Abstract
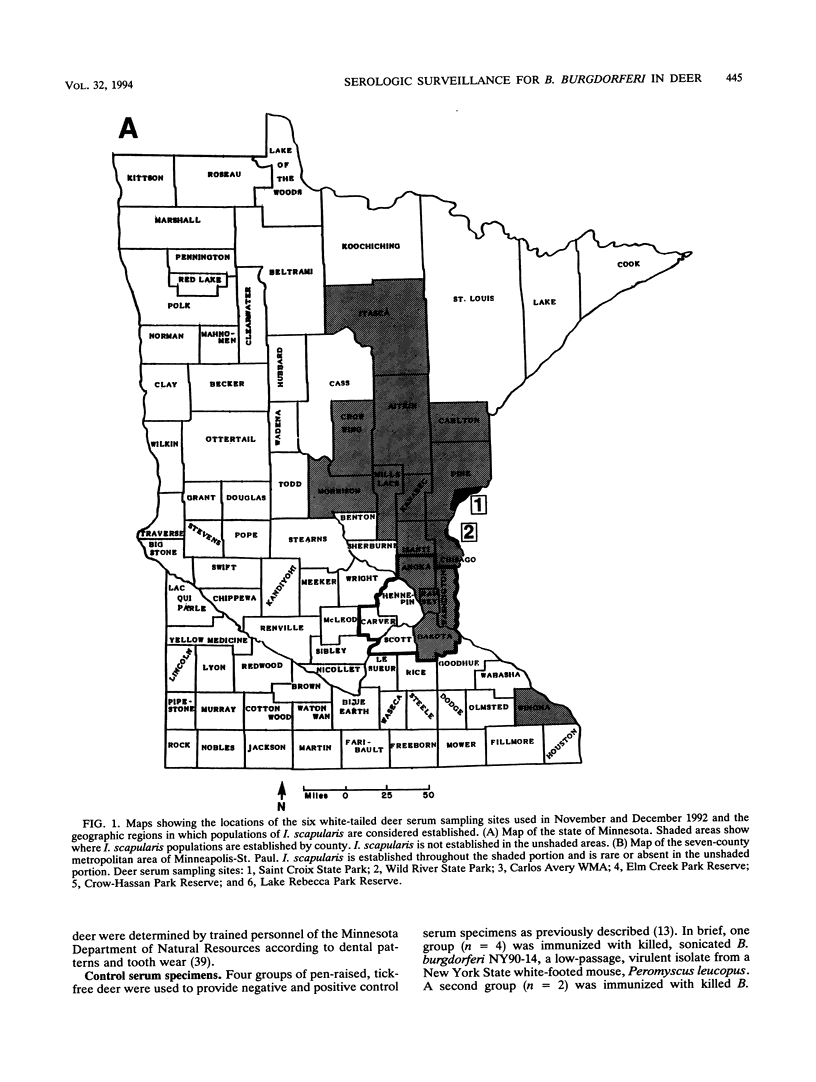
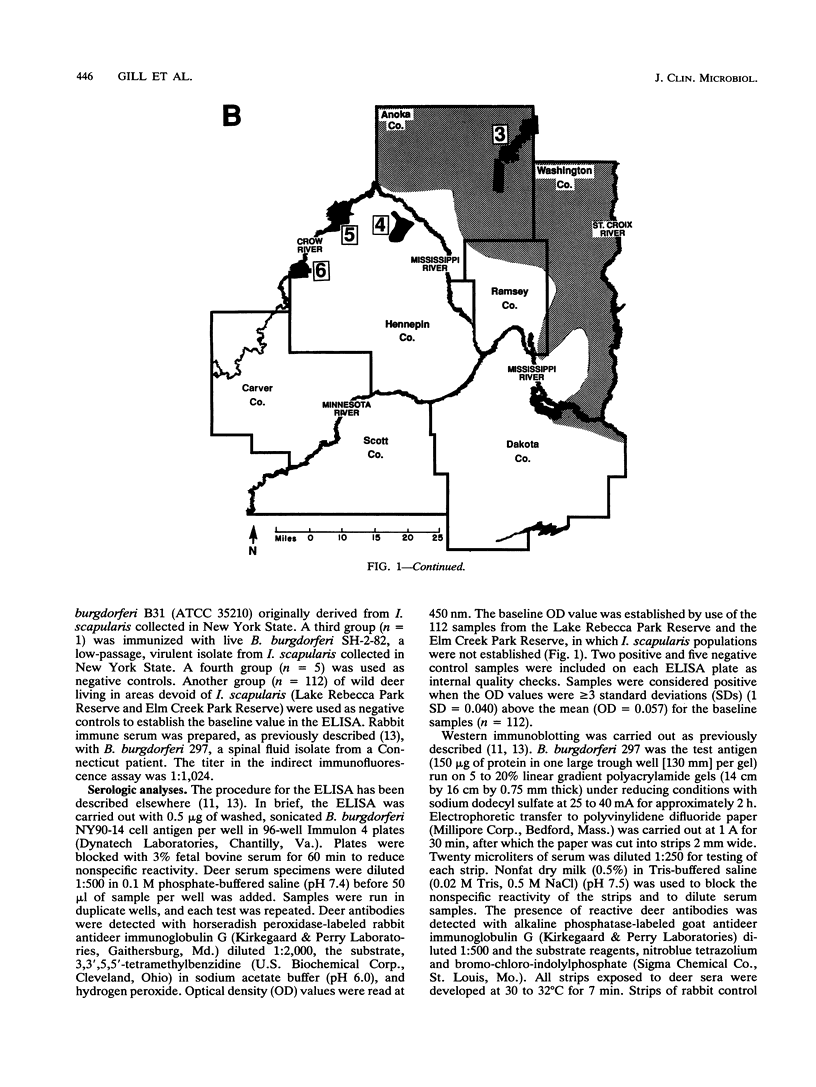
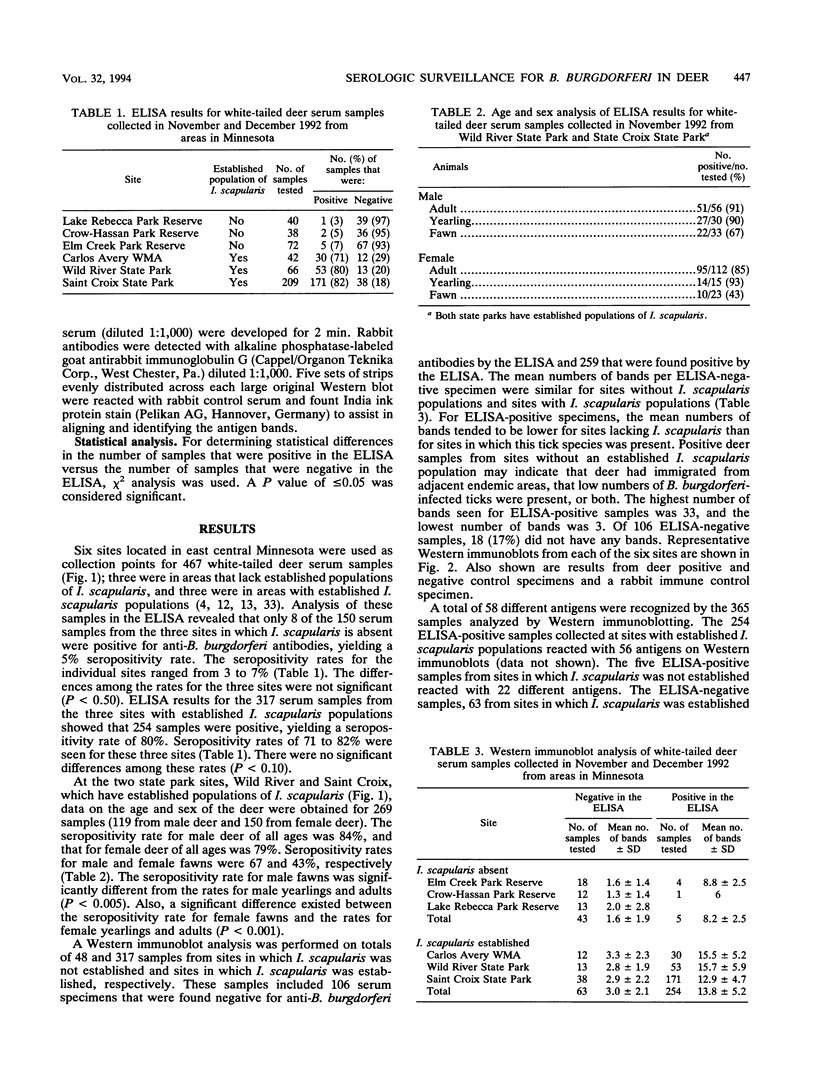
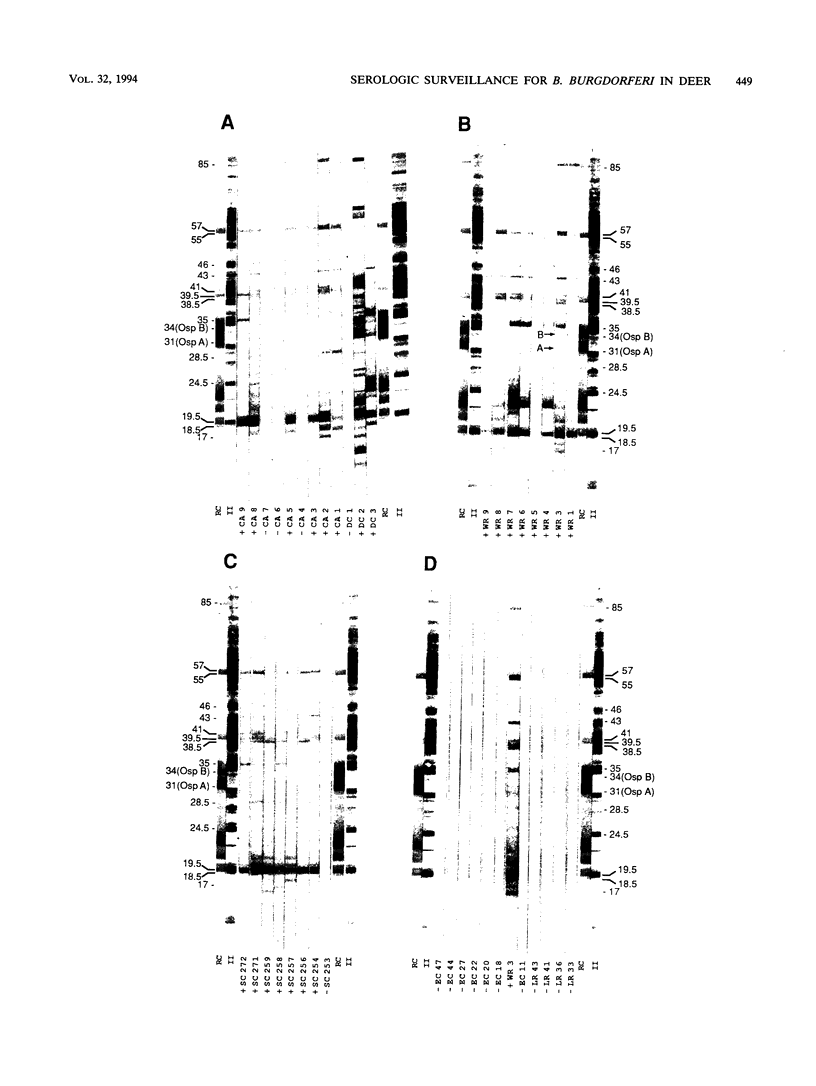
To determine the effectiveness of white-tailed deer as sentinel animals in serologic surveillance programs for Borrelia burgdorferi, we performed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western immunoblotting analyses on 467 deer serum samples. The seropositivity rate in the ELISA was 5% for the 150 samples collected at the three sites in which the tick Ixodes scapularis was absent. The three sites with established I. scapularis populations had a seropositivity rate of 80% for 317 samples. Results were similar for two closely situated sites, one with an established I. scapularis population and one without; these sites were only 15 km apart. Rates of seropositivity were significantly higher in yearling and adult deer than in fawns. The mean numbers of bands seen on Western immunoblots were 3.0 for samples negative in the ELISA and 13.8 for samples positive in the ELISA; all of these samples were collected from sites in which I. scapularis was established. At sites in which I. scapularis was absent, the mean numbers of bands seen were 1.6 for samples negative in the ELISA and 8.2 for samples positive in the ELISA. There were 14 different B. burgdorferi antigens that reacted with more than 50% of the ELISA-positive samples from areas with I. scapularis. A 19.5-kDa antigen reacted with 94% of the ELISA-positive samples. Reactivity against OspA and OspB was weak a infrequent (2%). Serologic analysis of white-tailed deer sera appears to be an accurate and sensitive surveillance method for determining whether B. burgdorferi is present in specific geographic locations.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F. Epizootiology of Borrelia in Ixodes tick vectors and reservoir hosts. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Sep-Oct;11 (Suppl 6):S1451–S1459. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_6.s1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Laboratory aspects of Lyme borreliosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Oct;1(4):399–414. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu H. J., Chavez L. G., Jr, Blumer B. M., Sebring R. W., Wasmoen T. L., Acree W. M. Immunogenicity and efficacy study of a commercial Borrelia burgdorferi bacterin. