Abstract
We designed a PCR assay targeted on repeated elements of the ribosomal intergenic spacer which produces highly polymorphic DNA band patterns for different strains of Trypanosoma cruzi. By labeling the PCR products with digoxigenin and by chemiluminescence detection, we improved the assay sensitivity by three orders of magnitude to get T. cruzi strain fingerprints in feces of the trypanosome-infected triatomine bug vector. We also developed a capture assay for the digoxigenin-labeled PCR products that allowed us to detect T. cruzi in triatomine bug vector feces and in human serum samples with a solid support.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avila H., Goncalves A. M., Nehme N. S., Morel C. M., Simpson L. Schizodeme analysis of Trypanosoma cruzi stocks from South and Central America by analysis of PCR-amplified minicircle variable region sequences. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Sep-Oct;42(2):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90160-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane G. G. Hyperreactive malarious splenomegaly (tropical splenomegaly syndrome). Parasitol Today. 1986 Jan;2(1):4–9. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(86)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak J. A., Hall T. E., Crane M. S., Engel J. C., McDaniel J. P., Uriegas R. Trypanosoma cruzi: flow cytometric analysis. I. Analysis of total DNA/organism by means of mithramycin-induced fluorescence. J Protozool. 1982 Aug;29(3):430–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb05427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engman D. M., Reddy L. V., Donelson J. E., Kirchhoff L. V. Trypanosoma cruzi exhibits inter- and intra-strain heterogeneity in molecular karyotype and chromosomal gene location. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jan 15;22(2-3):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch A. C., Reyes M. B. Diagnosis of Chagas disease using recombinant DNA technology. Parasitol Today. 