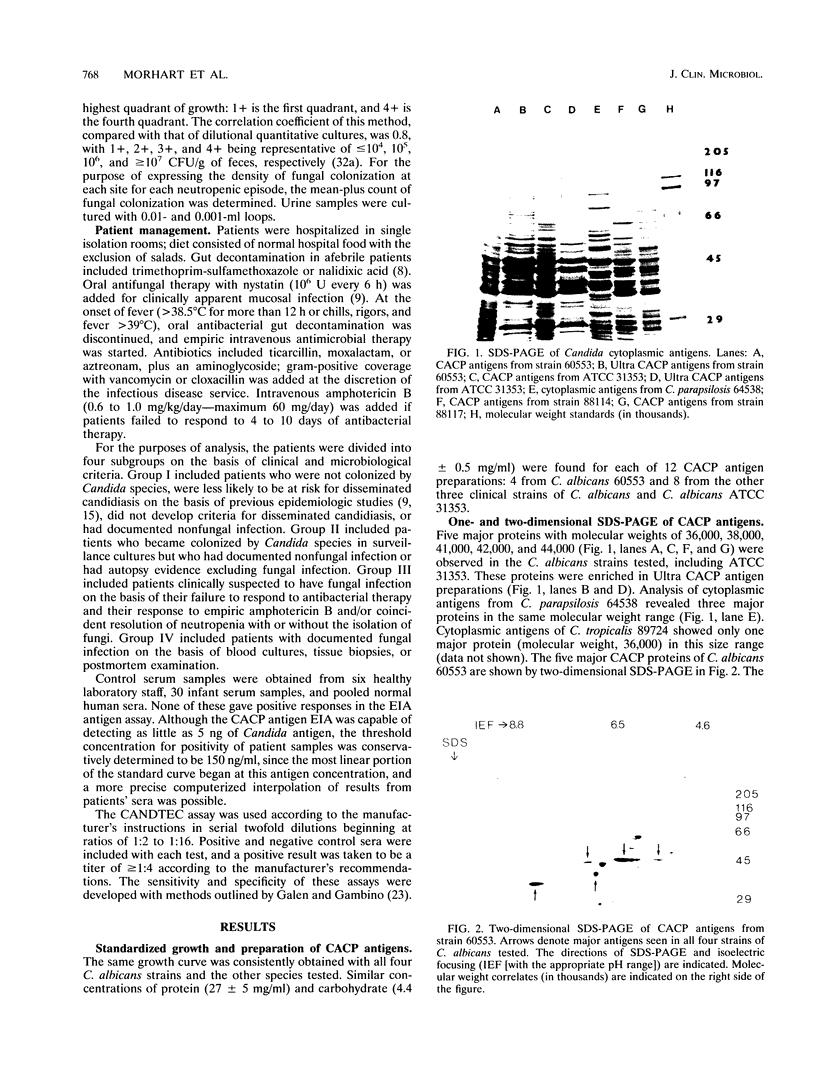
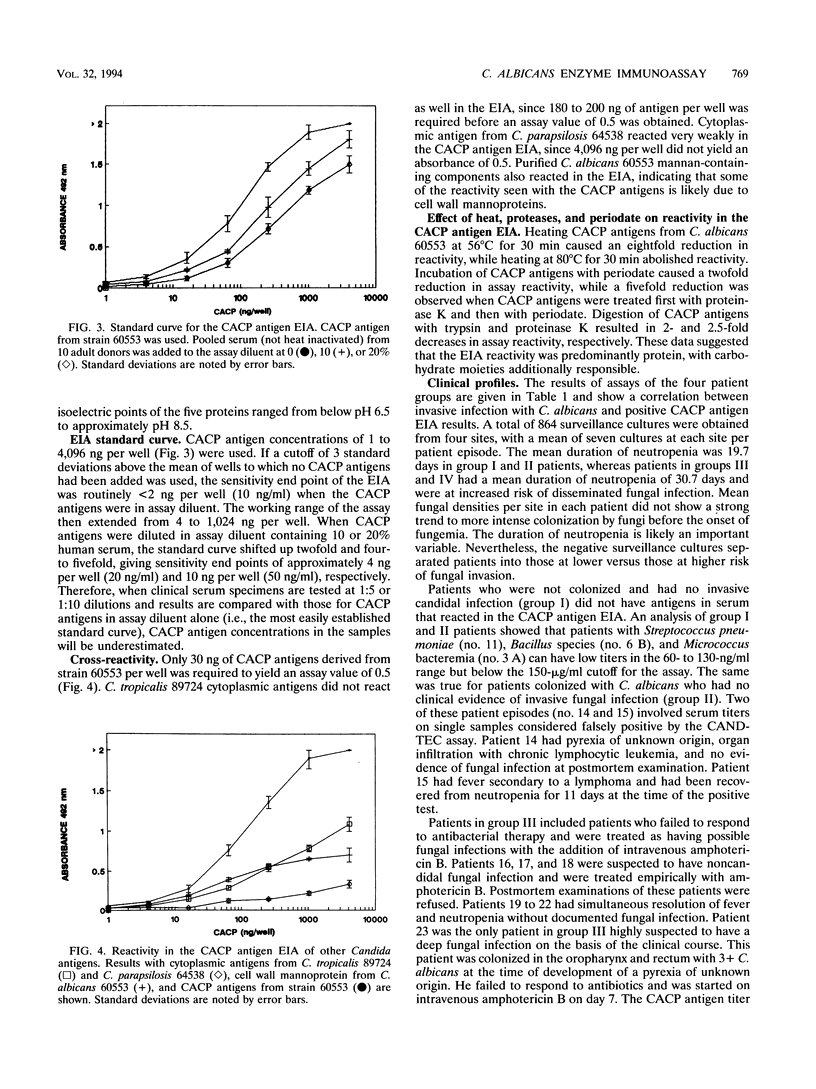
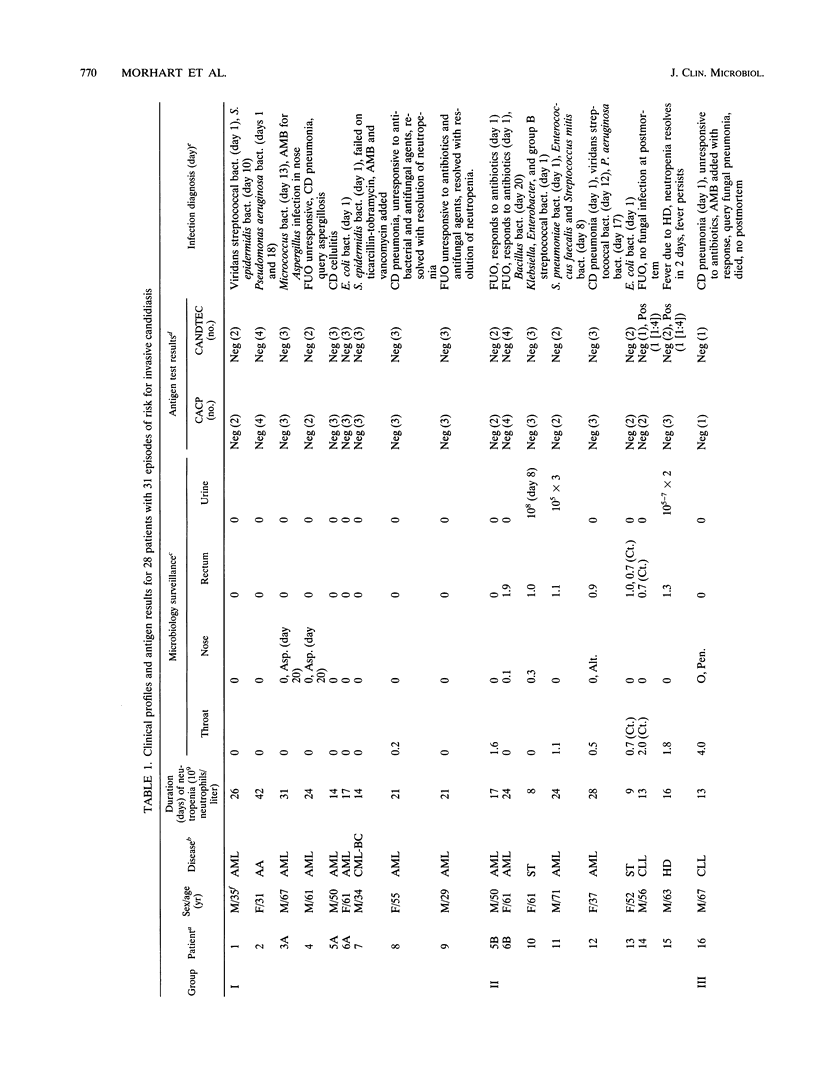
Abstract
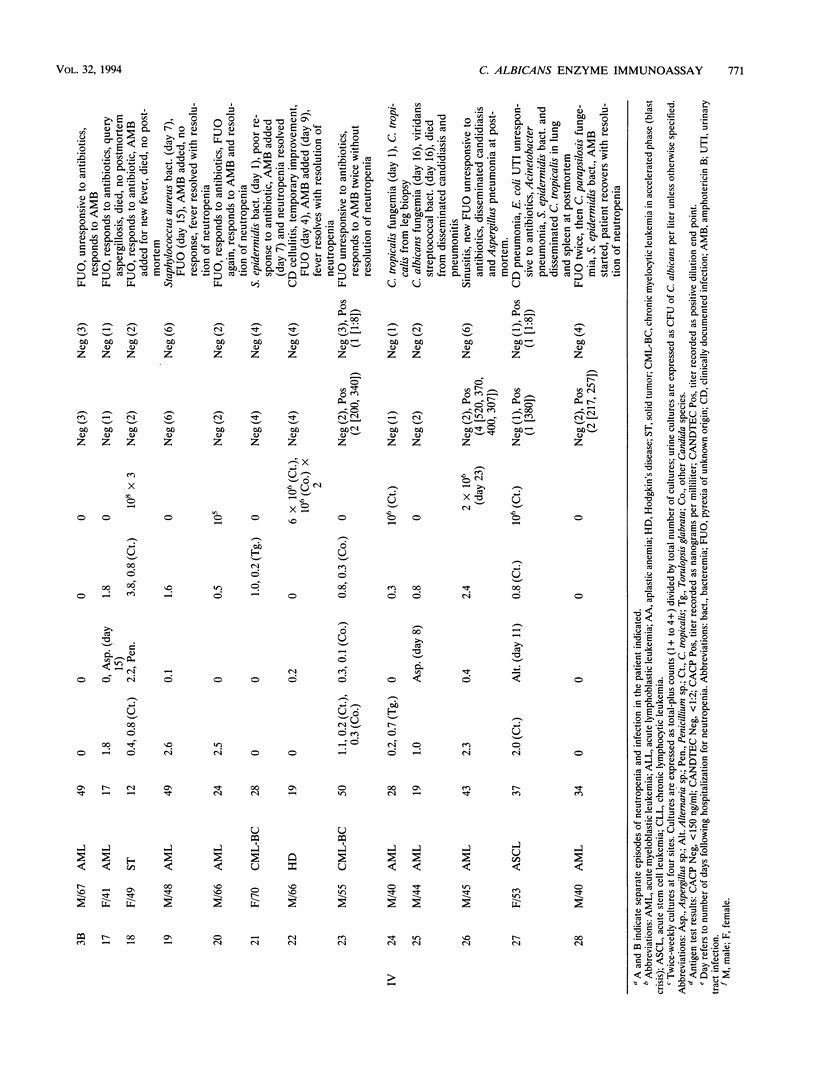
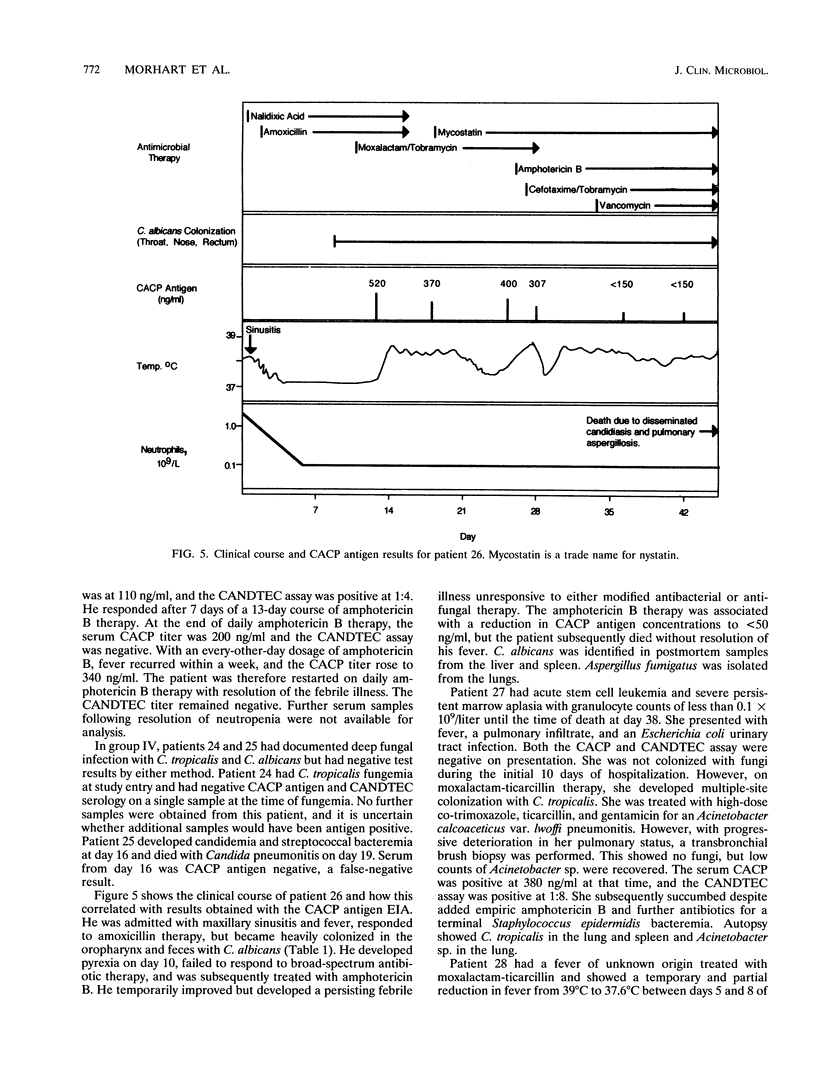
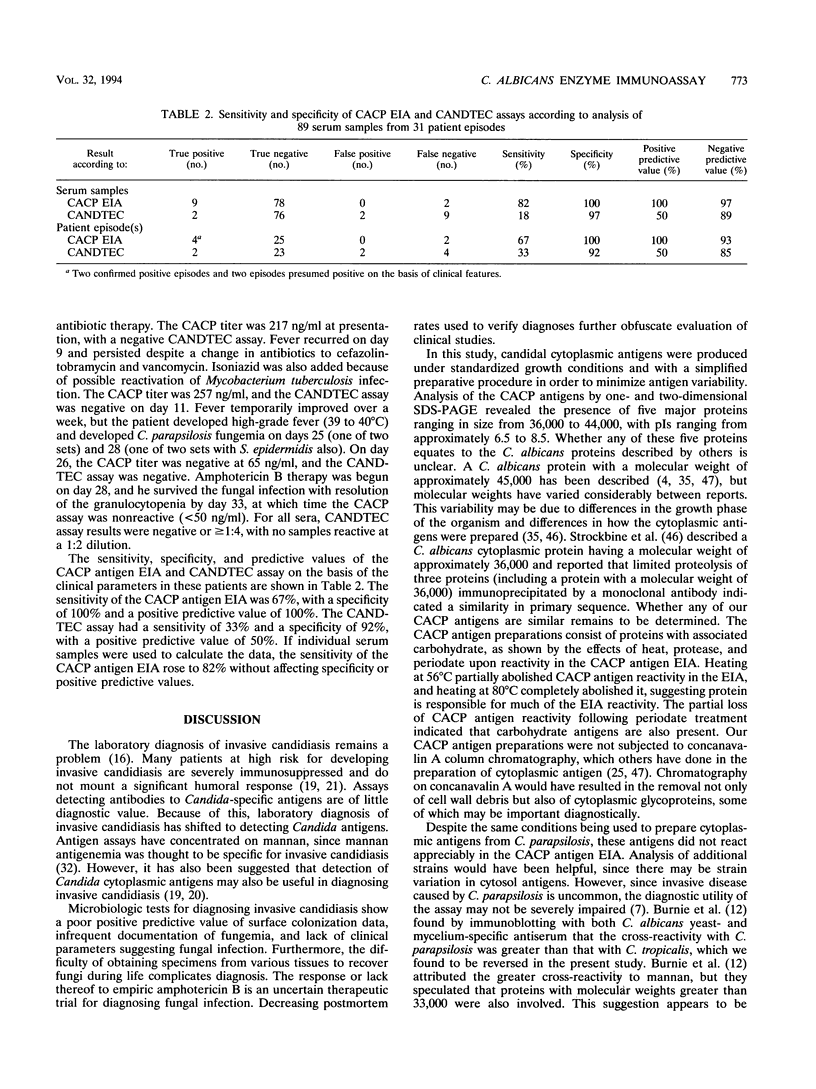
A Candida albicans cytoplasmic antigen enzyme immunoassay (CACP antigen EIA) was developed with antibodies raised against antigens prepared from yeast cells grown under standardized growth conditions. The C. albicans components reactive in the EIA were shown to be predominantly proteins with associated carbohydrates. Denaturing gel electrophoresis revealed the presence of five major CACP proteins with molecular weights between 36,000 and 44,000. The clinical usefulness of the CACP EIA was evaluated by retrospective blinded measurement of 89 serum samples from 31 granulocytopenic patient episodes. Twice-weekly surveillance cultures, sequential serum samples (approximately once per week or with change of the clinical course), and standard diagnostic criteria of fungal infection were used to categorize patients. The sensitivity and specificity of the CACP assay on the basis of serum samples were 82 and 100%, respectively (67 and 100% on the basis of patient episodes). The positive and negative predictive values were 100 and 97% for serum (100 and 93% for patient episodes). By comparison, the CANDTEC assay had low sensitivity (33%) and poor positive predictive values (50%). The CACP EIA may be a useful test suitable for further evaluations as a method for the diagnosis of invasive Candida infection in neutropenic cancer patients.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araj G. F., Hopfer R. L., Chesnut S., Fainstein V., Bodey G. P., Sr Diagnostic value of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Candida albicans cytoplasmic antigen in sera of cancer patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.46-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au-Young J. K., Troy F. A., Goldstein E. Serologic analysis of antigen-specific reactivity in patients with systemic candidiasis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;3(5):419–432. