Abstract
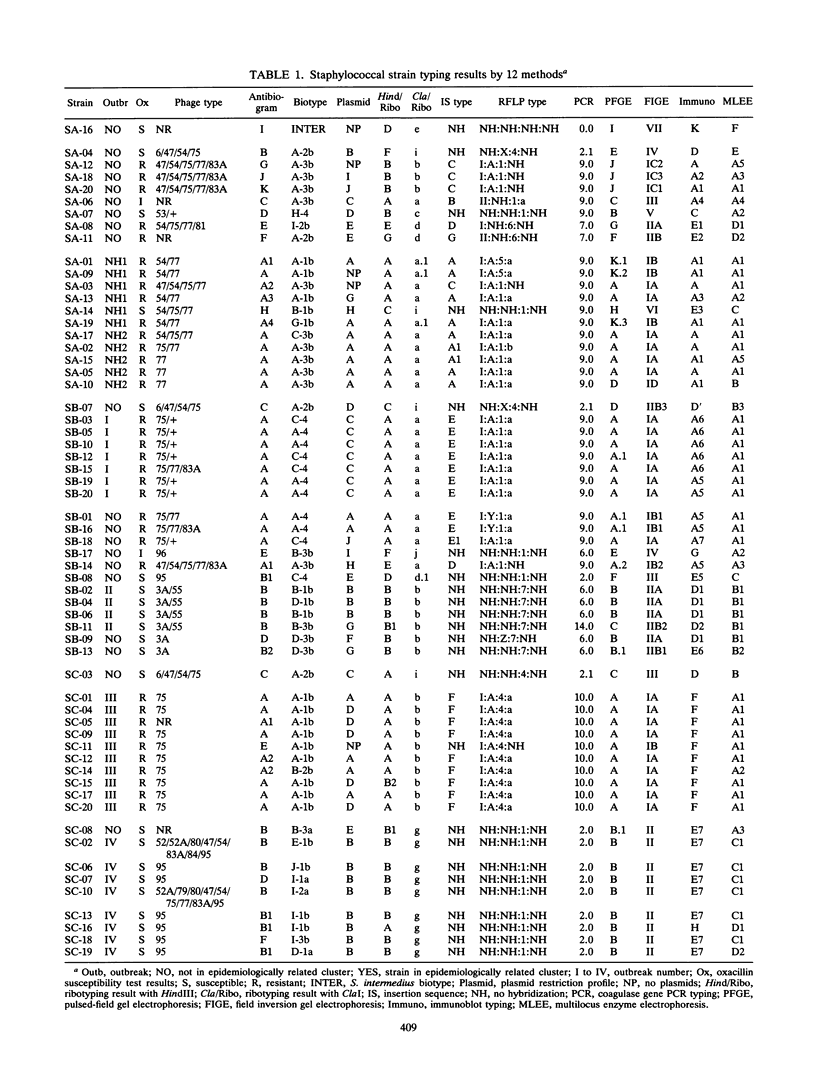
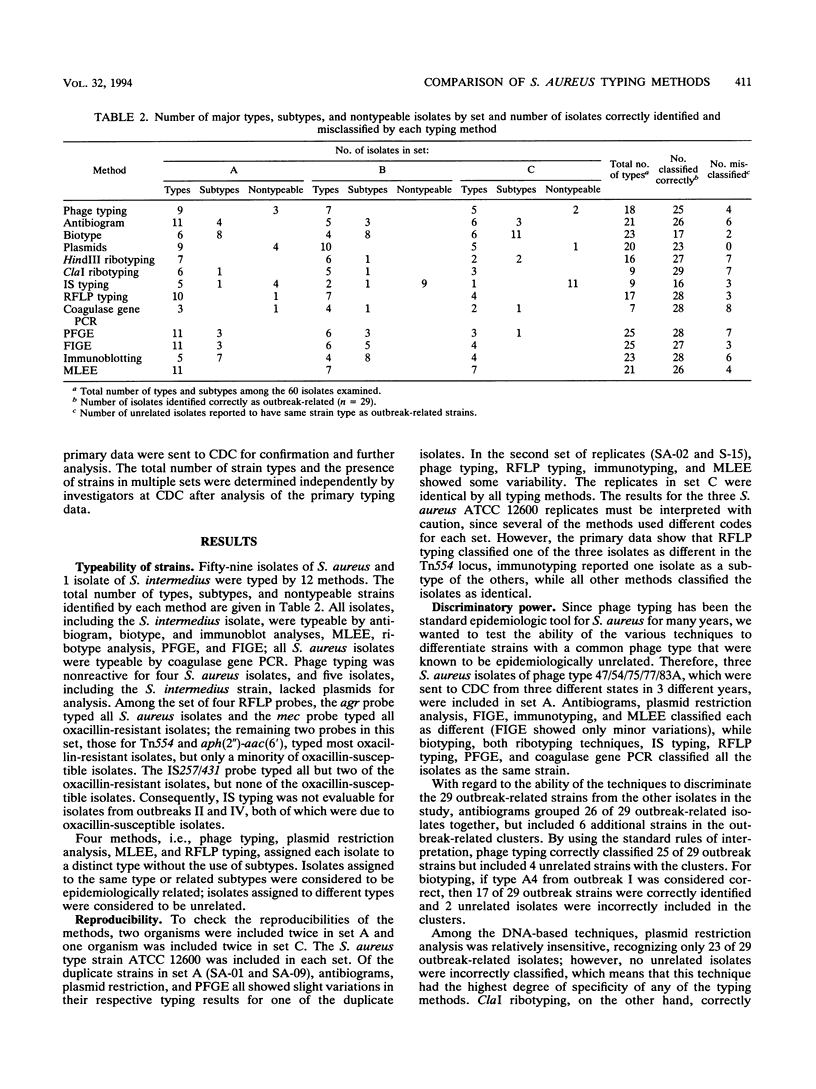
Fifty-nine Staphylococcus aureus isolates and 1 isolate of Staphylococcus intermedius were typed by investigators at eight institutions by using either antibiograms, bacteriophage typing, biotyping, immunoblotting, insertion sequence typing with IS257/431, multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, restriction analysis of plasmid DNA, pulsed-field or field inversion gel electrophoresis, restriction analysis of PCR-amplified coagulase gene sequences, restriction fragment length polymorphism typing by using four staphylococcal genes as probes, or ribotyping. Isolates from four well-characterized outbreaks (n = 29) and a collection of organisms from two nursing homes were mixed with epidemiologically unrelated stock strains from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Several isolates were included multiple times either within or between the sets of isolates to analyze the reproducibilities of the typing systems. Overall, the DNA-based techniques and immunoblotting were most effective in grouping outbreak-related strains, recognizing 27 to 29 of the 29 outbreak-related strains; however, they also tended to include 3 to 8 epidemiologically unrelated isolates in the same strain type. Restriction fragment length polymorphism methods with mec gene-associated loci were less useful than other techniques for typing oxacillin-susceptible isolates. Phage typing, plasmid DNA restriction analysis, and antibiogram analysis, the techniques most readily available to clinical laboratories, identified 23 to 26 of 29 outbreak-related isolates and assigned 0 to 6 unrelated isolates to outbreak strain types. No single technique was clearly superior to the others; however, biotyping, because it produced so many subtypes, did not effectively group outbreak-related strains of S. aureus.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbeit R. D., Arthur M., Dunn R., Kim C., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Resolution of recent evolutionary divergence among Escherichia coli from related lineages: the application of pulsed field electrophoresis to molecular epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):230–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Mayhall C. G. Comparison of epidemiological markers used in the investigation of an outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):395–399. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.395-399.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis-Maino L., Berger-Bächi B., Weber H., Beck W. D., Kayser F. H. IS431, a staphylococcal insertion sequence-like element related to IS26 from Proteus vulgaris. Gene. 1987;59(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H. M., Rimland D., Kiehlbauch J. A., Terry P. M., Wachsmuth I. K. Epidemiologic typing of Staphylococcus aureus by DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms of rRNA genes: elucidation of the clonal nature of a group of bacteriophage-nontypeable, ciprofloxacin-resistant, methicillin-susceptible S. aureus isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):362–369. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.362-369.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carles-Nurit M. J., Christophle B., Broche S., Gouby A., Bouziges N., Ramuz M. DNA polymorphisms in methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2092–2096. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2092-2096.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coia J. E., Thomson-Carter F., Baird D., Platt D. J. Characterisation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by biotyping, immunoblotting and restriction enzyme fragmentation patterns. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Feb;31(2):125–132. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-2-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson B. D., Phillips I. Epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):57–65. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M., Cookson B. D., Talsania H. G., Owen R. J. Numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2574–2581. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2574-2581.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner J. S., Jarvis W. R., Emori T. G., Horan T. C., Hughes J. M. CDC definitions for nosocomial infections, 1988. Am J Infect Control. 1988 Jun;16(3):128–140. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(88)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston M. A., Duff P. S., Naidoo J., Ellis K., Roberts J. I., Richardson J. F., Marples R. R., Cooke E. M. Evaluation of electrophoretic methods for typing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(3):189–197. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-3-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie M. T., Lyon B. R., Skurray R. A. Typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by antibiotic resistance phenotypes. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Jan;31(1):57–64. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Winters M. A. Rapid method for epidemiological evaluation of gram-positive cocci by field inversion gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):577–580. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.577-580.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz M. B., Mulligan M. E., Kwok R., O'Brien H., Caballes C., Garcia J. P. Management and epidemiologic analyses of an outbreak due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Med. 1992 Jun;92(6):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90778-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh S. H., Byrne S. K., Zhang J. L., Chow A. W. Molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus on the basis of coagulase gene polymorphisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1642–1645. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1642-1645.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartstein A. I., Morthland V. H., Eng S., Archer G. L., Schoenknecht F. D., Rashad A. L. Restriction enzyme analysis of plasmid DNA and bacteriophage typing of paired Staphylococcus aureus blood culture isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1874–1879. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1874-1879.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Cooksey R. C., Clark N. C., Hill B. C., Jarvis W. R., Thornsberry C. Biotyping coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1950–1956. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1950-1956.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa K. I., Heiba A. A., Hancock G. Nontypeable bacteriophage patterns of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus involved in a hospital outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2249–2251. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2249-2251.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B., Kornblum J., Arbeit R. D., Eisner W., Maslow J. N., McGeer A., Low D. E., Novick R. P. Evidence for a clonal origin of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):227–230. doi: 10.1126/science.8093647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maple P. A., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W. World-wide antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1989 Mar 11;1(8637):537–540. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslow J. N., Brecher S. M., Adams K. S., Durbin A., Loring S., Arbeit R. D. Relationship between indole production and differentiation of Klebsiella species: indole-positive and -negative isolates of Klebsiella determined to be clonal. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2000–2003. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2000-2003.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslow J. N., Mulligan M. E., Arbeit R. D. Molecular epidemiology: application of contemporary techniques to the typing of microorganisms. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;17(2):153–164. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal L. K., Facklam R., Reeves M., Hunter S., Swenson J. M., Hill B. C., Tenover F. C. Analysis of multiply antimicrobial-resistant isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae from the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Oct;36(10):2176–2184. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.10.2176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Arbeit R. D. Epidemiologic and clinical utility of typing systems for differentiating among strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1991 Jan;12(1):20–28. doi: 10.1086/646234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Kwok R. Y., Citron D. M., John J. F., Jr, Smith P. B. Immunoblots, antimicrobial resistance, and bacteriophage typing of oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2395–2401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2395-2401.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Wakefield D. S., Hollis R., Fredrickson M., Evans E., Massanari R. M. The clinical microbiology laboratory as an aid in infection control. The application of molecular techniques in epidemiologic studies of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 May-Jun;14(3):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(91)90034-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevost G., Jaulhac B., Piemont Y. DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis is more effective than ribotyping in distinguishing among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):967–973. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.967-973.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saulnier P., Bourneix C., Prévost G., Andremont A. Random amplified polymorphic DNA assay is less discriminant than pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for typing strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):982–985. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.982-985.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting C., Branger C., Fournier J. M., Witte W., Boutonnier A., Wolz C., Goullet P., Döring G. Typing of Staphylococcus aureus by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, zymotyping, capsular typing, and phage typing: resolution of clonal relationships. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.227-232.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struelens M. J., Deplano A., Godard C., Maes N., Serruys E. Epidemiologic typing and delineation of genetic relatedness of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by macrorestriction analysis of genomic DNA by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2599–2605. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2599-2605.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Peralta J. M., Simons A. R. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:377–391. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R. P., Nettleman M. D., Jones R. N., Pfaller M. A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: implications for the 1990s and effective control measures. Am J Med. 1991 Sep 16;91(3B):221S–227S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Hosein I. K., Shively R., MacLowry J. D. Phage pattern-specific oxacillin-resistant and borderline oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in U.S. hospitals: epidemiological significance. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):252–254. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.252-254.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuccarelli A. J., Roy I., Harding G. P., Couperus J. J. Diversity and stability of restriction enzyme profiles of plasmid DNA from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.97-102.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum A., Bax R., Peerbooms P., Goessens W. H., van Leeuwen N., Quint W. G. Comparison of phage typing and DNA fingerprinting by polymerase chain reaction for discrimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):798–803. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.798-803.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



