Abstract
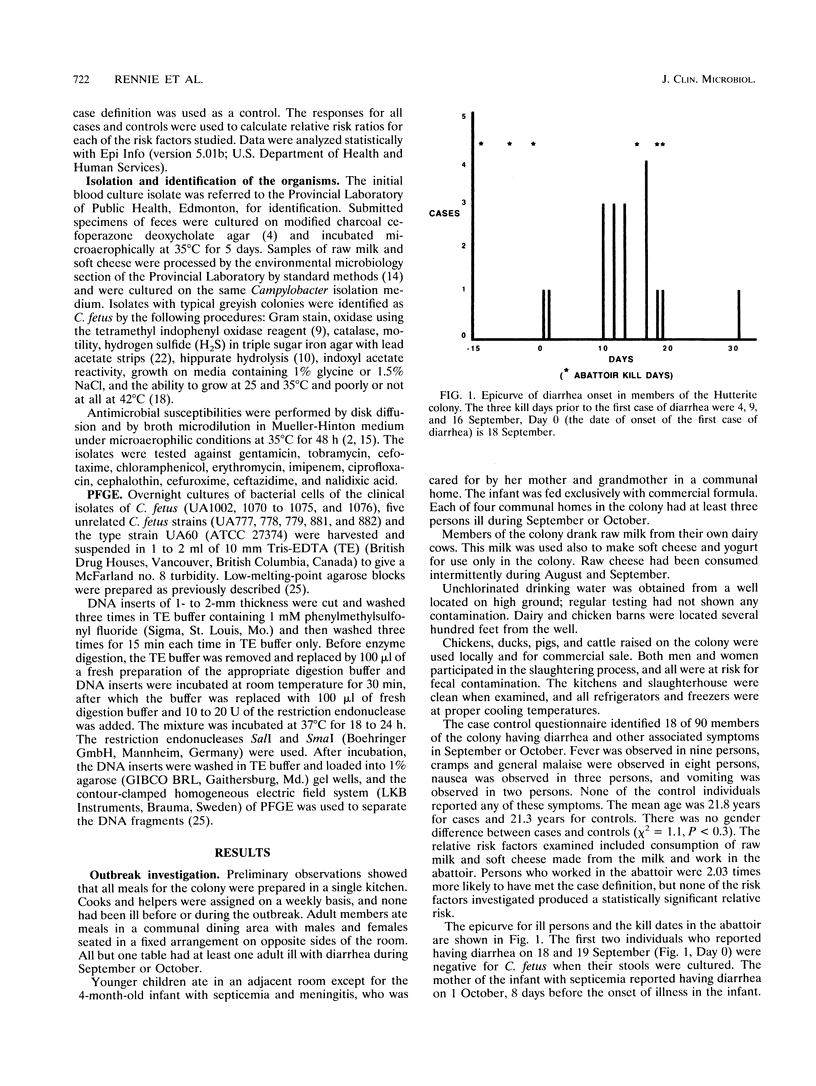
Following a case of Campylobacter fetus sepsis and meningitis in a 4-month-old female member of a Hutterite colony, an epidemiological investigation revealed at least 18 cases of diarrhea in other members of the colony. C. fetus was isolated from 7 of 15 fecal samples submitted from affected persons. A case control study suggested that persons who worked in the abattoir were 2.03 times more likely to have had diarrhea, but none of the risk factors studied were significant. The epicurve of the outbreak was inconclusive as to the likely mode of spread of C. fetus. All of the C. fetus strains isolated from the blood of the infant and from the fecal samples were the same by biochemical and antibiotic susceptibility tests. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis showed that all isolates produced identical restriction endonuclease patterns and differed from other nonepidemiologically related strains of C. fetus.
Full text
PDF


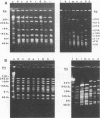
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Kuhns J. S., Vasil M. L., Gerding D. N., Janoff E. N. DNA fingerprinting by pulsed field gel electrophoresis and ribotyping to distinguish Pseudomonas cepacia isolates from a nosocomial outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):648–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.648-649.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham W. T., Chan A., Rennie R., Williams K. E., Sankarna K. Neonatal Campylobacter fetus meningitis: a report of an unusual case. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1992 Apr;31(4):255–256. doi: 10.1177/000992289203100416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Hutchinson D. N., Coates D. Blood-free selective medium for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):169–171. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.169-171.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang N., Taylor D. E. Use of pulsed-field agarose gel electrophoresis to size genomes of Campylobacter species and to construct a SalI map of Campylobacter jejuni UA580. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5211–5217. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5211-5217.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekeyser P., Gossuin-Detrain M., Butzler J. P., Sternon J. Acute enteritis due to related vibrio: first positive stool cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):390–392. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes J. C., Scheifele D. W. Early onset Campylobacter sepsis in a neonate. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 May;6(5):494–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gun-Munro J., Rennie R. P., Thornley J. H., Richardson H. L., Hodge D., Lynch J. Laboratory and clinical evaluation of isolation media for Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2274–2277. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2274-2277.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Simor A. E., Roscoe M., Fleming P. C., Smith S. S., Lane J. Evaluation of a blood-free, charcoal-based, selective medium for the isolation of Campylobacter organisms from feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):456–459. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.456-459.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B. S., Vergeront J. M., Blaser M. J., Edmonds P., Brenner D. J., Janssen D., Davis J. P. Campylobacter infection associated with raw milk. An outbreak of gastroenteritis due to Campylobacter jejuni and thermotolerant Campylobacter fetus subsp fetus. JAMA. 1986 Jan 17;255(3):361–364. doi: 10.1001/jama.255.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. M., Welliver R. C., La Scolea L. J., Jr Campylobacter meningitis in childhood. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1985 Sep-Oct;4(5):544–547. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198509000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morooka T., Oda T., Shigeoka H. In vitro evaluation of antibiotics for treatment of meningitis caused by Campylobacter fetus subspecies fetus. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Sep;8(9):653–654. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198909000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morooka T., Takeo H., Takeshita S., Mimatsu T., Yukitake K., Oda T. Nosocomial meningitis due to Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus in a neonatal intensive care unit. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Oct;148(1):89–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00441825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Singh K. V., Markowitz S. M., Lopardo H. A., Patterson J. E., Zervos M. J., Rubeglio E., Eliopoulos G. M., Rice L. B., Goldstein F. W. Evidence for clonal spread of a single strain of beta-lactamase-producing Enterococcus (Streptococcus) faecalis to six hospitals in five states. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):780–785. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salama S. M., Garcia M. M., Taylor D. E. Differentiation of the subspecies of Campylobacter fetus by genomic sizing. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):446–450. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smibert R. M. The genus Campylobacter. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:673–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy D. E., Bond W. W. Campylobacter fetus infections in children. Pediatrics. 1979 Dec;64(6):898–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan W., Chang N., Taylor D. E. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli genomic DNA and its epidemiologic application. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1068–1072. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]