H]cortisol metabolites whose entry is regulated by P-gp: for example, cortisone, in itself a low-affinity binder to corticosteroid receptors (13).
Another consideration is that mice in our experiments were not adrenalectomized. Although we did pre-perfuse the brains with ‘glucocorticoid free’ artificial plasma for 2.5 min, this may not have removed all the endogenous corticosterone from the hippocampal receptors. This is a limitation of our study, and may also contribute to the discrepant findings between our present study and Karssen et al. (13). As mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors are highly expressed in the hippocampus, they may regulate the accumulation of glucocorticoids in this region (13). It is known by in situ hybridization histochemistry that these receptors are expressed at similar levels in both P-gp deficient and wild-type mice (3). Although, binding of endogenous corticosterone to the mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors in the hippocampus could be seen as affecting the driving force of the concentration gradient for free [3H]cortisol across the blood-brain barrier, it is important to note that [3H]cortisol in the hippocampus only reached a maximum concentration of 20% of that in the plasma. Glucocorticoids are highly lipophilic molecules (see octanol-saline partition coefficients) and would be free to cross cell membranes by passive diffusion; therefore [3H]cortisol, whether eventually being bound or unbound to receptors in the hippocampus, would still passively diffuse from plasma to brain down the concentration gradient. Furthermore, if endogenous corticosterone had remained bound to the receptors, thereby preventing [3H]cortisol binding, the influence of P-gp on the removal of this free [3H]cortisol would likely be more apparent. Therefore, we suggest that the lack of adrenalectomy in our study is likely to have had little impact on the results of the brain perfusion experiments, and that the differences between our findings and those of Karssen et al. (13) in cortisol regulation by P-gp at the hippocampus are driven by the use of systemic administration in this previous study.
Interestingly, we did find a significant difference in the uptake of [3H]cortisol in the hypothalamus of abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice, confirming that [3H]cortisol is a substrate for P-gp (6,12,13). The hypothalamus is the only BBB-protected region of the HPA axis, and it is interesting that here we found P-gp efflux of cortisol, especially considering that mice do not physiologically produce cortisol. Interestingly, we also found evidence of higher vascularity in the hypothalamus, as shown by the higher [14C]sucrose values. The murine infundibular, lateral hypothalamic, and ventral thalamic arteries all run through or around the hypothalamus, which could provide greater capillary density compared with other brain structures (32). While there is currently no evidence of increased expression of P-gp in the hypothalamus, the possibility of higher vascularity in this region could lead to a greater density of P-gp.
Our paper finally resolves the conflicting data from the systemic administration studies of Karssen et al (13) and Uhr et al (21) concerning whether corticosterone is regulated by P-gp at the murine BBB. Karssen et al (13) found no increase in the brain concentration of [3H]corticosterone in abcb1a-deficient mice, one hour after subcutaneous injection, while Uhr et al (21) found the brain uptake of [3H]corticosterone increased in abcb1a and 1b-deficient mice, two hours following subcutaneous injection. Our brain perfusion data demonstrate that corticosterone is not effluxed at the BBB by either abcb1a or, if present (see below), abcb1b. Furthermore, our HPLC analysis of plasma samples two hours following systemic administration show very little untransformed [3H]corticosterone, with the majority of the radioactive signal not co-eluting with the unlabelled corticosterone standard. Therefore, based on the present study, previous results based on systemic administration of [3H]corticosterone (21), where an effect of P-gp at the BBB was demonstrated, should now be re-interpreted as reflecting the high levels of radiolabeled breakdown products observed. For example, aldosterone, one metabolite of corticosterone, is transported by P-gp (33). Indeed, there is currently no direct evidence that abcb1b is found at the BBB (22): though abcb1b can be found in capillary endothelial cells in vitro, it is highly unlikely that it is present in these cells in vivo (15, 34).
Clearly, it has to be emphasized that although P-gp does not regulate corticosterone entry into the murine brain, the possibility exists that P-gp has a role in mouse HPA axis physiology in other ways. Indeed, two studies have now independently replicated that corticosterone plasma levels are lower in abcb1a/b (-/-) compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (2, 3). Moreover, the latter study has also shown that antidepressants have different effects on hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor expression and corticosterone levels in abcb1a/b (-/-) mice compared with abcb1a/b (+/+) mice (3), a finding that confirms previous work consistently showing that a large number of antidepressants inhibit P-gp function, and that some antidepressants are themselves substrates of P-gp (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 35, 36). Therefore, P-gp in other tissues relevant for HPA axis function, possibly expressed by the abcb1b gene, might be involved in these effects. Indeed, abcb1b is highly and diffusely expressed in the adrenal gland, and it has been shown to help secrete aldosterone out of this gland (33). This could also be the case for corticosterone, and therefore the absence of abcb1b at the mouse adrenal gland (or its regulation by antidepressants) could explain the findings discussed above.