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. W., Sada E., Brass C., Bennett J. E. Diagnosis of systemic candidiasis by latex agglutination for serum antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):749–752. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.749-752.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. E. Rapid diagnosis of candidiasis and aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Mar-Apr;9(2):398–402. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.2.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bow E. J., Rayner E., Scott B. A., Louie T. J. Selective gut decontamination with nalidixic acid or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for infection prophylaxis in neutropenic cancer patients: relationship of efficacy to antimicrobial spectrum and timing of administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):551–557. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan A. G., Riben P. D., Rayner E. N., Parker S. E., Ronald A. R., Louie T. J. Nystatin prophylaxis of fungal colonization and infection in granulocytopenic patients: correlation of colonization and clinical outcome. Clin Invest Med. 1985;8(2):139–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley H. R., Richardson M. D., Evans E. G., Wheat L. J. Immunodiagnosis of invasive fungal infection. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30 (Suppl 1):249–260. doi: 10.1080/02681219280000941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Matthews R. C., Fox A., Tabaqchali S. Use of immunoblotting to identify antigenic differences between the yeast and mycelial phases of Candida albicans. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jun;38(6):701–706. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Williams J. D. Evaluation of the Ramco latex agglutination test in the early diagnosis of systemic candidiasis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):98–101. doi: 10.1007/BF02013571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. A reverse passive latex agglutination test for the diagnosis of systemic candidosis. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Oct 10;82(2):267–280. