Abstract
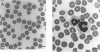
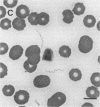
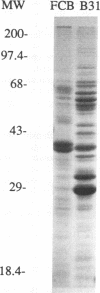
Spirochetemia is a rarely reported observation in dogs. We describe the clinical, hematologic, and immunodiagnostic features of two spirochetemic dogs from northern Florida and the subsequent isolation and preliminary characterization of a Borrelia species from one dog in which culture of a sample for spirochetes was attempted. Results of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, monoclonal antibody testing, and PCR analysis indicate that the Florida isolate is not Borrelia burgdorferi, the only other member of the genus that has been isolated in Florida. Our findings also indicate that a member of the genus Borrelia potentially causes disease in dogs in Florida and that serologic cross-reactivity of the Florida canine Borrelia isolate with B. burgdorferi probably contributes to the inaccurate diagnosis of canine Lyme disease in the region.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Barthold S. W., Magnarelli L. A. Infectious but nonpathogenic isolate of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2693–2699. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2693-2699.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appel M. J., Allan S., Jacobson R. H., Lauderdale T. L., Chang Y. F., Shin S. J., Thomford J. W., Todhunter R. J., Summers B. A. Experimental Lyme disease in dogs produces arthritis and persistent infection. J Infect Dis. 1993 Mar;167(3):651–664. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.3.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Antigenic variation of a relapsing fever Borrelia species. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:155–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSENFELD O. BORRELIAE, HUMAN RELAPSING FEVER, AND PARASITE-VECTOR-HOST RELATIONSHIPS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:46–74. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.46-74.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. T., Levine J. F., Breitschwerdt E. B., Berkhoff H. A. Antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in dogs in North Carolina. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Apr;49(4):473–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmeister E. K., Markham R. B., Childs J. E., Arthur R. R. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and culture for detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in naturally infected Peromyscus leucopus and experimentally infected C.B-17 scid/scid mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2625–2631. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2625-2631.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. In vitro and in vivo susceptibility of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, to four antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):164–167. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. F., Dykstra M. J., Nicholson W. L., Walker R. L., Massey G., Barnes H. J. Attenuation of Borrelia anserina by serial passage in liquid medium. Res Vet Sci. 1990 Jan;48(1):64–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissman B. A., Bosler E. M., Camay H., Ormiston B. G., Benach J. L. Spirochete-associated arthritis (Lyme disease) in a dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Jul 15;185(2):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Schreier A. B. Persistence of antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in dogs of New York and Connecticut. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1990 Apr 1;196(7):1064–1068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. K., Jr, Robertson C. S., Goodman J. C. Spinal cord ischemia-induced elevation of amino acids: extracellular measurement with microdialysis. Neurochem Res. 1990 Jun;15(6):635–639. doi: 10.1007/BF00973755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmoen T. L., Sebring R. W., Blumer B. M., Chavez L. G., Jr, Chu H. J., Acree W. M. Examination of Koch's postulates for Borrelia burgdorferi as the causative agent of limb/joint dysfunction in dogs with borreliosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1992 Aug 1;201(3):412–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Heim U., Schäfer R. Zum Vorkommen von Antikörpern gegen Borrelia burgdorferi bei Hunden einer Kleintierpraxis in Nordbayern. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1991 Nov 1;104(11):384–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]