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1992 Aug 1;201(3):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels T. J., Fish D., Levine J. F., Greco M. A., Eaton A. T., Padgett P. J., LaPointe D. A. Canine exposure to Borrelia burgdorferi and prevalence of Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) on deer as a measure of Lyme disease risk in the northeastern United States. J Med Entomol. 1993 Jan;30(1):171–178. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridriksdóttir V., Nesse L. L., Gudding R. Seroepidemiological studies of Borrelia burgdorferi infection in sheep in Norway. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1271–1277. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1271-1277.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. S., Johnson R. C., Sinclair M. K., Weisbrod A. R. Prevalence of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, in deer ticks (Ixodes dammini) collected from white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in Saint Croix State Park, Minnesota. J Wildl Dis. 1993 Jan;29(1):64–72. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-29.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. S., McLean R. G., Neitzel D. F., Johnson R. C. Serologic analysis of white-tailed deer sera for antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and western immunoblotting. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):318–322. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.318-322.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. T., Walker R. L., Nicholson W. L., Heidner H. W., Levine J. F., Burgess E. C., Wyand M., Breitschwerdt E. B., Berkhoff H. A. Immunoblot analysis of immunoglobulin G response to the Lyme disease agent (Borrelia burgdorferi) in experimentally and naturally exposed dogs. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):648–653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.648-653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde F. W., Johnson R. C. Genetic relationship of lyme disease spirochetes to Borrelia, Treponema, and Leptospira spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):151–154. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.151-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma B., Christen B., Leung D., Vigo-Pelfrey C. Serodiagnosis of Lyme borreliosis by western immunoblot: reactivity of various significant antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):370–376. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.370-376.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Apperson C. S., Fish D., Johnson R. C., Chappell W. A. Spirochetes in ticks and antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in white-tailed deer from Connecticut, New York State, and North Carolina. J Wildl Dis. 1986 Apr;22(2):178–188. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-22.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Burgdorfer W., Chappell W. A. Parasitism by Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) and antibodies to spirochetes in mammals at Lyme disease foci in Connecticut, USA. J Med Entomol. 1984 Jan 26;21(1):52–57. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/21.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Oliver J. H., Jr, Hutcheson H. J., Anderson J. F. Antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in deer and raccoons. J Wildl Dis. 1991 Oct;27(4):562–568. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-27.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Oliver J. H., Jr, Hutcheson H. J., Boone J. L., Anderson J. F. Antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in rodents in the eastern and southern United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1449–1452. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1449-1452.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahnke G. L., Stallknecht D. E., Greene C. E., Nettles V. F., Marks M. A. Serologic survey for antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in white-tailed deer in Georgia. J Wildl Dis. 1993 Apr;29(2):230–236. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-29.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Samuels D. S., Garon C. F. Transcriptional analyses and mapping of the ospC gene in Lyme disease spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):926–932. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.926-932.