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabezudo I., Pfaller M., Gerarden T., Koontz F., Wenzel R., Gingrich R., Heckman K., Burns C. P. Value of the Cand-Tec Candida antigen assay in the diagnosis and therapy of systemic candidiasis in high-risk patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;8(9):770–777. doi: 10.1007/BF02185843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Murphy M. T., Counts G. W., Buckner C. D., Clift R. A., Meyers J. D. Prediction by surveillance cultures of bacteremia among neutropenic patients treated in a protective environment. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):789–793. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth J. H., Reiss E., Bradley R. L., Chmel H., Armstrong D. Comparative serological and cutaneous reactivity of candidal cytoplasmic proteins and mannan separated by affinity for concanavalin A. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.91-99.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filice G., Yu B., Armstrong D. Immunodiffusion and agglutination tests for Candida in patients with neoplastic disease: inconsistent correlation of results with invasive infections. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):349–357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung J. C., Donta S. T., Tilton R. C. Candida detection system (CAND-TEC) to differentiate between Candida albicans colonization and disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):542–547. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.542-547.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O., Wilkinson I. D., Lea A. S., Price M. F. Latex agglutination test for detection of Candida antigen in patients with disseminated disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):122–128. doi: 10.1007/BF02001577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield R. A., Jones J. M. Purification and characterization of a major cytoplasmic antigen of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):469–477. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.469-477.