Abstract
During a 14-month period, a unique strain of Corynebacterium striatum that produces a diffusible brown pigment was isolated from purulent sputa of nine patients and from nonrespiratory sites of two additional patients. Seven nonpigmented clinical isolates from the same period and three reference strains of C. striatum were compared with the brown isolates. Most patients had multiple sputum cultures with no coryneforms before the brown strain emerged, suggesting that the organism was hospital acquired. DNA restriction fragment patterns and Southern hybridization with the att site probe of Corynebacterium diphtheriae indicated that the brown isolates were a single strain which was distinct from the heterogeneous nonpigmented strains. A common source for the brown C. striatum was not recognized, although all of these patients were located in two adjoining intensive care units. All of the brown isolates, three of the nonpigmented clinical isolates, and two reference strains had positive CAMP reactions with Staphylococcus aureus, which has not been reported for C. striatum prior to this study.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguado J. M., Ponte C., Soriano F. Bacteriuria with a multiply resistant species of Corynebacterium (Corynebacterium group D2): an unnoticed cause of urinary tract infection. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):144–150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr J. G., Murphy P. G. Corynebacterium striatum: an unusual organism isolated in pure culture from sputum. J Infect. 1986 Nov;13(3):297–298. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(86)91454-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowstead T. T., Santiago S. M. Pleuropulmonary infection due to Corynebacterium striatum. Br J Dis Chest. 1980 Apr;74(2):198–200. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(80)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
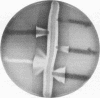
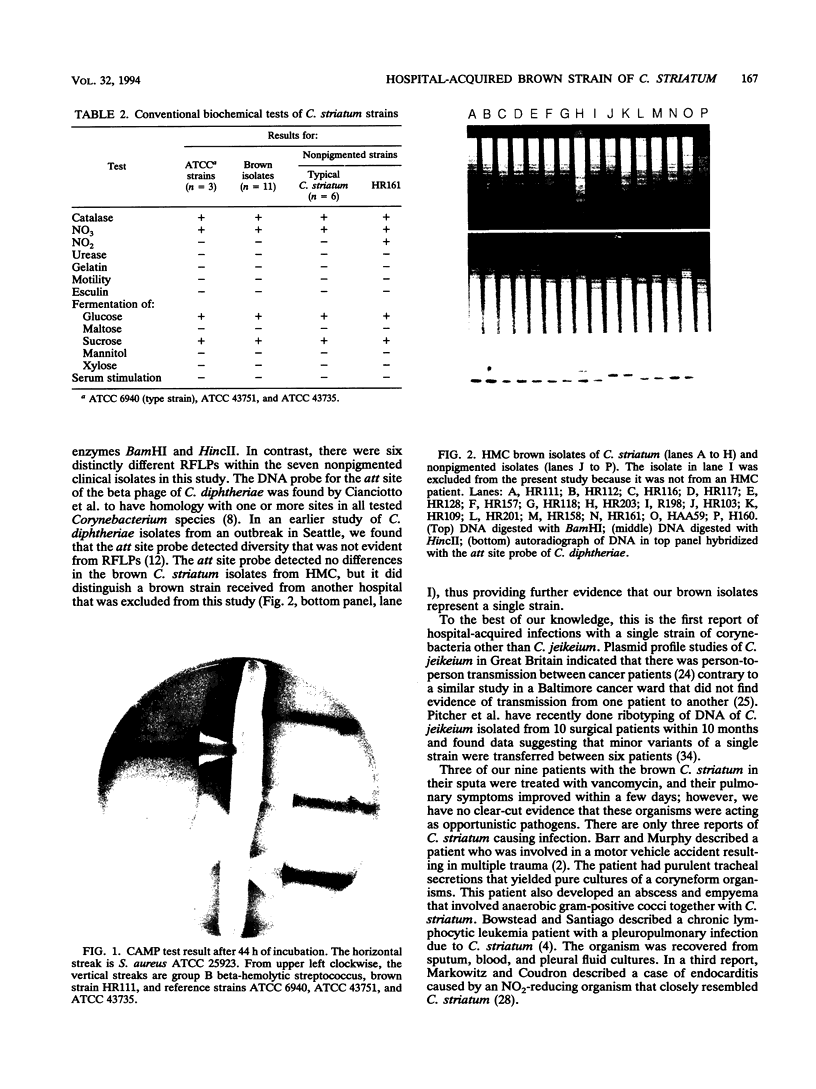
- Brzin B. Accentuation of Staphylococcal hemolysis (CAMP-like test) by pneumococci. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1977 Jun;238(2):281–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck G. A., Groman N. B. Physical mapping of beta-converting and gamma-nonconverting corynebacteriophage genomes. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):131–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.131-142.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury T. K. Synergistic lysis of erythrocytes by Propionibacterium acnes. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.238-241.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N., Rappuoli R., Groman N. Detection of homology to the beta bacteriophage integration site in a wide variety of Corynebacterium spp. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):103–108. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.103-108.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle M. B., Groman N. B., Russell J. Q., Harnisch J. P., Rabin M., Holmes K. K. The molecular epidemiology of three biotypes of Corynebacterium diphtheriae in the Seattle outbreak, 1972-1982. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):670–679. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle M. B., Leonard R. B., Nowowiejski D. J., Malekniazi A., Finn D. J. Evidence of multiple taxa within commercially available reference strains of Corynebacterium xerosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1788–1793. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1788-1793.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle M. B., Lipsky B. A. Coryneform bacteria in infectious diseases: clinical and laboratory aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):227–246. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Briel D., Langs J. C., Rougeron G., Chabot P., Le Faou A. Multiresistant corynebacteria in bacteriuria: a comparative study of the role of Corynebacterium group D2 and Corynebacterium jeikeium. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Jan;17(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90075-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin S. E., Leonard R. B., Briselden A. M., Coyle M. B. Evaluation of the rapid CORYNE identification system for Corynebacterium species and other coryneforms. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1692–1695. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1692-1695.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Hancock G. A. Synergistic hemolysis exhibited by species of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):409–415. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.409-415.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerry-Williams S. M., Noble W. C. Plasmids in group JK coryneform bacteria isolated in a single hospital. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Oct;97(2):255–263. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khabbaz R. F., Kaper J. B., Moody M. R., Schimpff S. C., Tenney J. H. Molecular epidemiology of group JK Corynebacterium on a cancer ward: lack of evidence for patient-to-patient transmission. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):95–99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Rhodes J. C. Encapsulation and melanin formation as indicators of virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):218–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.218-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNCH-PETERSEN E. A corynebacterial agent which protects ruminant erythrocytes against staphylococcal beta toxin. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1954 Jun;32(3):361–368. doi: 10.1038/icb.1954.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Coudron P. E. Native valve endocarditis caused by an organism resembling Corynebacterium striatum. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):8–10. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.8-10.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal L. K., Thornsberry C. New recommendations for disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility tests for methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):482–488. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.482-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr JK coryneforms: a continuing problem for hospital infection control. J Hosp Infect. 1988 Feb;11 (Suppl A):358–366. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90211-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher D., Johnson A., Allerberger F., Woodford N., George R. An investigation of nosocomial infection with Corynebacterium jeikeium in surgical patients using a ribosomal RNA gene probe. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;9(9):643–648. doi: 10.1007/BF01964264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F. Rhodococcus equi: an animal and human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):20–34. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Arnow P. M., Weil D., Rosenbluth J. Outbreak of JK diphtheroid infections associated with environmental contamination. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):668–671. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.668-671.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. C., Leonard R. B., Briselden A., Schoenknecht F. D., Coyle M. B. Characterization of antibiotic-resistant Corynebacterium striatum strains. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Oct;30(4):463–474. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.4.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E., Tompkins L. S., Wagner K. F., Counts G. W., Thomas E. D., Meyers J. D. Infection due to Corynebacterium species in marrow transplant patients. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):167–173. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]