Abstract
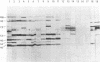
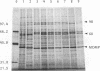
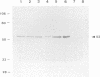
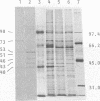
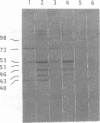
Proteins of Chlamydia pneumoniae immunodominant in humans were characterized with the sera of 13 patients who were not likely to have been exposed to C. trachomatis or C. psittaci. The serological responses among these patients were similar on a qualitative basis, but some differences were found quantitatively. However, the serological responses of the patients who were infected with C. pneumoniae differed markedly from those of two patients who were infected with C. trachomatis and two who were infected with C. psittaci and those of mice that were transtracheally infected with C. pneumoniae. Among proteins immunodominant in the patients who were infected with C. pneumoniae, a 40-kDa major outer membrane protein was genus specific and 53-, 46-, and 43-kDa proteins were species specific in their reactions with the majority of the human sera used. A few sera reacted strongly with a 73-kDa protein genus specifically. Some proteins with weak immunogenicity exhibited species specificity. An antigenic analysis with human sera and murine monoclonal antibodies against the 53-kDa protein showed that hte antigenicities were strictly conserved among the seven strains of C. pneumoniae tested. The genus-specific 73-kDa protein was solubilized with octylglucoside. All of the species-specific immunodominant proteins were solubilized with sodium dodecyl sulfate, but the genus-specific major outer membrane protein was not. These results suggest that a serological diagnosis of C. pneumoniae infection could be achieved species specifically by comparison of the serum responses to sodium dodecyl sulfate- and octylglucoside-soluble fractions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black C. M., Johnson J. E., Farshy C. E., Brown T. M., Berdal B. P. Antigenic variation among strains of Chlamydia pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1312–1316. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1312-1316.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Hitchcock P. J. Monoclonal antibody against a genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia species: location of the epitope on chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. A., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. Structural and antigenic analysis of Chlamydia pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):93–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.93-97.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. A., Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Serological response to Chlamydia pneumoniae infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1261–1264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1261-1264.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. W., al-Mahdawi S. A., Giles I. G., Treharne J. D., Ward M. E., Clark I. N. Nucleotide sequence and taxonomic value of the major outer membrane protein gene of Chlamydia pneumoniae IOL-207. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):465–475. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer R. S., Treharne J. D., Jones B. R., Herring J. Chlamydial infection. Results of micro-immunofluorescence tests for the detection of type-specific antibody in certain chlamydial infections. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):452–459. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushi H., Hirai K. Proposal of Chlamydia pecorum sp. nov. for Chlamydia strains derived from ruminants. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;42(2):306–308. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-2-306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Altman J. A new Chlamydia psittaci strain, TWAR, isolated in acute respiratory tract infections. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 17;315(3):161–168. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607173150305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Campbell L. A. Current knowledge on Chlamydia pneumoniae, strain TWAR, an important cause of pneumonia and other acute respiratory diseases. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;8(3):191–202. doi: 10.1007/BF01965260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamoto Y., Iijima Y., Miyashita N., Matsumoto A., Sakano T. Antigenic characterization of Chlamydia pneumoniae isolated in Hiroshima, Japan. Microbiol Immunol. 1993;37(6):495–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1993.tb03241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamoto Y., Sakano T. [Isolation of Chlamydia pneumoniae from a patient with acute bronchitis]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1992 May;66(5):637–642. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.66.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornak J. M., Kuo C. C., Campbell L. A. Sequence analysis of the gene encoding the Chlamydia pneumoniae DnaK protein homolog. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):721–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.721-725.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Chen H. H., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Identification of a new group of Chlamydia psittaci strains called TWAR. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):1034–1037. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.1034-1037.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladany S., Black C. M., Farshy C. E., Ossewaarde J. M., Barnes R. C. Enzyme immunoassay to determine exposure to Chlamydia pneumoniae (strain TWAR). J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2778–2783. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2778-2783.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclean I. W., Peeling R. W., Brunham R. C. Characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis antigens with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):141–147. doi: 10.1139/m88-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manire G. P., Tamura A. Preparation and chemical composition of the cell walls of mature infectious dense forms of meningopneumonitis organisms. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1178–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1178-1183.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita N., Matsumoto A. Establishment of a particle-counting method for purified elementary bodies of chlamydiae and evaluation of sensitivities of the IDEIA Chlamydia kit and DNA probe by using the purified elementary bodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2911–2916. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2911-2916.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Interaction of chlamydiae and host cells in vitro. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):143–190. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.143-190.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osser S., Persson K. Immune response to genital chlamydial infection and influence of Chlamydia pneumoniae (TWAR) antibodies. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Jun;8(6):532–535. doi: 10.1007/BF01967475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popov V. L., Shatkin A. A., Pankratova V. N., Smirnova N. S., von Bonsdorff C. H., Ekman M. R., Mörttinen A., Saikku P. Ultrastructure of Chlamydia pneumoniae in cell culture. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Nov 15;68(2):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90115-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Sanchez-Pescador R., Wagar E. A., Inouye C., Urdea M. S. Diversity of Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3879–3885. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3879-3885.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Tam M. R., Kuo C. C., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis: antibody specificities and antigen characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMURA A., HIGASHI N. PURIFICATION AND CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF MENINGOPNEUMONITIS VIRUS. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:596–604. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]