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield R. A., Troutt D. L., Rickard R. C., Altmiller D. H. Comparison of antibody, antigen, and metabolite assays in rat models of systemic and gastrointestinal candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):409–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.409-417.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkering T. M., Espinel-Ingroff A., Shadomy S. Detection of candida antigenemia by counterimmunoelectrophoresis in patients with invasive candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):659–664. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn T. E., Bernard E. M., Gold J. W., Armstrong D. Candidiasis: detection by gas-liquid chromatography of D-arabinitol, a fungal metabolite, in human serum. Science. 1979 Nov 2;206(4418):577–580. doi: 10.1126/science.493963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux C., St-Germain G., Vincelette J., Kaufman L., de Repentigny L. Collaborative evaluation of antigen detection by a commercial latex agglutination test and enzyme immunoassay in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):249–253. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.249-253.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew M. A., Siber G. R., Donahue D. M., Maiorca F. Enhanced detection with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of candida mannan in antibody-containing serum after heat extraction. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jan;145(1):45–56. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. B., Brandt M. E., Buckley H. R. Enolase activity associated with a C. albicans cytoplasmic antigen. Yeast. 1989 Apr;5(Spec No):S231–S239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. C., Burnie J. P., Tabaqchali S. Isolation of immunodominant antigens from sera of patients with systemic candidiasis and characterization of serological response to Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):230–237. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.230-237.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R., Burnie J. Diagnosis of systemic candidiasis by an enzyme-linked dot immunobinding assay for a circulating immunodominant 47-kilodalton antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):459–463. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.459-463.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness M. J., Vaughan W. P., Woods G. L. Candida antigen latex test for detection of invasive candidiasis in immunocompromised patients. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):495–502. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Cabezudo I., Buschelman B., Bale M., Howe T., Vitug M., Linton H. J., Densel M. Value of the Hybritech ICON Candida Assay in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis in high-risk patients. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;16(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(93)90130-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P., Dowd A., Jewesson P., Radigan G., Tweeddale M. G., Clarke A., Geere I., Kelly M. Nonvalue of antigen detection immunoassays for diagnosis of candidemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2320–2326. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2320-2326.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piens M. A., Guyotat D., Archimbaud E., Plotton C., Maupas J., Mojon M., Fiere D. Evaluation of a Candida antigen detection test (Cand-Tec) in the diagnosis of deep candidiasis in neutropenic patients. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Oct;24(10):1655–1659. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(88)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Pfaller M. A., Gueho E., Rogers T. R., De Vroey C., Merz W. G. Developments in the diagnostic mycology laboratory. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30 (Suppl 1):241–248. doi: 10.1080/02681219280000931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Berg R. A., Pizzo P. A., Bennett J. E. Detection of Candida antigen in sera of patients with candidiasis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-inhibition technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):116–118. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.116-118.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Huang S., Young L. S., Berdischewsky M. Detection of candida antigenemia in human invasive candidiasis by a new solid phase radioimmunoassay. Infection. 