Abstract
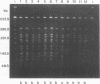
We used pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) of chromosomal DNA digested with XbaI to determine the distribution of different Bordetella pertussis strains from clinical isolates obtained during a large whooping cough outbreak that occurred in Alberta, Canada, from December 1989 to May 1991. Our initial study analyzed 28 clinical isolates, 14 from the city of Edmonton and 1 from each of 14 northern Alberta towns. These clinical isolates were randomly chosen over the course of the 18-month outbreak. The DNA profiles were more heterogeneous than anticipated and caused concern that PFGE was too sensitive a technique to characterize strains. Further analysis showed that this was not the case, as clusters of similar PFGE patterns were observed in strains isolated from the same outlying town. Identical PFGE patterns were also seen in clinical strains obtained from different members of the same family. Two PFGE pattern types, a and b, predominated in the outbreak, accounting overall for 44 of 70 B. pertussis strains tested. Results from isolates from outlying towns, however, indicated involvement of local strains rather than a single, highly infectious strain in the whooping cough outbreak in Alberta.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbeit R. D., Arthur M., Dunn R., Kim C., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Resolution of recent evolutionary divergence among Escherichia coli from related lineages: the application of pulsed field electrophoresis to molecular epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):230–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosch R., Buchrieser C., Rocourt J. Subtyping of Listeria monocytogenes serovar 4b by use of low-frequency-cleavage restriction endonucleases and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jul-Aug;142(6):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90080-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. Variation in Bordetella pertussis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):367–374. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang N., Taylor D. E. Use of pulsed-field agarose gel electrophoresis to size genomes of Campylobacter species and to construct a SalI map of Campylobacter jejuni UA580. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5211–5217. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5211-5217.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewanowich C. A., Chui L. W., Paranchych M. G., Peppler M. S., Marusyk R. G., Albritton W. L. Major outbreak of pertussis in northern Alberta, Canada: analysis of discrepant direct fluorescent-antibody and culture results by using polymerase chain reaction methodology. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1715–1725. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1715-1725.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordillo M. E., Reeve G. R., Pappas J., Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L., Murray B. E. Molecular characterization of strains of enteroinvasive Escherichia coli O143, including isolates from a large outbreak in Houston, Texas. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):889–893. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.889-893.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiyama S., Ohta M., Shimokata K., Kato N., Takeuchi J. Genomic DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as an epidemiological marker for study of nosocomial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2690–2695. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2690-2695.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khattak M. N., Matthews R. C., Burnie J. P. Is Bordetella pertussis clonal? BMJ. 1992 Mar 28;304(6830):813–815. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6830.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khattak M. N., Matthews R. C. Genetic relatedness of Bordetella species as determined by macrorestriction digests resolved by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;43(4):659–664. doi: 10.1099/00207713-43-4-659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTON N. W. EFFECTIVENESS OF PERTUSSIS VACCINES. Br Med J. 1965 Jul 3;2(5452):11–13. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5452.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTON N. W. TYPE-SPECIFIC IMMUNITY AGAINST WHOOPING-COUGH. Br Med J. 1963 Sep 21;2(5359):724–726. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5359.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston N. W., Stanbridge T. N. Efficacy of pertussis vaccines: a brighter horizon. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 19;3(5824):448–451. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5824.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römling U., Grothues D., Bautsch W., Tümmler B. A physical genome map of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4081–4089. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonmaker D., Heimberger T., Birkhead G. Comparison of ribotyping and restriction enzyme analysis using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for distinguishing Legionella pneumophila isolates obtained during a nosocomial outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1491–1498. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1491-1498.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldati L., Piffaretti J. C. Molecular typing of Shigella strains using pulsed field gel electrophoresis and genome hybridization with insertion sequences. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jun;142(5):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90182-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge T. N., Preston N. W. Variation of serotype in strains of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Oct;73(2):305–310. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Garletts T. L. Derivation of a physical map of the chromosome of Bordetella pertussis Tohama I. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7770–7777. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7770-7777.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varughese P. V., Grauwiler A., Carter A. O., Duclos P. Pertussis outbreak in the Yukon Territory--1989. Can Dis Wkly Rep. 1990 Apr 7;16(14):63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan W., Chang N., Taylor D. E. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli genomic DNA and its epidemiologic application. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1068–1072. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]