Abstract
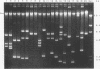
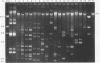
During the last years Acinetobacter species have emerged as clinically significant pathogens. Most infections are nosocomially acquired and mainly due to Acinetobacter baumannii. Little is known about the epidemiology and clinical significance of unnamed Acinetobacter species 3 (the second most often encountered member of the genus Acinetobacter) and other Acinetobacter species such as A. johnsonii, A. junii, and A. lwoffii. Seventy-five clinical isolates of Acinetobacter species other than A. baumannii (Acinetobacter species 3, n = 37; A. johnsonii, n = 20; A. junii, n = 8; A. lwoffii, n = 10) recovered from 66 patients over a period of 12 months were analyzed by plasmid DNA fingerprinting. Plasmids were found in 84.4% of Acinetobacter species 3 isolates and in all A. johnsonii, A. junii, and A. lwoffii isolates. Strains harbored up to 15 plasmids each. Almost every isolate gave a unique plasmid pattern. With one exception, identical plasmid profiles were detected only in corresponding isolates recovered from blood cultures and intravascular catheters from a given patient. Plasmid DNA fingerprinting proved to be useful for typing Acinetobacter species other than A. baumannii. There was no evidence of patient-to-patient transmission or hospital outbreaks due to these species. This finding is in contrast to the results obtained in studies of the hospital epidemiology of A. baumannii.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M., Rahman M., Taylor M., Noble W. C. A study of the value of electrophoretic and other techniques for typing Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Hosp Infect. 1988 Nov;12(4):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allardet-Servent A., Bouziges N., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bourg G., Gouby A., Ramuz M. Use of low-frequency-cleavage restriction endonucleases for DNA analysis in epidemiological investigations of nosocomial bacterial infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2057–2061. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2057-2061.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck-Sagué C. M., Jarvis W. R., Brook J. H., Culver D. H., Potts A., Gay E., Shotts B. W., Hill B., Anderson R. L., Weinstein M. P. Epidemic bacteremia due to Acinetobacter baumannii in five intensive care units. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Oct;132(4):723–733. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergogne-Bérézin E., Joly-Guillou M. L. Hospital infection with Acinetobacter spp.: an increasing problem. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Jun;18 (Suppl A):250–255. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90030-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk S. L., McCabe W. R. Meningitis caused by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var anitratus. A specific hazard in neurosurgical patients. Arch Neurol. 1981 Feb;38(2):95–98. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510020053007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P. J., Grimont P. A. Identification and biotyping of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Sep-Oct;138(5):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P. J., Jeanjean S., Vieu J. F., Dijkshoorn L. Species, biotype, and bacteriophage type determinations compared with cell envelope protein profiles for typing Acinetobacter strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.170-176.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cefai C., Richards J., Gould F. K., McPeake P. An outbreak of Acinetobacter respiratory tract infection resulting from incomplete disinfection of ventilatory equipment. J Hosp Infect. 1990 Feb;15(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(90)90128-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkshoorn L., Aucken H. M., Gerner-Smidt P., Kaufmann M. E., Ursing J., Pitt T. L. Correlation of typing methods for Acinetobacter isolates from hospital outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):702–705. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.702-705.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkshoorn L., Michel M. F., Degener J. E. Cell envelope protein profiles of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus strains isolated in hospitals. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Jun;23(4):313–319. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-4-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerner-Smidt P. Frequency of plasmids in strains of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Hosp Infect. 1989 Jul;14(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(89)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerner-Smidt P. Ribotyping of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter baumannii complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2680–2685. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2680-2685.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervich D. H., Grout C. S. An outbreak of nosocomial Acinetobacter infections from humidifiers. Am J Infect Control. 1985 Oct;13(5):210–215. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(85)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giammanco A., Vieu J. F., Bouvet P. J., Sarzana A., Sinatra A. A comparative assay of epidemiological markers for Acinetobacter strains isolated in a hospital. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1989 Dec;272(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(89)80012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartstein A. I., Morthland V. H., Rourke J. W., Jr, Freeman J., Garber S., Sykes R., Rashad A. L. Plasmid DNA fingerprinting of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus subspecies anitratus from intubated and mechanically ventilated patients. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1990 Oct;11(10):531–538. doi: 10.1086/646087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly-Guillou M. L., Bergogne-Berezin E., Vieu J. F. A study of the relationships between antibiotic resistance phenotypes, phage-typing and biotyping of 117 clinical isolates of Acinetobacter spp. J Hosp Infect. 1990 Jul;16(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(90)90048-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly-Guillou M. L., Bergogne-Berezin E., Vieu J. F. Epidémiologie et résistance aux antibiotiques des Acinetobacter en milieu hospitalier. Bilan de 5 années. Presse Med. 1990 Mar 3;19(8):357–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E. Interspecies transformation of Acinetobacter: genetic evidence for a ubiquitous genus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):917–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.917-931.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W. Use of plasmid profiles in epidemiologic surveillance of disease outbreaks and in tracing the transmission of antibiotic resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):228–243. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. E., Vecchio J., Pantelick E. L., Farrel P., Mazon D., Zervos M. J., Hierholzer W. J., Jr Association of contaminated gloves with transmission of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. anitratus in an intensive care unit. Am J Med. 1991 Nov;91(5):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal S., Tager I. B. Prevalence of gram-negative rods in the normal pharyngeal flora. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Sep;83(3):355–357. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata H., Fujita K., Maruyama S., Kakehashi H., Mori Y., Yoshioka H. Acinetobacter calcoaceticus biovar anitratus septicaemia in a neonatal intensive care unit: epidemiology and control. J Hosp Infect. 1989 Jul;14(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(89)90129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos Ferreira M. O., Vieu J. F., Klein B. Phage-types and susceptibility to 26 antibiotics of nosocomial strains of Acinetobacter isolated in Portugal. J Int Med Res. 1984;12(6):364–368. doi: 10.1177/030006058401200609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H., Baginski R., Schulze A., Pulverer G. The distribution of Acinetobacter species in clinical culture materials. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Nov;279(4):544–552. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H., Baginski R. The clinical significance of Acinetobacter baumannii in blood cultures. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jul;277(2):210–218. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80615-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H., Strate A., Schulze A., Pulverer G. Vascular catheter-related bloodstream infection due to Acinetobacter johnsonii (formerly Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. lwoffi): report of 13 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;17(4):632–636. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.4.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherertz R. J., Sullivan M. L. An outbreak of infections with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus in burn patients: contamination of patients' mattresses. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):252–258. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Acinetobacter baumannii serotyping for delineation of outbreaks of nosocomial cross-infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2713–2716. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2713-2716.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Serotyping of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter: serovars of genospecies 3. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 May;273(1):12–23. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]