1980;8 (Suppl 3):S–338. doi: 10.1007/BF01639607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Largen M. T., Buckley H. R. Production and characterization of three monoclonal antibodies to Candida albicans proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1012–1018. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1012-1018.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Hathorn J. W., Sobel J. D., Merz W. G., Sanchez V., Maret S. M., Buckley H. R., Pfaller M. A., Schaufele R., Sliva C. Detection of circulating candida enolase by immunoassay in patients with cancer and invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 11;324(15):1026–1031. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104113241504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. H., Coats-Stephen M. Immunodiagnosis of systemic candidiasis: mannan antigenemia detected by radioimmunoassay in experimental and human infections. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):989–993. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Sirany M. S., Blazevic D. J. Evaluation of serum arabinitol as a diagnostic test for candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):353–357. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.353-357.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Kuykendall R. J., Chandler F. W., Broderson J. R., Reiss E. Comparison of serum mannan, arabinitol, and mannose in experimental disseminated candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):804–812. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.804-812.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Marr L. D., Keller J. W., Carter A. W., Kuykendall R. J., Kaufman L., Reiss E. Comparison of enzyme immunoassay and gas-liquid chromatography for the rapid diagnosis of invasive candidiasis in cancer patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):972–979. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.972-979.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Reiss E. Current trends in immunodiagnosis of candidiasis and aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):301–312. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]