1990 Apr;6(4):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90234-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo I., Ramírez Ochoa J. L. Study of Leishmania mexicana electrokaryotype by clamped homogeneous electric field electrophoresis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 May 15;34(3):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo I., Rangel-Aldao R., Ramírez J. L. A combined polymerase chain reaction-colour development hybridization assay in a microtitre format for the detection of Clostridium spp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1993 Jul;39(4-5):553–557. doi: 10.1007/BF00205050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez A., Prediger E., Huecas M. E., Nogueira N., Lizardi P. M. Minichromosomal repetitive DNA in Trypanosoma cruzi: its use in a high-sensitivity parasite detection assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3356–3360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guevara P., Alonso G., da Silveira J. F., de Mello M., Scorza J. V., Añez N., Ramírez J. L. Identification of new world Leishmania using ribosomal gene spacer probes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Nov;56(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90150-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guevara P., Ramírez J. L., Rojas E., Scorza J. V., González N., Añez N. Leishmania braziliensis in blood 30 years after cure. Lancet. 1993 May 22;341(8856):1341–1341. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf A., Reckmann B., Pingoud A. Direct analysis of polymerase chain reaction products using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay techniques. Anal Biochem. 1991 Oct;198(1):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90510-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson J. M., Gajadhar A. A. Random amplified polymorphic DNA. Parasitol Today. 1992 Jul;8(7):235–235. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(92)90120-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles M. A., Cibulskis R. E. Zymodeme characterization of Trypanosoma cruzi. Parasitol Today. 1986 Apr;2(4):94–97. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(86)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser D. R., Kirchhoff L. V., Donelson J. E. Detection of Trypanosoma cruzi by DNA amplification using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1477–1482. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1477-1482.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
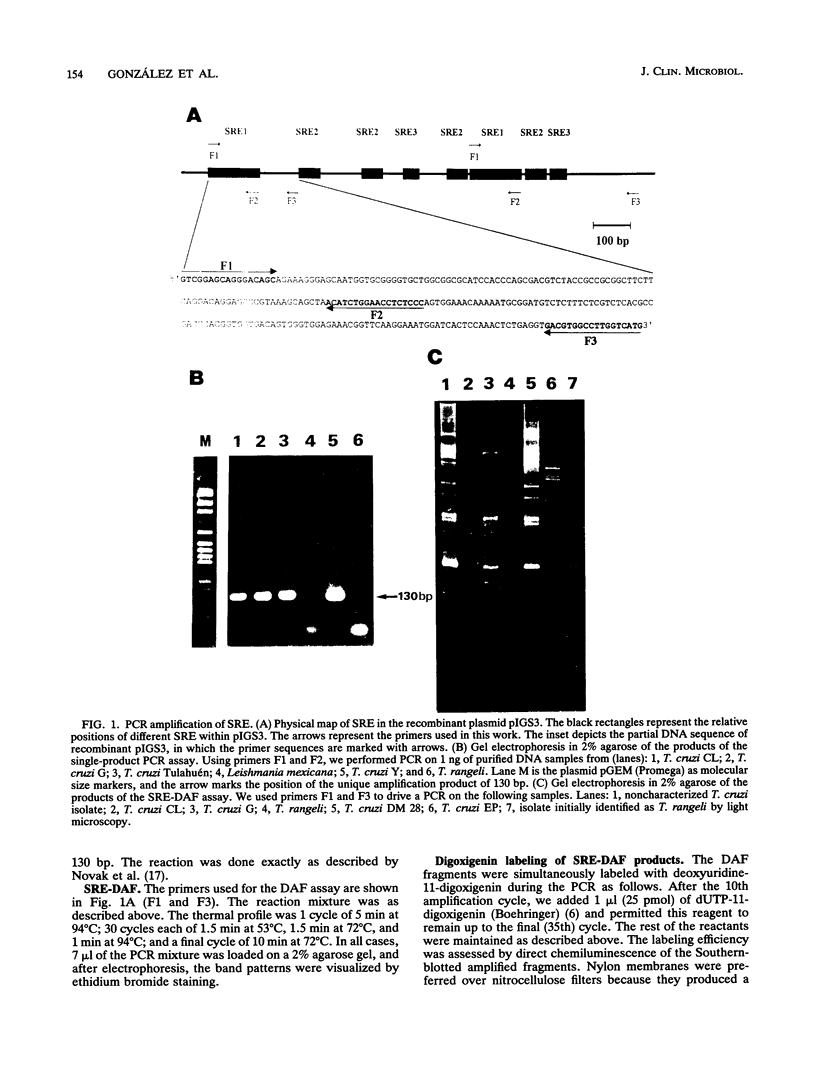
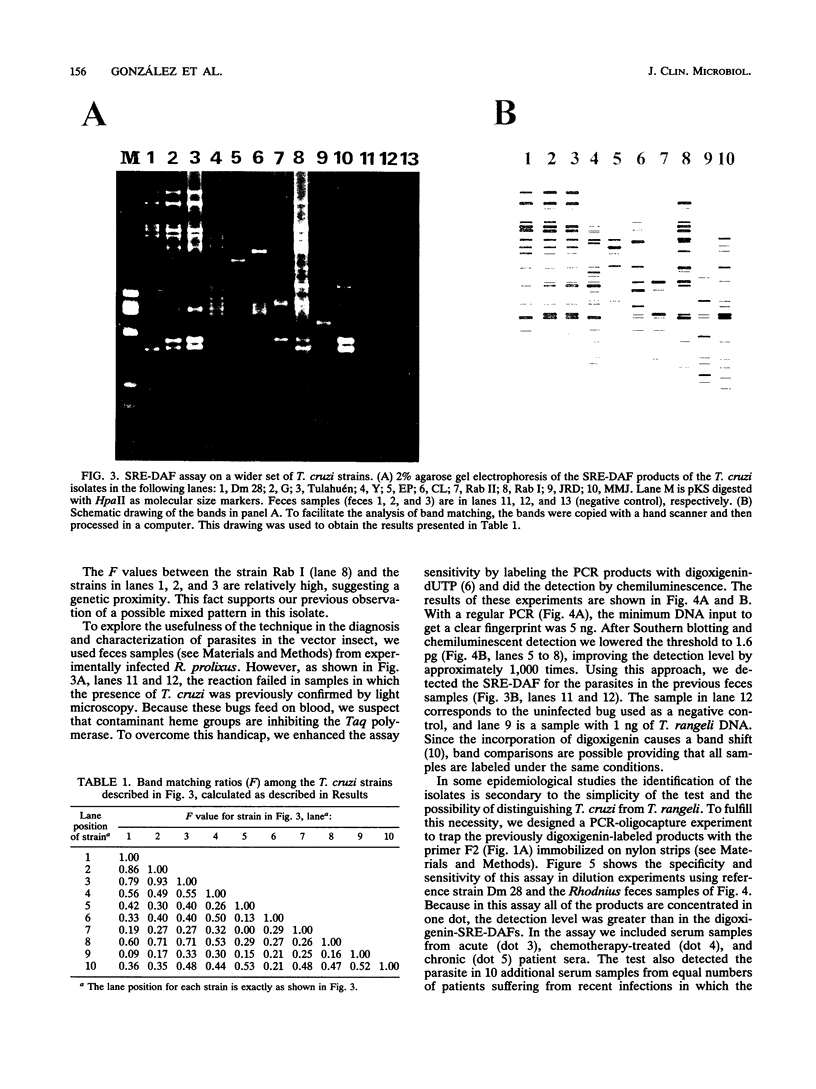