Interestingly, the in situ brain perfusion studies conducted in wild-type mice show that the percentage brain uptake of [3H]cortisol was nearly ten times less than that of [3H]corticosterone. This difference cannot simply be explained by different lipophilicity (octanol-saline partition coefficient) or protein binding characteristics, as both these measures were very similar for cortisol and corticosterone. In agreement with our present data, earlier studies have shown that cortisol does not accumulate as efficiently as corticosterone in the brains of rodents (8, 20), and Karssen et al. (13) have shown that even a lower dose of [3H]corticosterone more heavily labels the hippocampus compared with [3H]cortisol. Finally, this is consistent with post-mortem studies by the same authors, which have also shown differential entry of cortisol and corticosterone to the human brain (13). This finding had been interpreted as indicating a lower affinity of cortisol for rodent corticosteroid receptors (37), and later thought to be related to the ability of P-gp to expel cortisol, but not corticosterone (13). Taken together with our data, these findings may also suggest that additional transporters, other than P-gp, may play a role in the distribution of endogenous glucocorticoids to the brain.
In summary, P-gp at the BBB, as expressed by abcb1a and 1b, is a limiting mechanism for dexamethasone, but not corticosterone, entry to the brain. P-gp can limit cortisol entry to the hypothalamus, but this affect was not detected in any other brain regions. Because the hypothalamus is highly vascularised, this may provide a greater density of P-gp expression, allowing this effect to be detected in this area.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by a UK Medical Research Council (MRC) Clinician Scientist Fellowship to C. M. Pariante (G108/603), and by a multi-user equipment grant from the Wellcome Trust to S. A. Thomas (grant code: 080268). Abstracts of this work have been presented by B. L. Mason at the 2007 Cerebral Vascular Biology and British Association for Psychopharmacology Meetings.
Footnotes
Disclosure statement: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
REFERENCES
- 1.Pariante CM. The role of multidrug resistance p-glycoprotein in glucocorticoid function: studies in animals and relevance in humans. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.067. in press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Muller MB, Keck ME, Binder EB, Kresse AE, Hagemeyer TP, Landgraf R. ABCB1 (MDR1)-type P-glycoproteins at the blood-brain barrier modulate the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical system: implications for affective disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28:1991–1999. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yau JL, Noble J, Thomas S, Kerwin R, Morgan PE, Lightman S. The antidepressant desipramine requires the ABCB1 (Mdr1)-type p-glycoprotein to upregulate the glucocorticoid receptor in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007;32:2520–2529. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pariante CM, Thomas SA, Lovestone S, Makoff A, Kerwin RW. Do antidepressants regulate how cortisol affects the brain? Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2004;29:423–447. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2003.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pariante CM, Makoff A, Lovestone S, Feroli S, Heyden A, Miller AH. Antidepressants enhance glucocorticoid receptor function in vitro by modulating the membrane steroid transporters. Br J Pharmacol. 2001;134:1335–1343. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pariante CM, Hye A, Williamson R, Makoff A, Lovestone S, Kerwin RW. The antidepressant clomipramine regulates cortisol intracellular concentrations and glucocorticoid receptor expression in fibroblasts and rat primary neurones. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28:1553–1561. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pariante CM, Kim RB, Makoff A, Kerwin RW. Antidepressant fluoxetine enhances glucocorticoid receptor function in vitro by modulating membrane steroid transporters. Br J Pharmacol. 2003;139:1111–1118. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pardridge WM, Mietus LJ. Transport of steroid hormones through the rat blood-brain barrier. Primary role of albumin-bound hormone. J Clin Invest. 1979;64:145–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI109433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schinkel AH. P-Glycoprotein, a gatekeeper in the blood-brain barrier. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1999;36:179–194. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(98)00085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cordon-Cardo C, O’Brien JP, Casals D, Rittman-Grauer L, Biedler JL, Melamed MR. Multidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood-brain barrier sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:695–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sun H, Dai H, Shaik N, Elmquist WF. Drug efflux transporters in the CNS. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55:83–105. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(02)00172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ueda K, Okamura N, Hirai M, Tanigawara Y, Saeki T, Kioka N. Human P-glycoprotein transports cortisol, aldosterone, and dexamethasone, but not progesterone. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:24248–24252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Karssen AM, Meijer OC, van der Sandt I, Lucassen PJ, de Lange EC, de Boer AG. Multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein hampers the access of cortisol but not of corticosterone to mouse and human brain. Endocrinology. 2001;142:2686–2694. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.6.8213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Borst P, Schinkel AH. What have we learnt thus far from mice with disrupted P-glycoprotein genes? Eur J Cancer. 1996;32A:985–990. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(96)00063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schinkel AH, Mayer U, Wagenaar E, Mol CA, van Deemter L, Smit JJ. Normal viability and altered pharmacokinetics in mice lacking mdr1-type (drug-transporting) P-glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:4028–4033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cisternino S, Rousselle C, Debray M, Scherrmann JM. In situ transport of vinblastine and selected P-glycoprotein substrates: implications for drug-drug interactions at the mouse blood-brain barrier. Pharm Res. 2004;21:1382–1389. doi: 10.1023/b:pham.0000036911.49191.da. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Altuvia S, Stein WD, Goldenberg S, Kane SE, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. Targeted disruption of the mouse mdr1b gene reveals that steroid hormones enhance mdr gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:27127–27132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Regina A, Koman A, Piciotti M, El Hafny B, Center MS, Bergmann R. Mrp1 multidrug resistance-associated protein and P-glycoprotein expression in rat brain microvessel endothelial cells. J Neurochem. 1998;71:705–715. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.71020705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Meijer OC, de Lange EC, Breimer DD, de Boer AG, Workel JO, de Kloet ER. Penetration of dexamethasone into brain glucocorticoid targets is enhanced in mdr1A P-glycoprotein knockout mice. Endocrinology. 1998;139:1789–1793. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.4.5917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McEwen BS, de Kloet R, Wallach G. Interactions in vivo and in vitro of corticoids and progesterone with cell nuclei and soluble macromolecules from rat brain regions and pituitary. Brain Res. 1976;105:129–136. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90928-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Uhr M, Holsboer F, Muller MB. Penetration of endogenous steroid hormones corticosterone, cortisol, aldosterone and progesterone into the brain is enhanced in mice deficient for both mdr1a and mdr1b P-glycoproteins. J Neuroendocrinol. 2002;14:753–759. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2826.2002.00836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dagenais C, Rousselle C, Pollack GM, Scherrmann JM. Development of an in-situ mouse brain perfusion model and its application to mdr1a P-glycoprotein-deficient mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:381–386. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200002000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sanderson L, Khan A, Thomas S. Distribution of suramin, an antitrypanosomal drug, across the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid interfaces in wild-type and P-glycoprotein transporter-deficient mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51:3136–3146. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00372-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Triguero D, Buciak J, Pardridge WM. Capillary depletion method for quantification of blood-brain barrier transport of circulating peptides and plasma proteins. J Neurochem. 1990;54:1882–1888. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gibbs JE, Thomas SA. The distribution of the anti-HIV drug, 2′3′-dideoxycytidine (ddC), across the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers and the influence of organic anion transport inhibitors. J Neurochem. 2002;80:392–404. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-3042.2001.00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hay M, Mormede P. Improved determination of urinary cortisol and cortisone, or corticosterone and 11-dehydrocorticosterone by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet absorbance detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1997;702:33–39. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(97)00361-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Katoh M, Suzuyama N, Takeuchi T, Yoshitomi S, Asahi S, Yokoi T. Kinetic analyses for species differences in P-glycoprotein-mediated drug transport. J Pharm Sci. 2006;95:2673–2683. doi: 10.1002/jps.20686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Suzuyama N, Katoh M, Takeuchi T, Yoshitomi S, Higuchi T, Asashi S. Species differences of inhibitory effects on P-glycoprotein-mediated drug transport. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96:1609–1618. doi: 10.1002/jps.20787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miller AH, Spencer RL, Pulera M, Kang S, McEwen BS, Stein M. Adrenal steroid receptor activation in rat brain and pituitary following dexamethasone: implications for the dexamethasone suppression test. Biol Psychiatry. 1992;32:850–869. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(92)90175-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Karssen AM, Meijer OC, Berry A, Sanjuan PR, de Kloet ER. Low doses of dexamethasone can produce a hypocorticosteroid state in the brain. Endocrinology. 2005;146:5587–5595. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dorr A, Sled JG, Kabani N. Three-dimensional cerebral vasculature of the CBA mouse brain: a magnetic resonance imaging and micro computed tomography study. Neuroimage. 2007;35:1409–1423. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.12.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bello-Reuss E, Ernest S, Holland OB, Hellmich MR. Role of multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein in the secretion of aldosterone by human adrenal NCI-H295 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000;278:C1256–C1265. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2000.278.6.C1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Barrand MA, Robertson KJ, von Weikersthal SF. Comparisons of P-glycoprotein expression in isolated rat brain microvessels and in primary cultures of endothelial cells derived from microvasculature of rat brain, epididymal fat pad and from aorta. FEBS Lett. 1995;374:179–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01104-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Miller AH, Vogt GJ, Pearce BD. The phosphodiesterase type 4 inhibitor, rolipram, enhances glucocorticoid receptor function. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;27:939–948. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Uhr M, Steckler T, Yassouridis A, Holsboer F. Penetration of amitriptyline, but not of fluoxetine, into brain is enhanced in mice with blood-brain barrier deficiency due to mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene disruption. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000;22:380–387. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.de Kloet ER, Veldhuis HD, Wagenaars JL, Bergink EW. Relative binding affinity of steroids for the corticosterone receptor system in the rat hippocampus. J Steroid Biochem. 1984;21:173–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90380-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]