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukolwe S. W., Kocan A. A., Wyckoff J. H., 3rd Serological survey for Lyme disease in domestic dogs and white-tailed deer from Oklahoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Jun 16;653:172–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb19641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal D., Taverna C., Hitzig W. H. Immunoblot analysis of antibody binding to polypeptides of Borrelia burgdorferi in children with different clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Pediatr Res. 1989 Oct;26(4):377–382. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198910000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Carter C. J., Howell J. K., Barbour A. G. Low-passage-associated proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi B31: characterization and molecular cloning of OspD, a surface-exposed, plasmid-encoded lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4662–4672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4662-4672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. H., Jr, Owsley M. R., Hutcheson H. J., James A. M., Chen C., Irby W. S., Dotson E. M., McLain D. K. Conspecificity of the ticks Ixodes scapularis and I. dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1993 Jan;30(1):54–63. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp M. T., Aydintug M. K., Bohm R. P., Jr, Cogswell F. B., Dennis V. A., Lanners H. N., Lowrie R. C., Jr, Roberts E. D., Conway M. D., Karaçorlu M. Early and early disseminated phases of Lyme disease in the rhesus monkey: a model for infection in humans. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):3047–3059. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.3047-3059.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T., Piesman J., Hunt A. R., Keen M. G., Happ C. M., Johnson B. J. The hamster immune response to tick-transmitted Borrelia burgdorferi differs from the response to needle-inoculated, cultured organisms. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3648–3653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod A. R., Johnson R. C. Lyme disease and migrating birds in the Saint Croix River Valley. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):1921–1924. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1921-1924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]