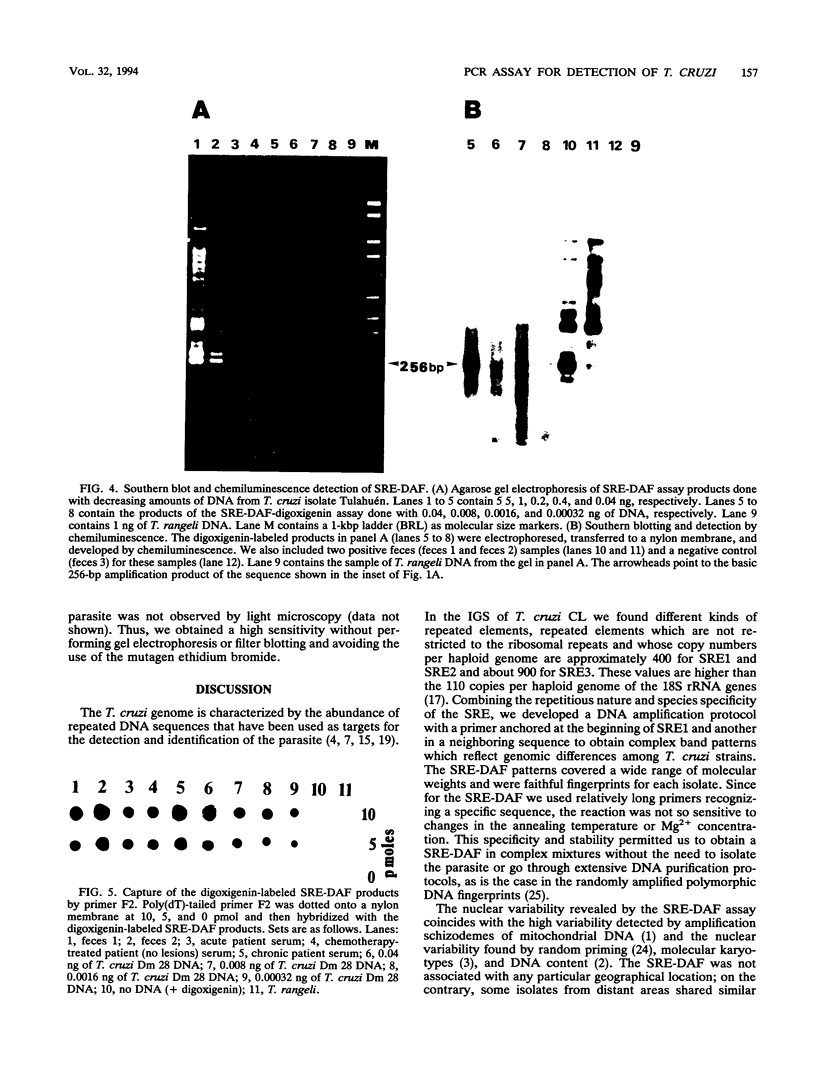
- Novak E. M., de Mello M. P., Gomes H. B., Galindo I., Guevara P., Ramirez J. L., da Silveira J. F. Repetitive sequences in the ribosomal intergenic spacer of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Aug;60(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90138-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez J. L., Guevara P. The ribosomal gene spacer as a tool for the taxonomy of Leishmania. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jan 15;22(2-3):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Requena J. M., Jimenez-Ruiz A., Soto M., Lopez M. C., Alonso C. Characterization of a highly repeated interspersed DNA sequence of Trypanosoma cruzi: its potential use in diagnosis and strain classification. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Apr;51(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90077-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russomando G., Figueredo A., Almirón M., Sakamoto M., Morita K. Polymerase chain reaction-based detection of Trypanosoma cruzi DNA in serum. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2864–2868. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2864-2868.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm N. R., Degrave W., Morel C., Simpson L. Sensitive detection and schizodeme classification of Trypanosoma cruzi cells by amplification of kinetoplast minicircle DNA sequences: use in diagnosis of Chagas' disease. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Mar 15;33(3):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90082-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibayrenc M., Kjellberg F., Ayala F. J. A clonal theory of parasitic protozoa: the population structures of Entamoeba, Giardia, Leishmania, Naegleria, Plasmodium, Trichomonas, and Trypanosoma and their medical and taxonomical consequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2414–2418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibayrenc M., Neubauer K., Barnabé C., Guerrini F., Skarecky D., Ayala F. J. Genetic characterization of six parasitic protozoa: parity between random-primer DNA typing and multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1335–1339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]