Abstract
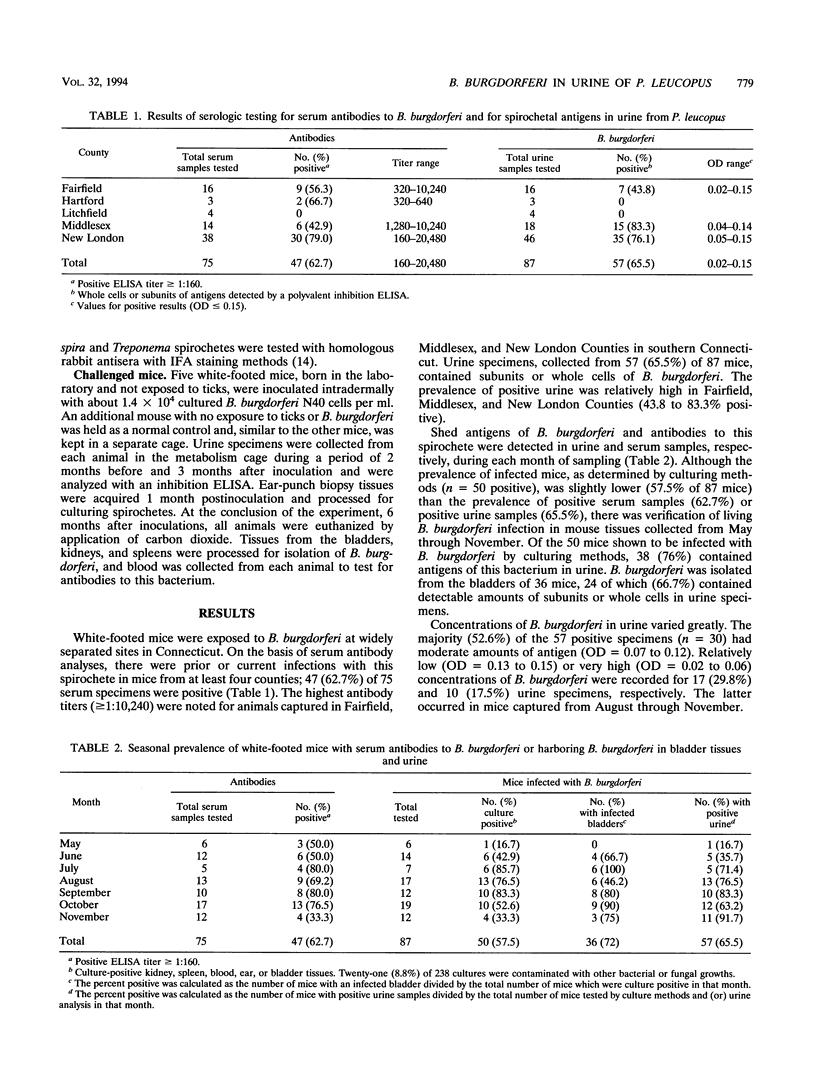
An inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was developed to detect Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiologic agent of Lyme borreliosis, in urine from white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus). Of the 87 urine specimens tested from 87 mice collected in widely separated tick-infested sites in Connecticut, 57 (65.5%) contained detectable concentrations of spirochetal antigens. Forty-seven (62.7%) of 75 serum samples analyzed contained antibodies to B. burgdorferi. In culture work with tissues from bladders, kidneys, spleens, or ears, 50 of 87 mice (57.5%) were infected with B. burgdorferi. Thirty-eight (76%) of 50 infected mice had antigens of this spirochete in urine, while 36 (72%) individuals had infected bladders. Of those with infected bladders, 24 (66.7%) mice excreted subunits or whole cells of B. burgdorferi into urine. Successful culturing of B. burgdorferi from mouse tissues, the presence of serum antibodies to this bacterium, and detection of antigens to this spirochete in urine provide further evidence that multiple assays can be performed to verify the presence of B. burgdorferi in P. leucopus.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A. Seasonal prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in natural populations of white-footed mice, Peromyscus leucopus. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1564–1566. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1564-1566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G. Spirochetes in Ixodes dammini and mammals from Connecticut. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jul;32(4):818–824. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosler E. M., Schulze T. L. The prevalence and significance of Borrelia burgdorferi in the urine of feral reservoir hosts. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):40–44. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartter M. L., Mshar P., Hadler J. L. The epidemiology of Lyme disease in Connecticut. Conn Med. 1989 Jun;53(6):320–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue J. G., Piesman J., Spielman A. Reservoir competence of white-footed mice for Lyme disease spirochetes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jan;36(1):92–96. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorward D. W., Schwan T. G., Garon C. F. Immune capture and detection of Borrelia burgdorferi antigens in urine, blood, or tissues from infected ticks, mice, dogs, and humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1162–1170. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1162-1170.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya Y., Yamamoto S., Otu M., Yoshida Y., Ohashi N., Murata M., Kawabata N., Tamura A., Kawamura A., Jr Use of monoclonal antibodies against Rickettsia tsutsugamushi Kawasaki for serodiagnosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.340-345.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. L., Jurkovich P., Kramber J. M., Johnson R. C. Molecular detection of persistent Borrelia burgdorferi in the urine of patients with active Lyme disease. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):269–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.269-278.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde F. W., Johnson R. C., White T. J., Shelburne C. E. Detection of antigens in urine of mice and humans infected with Borrelia burgdorferi, etiologic agent of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.58-61.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. F., Wilson M. L., Spielman A. Mice as reservoirs of the Lyme disease spirochete. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Mar;34(2):355–360. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loken K. I., Wu C. C., Johnson R. C., Bey R. F. Isolation of the Lyme disease spirochete from mammals in Minnesota. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Jul;179(3):300–302. doi: 10.3181/00379727-179-42100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Apperson C. S., Fish D., Johnson R. C., Chappell W. A. Spirochetes in ticks and antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in white-tailed deer from Connecticut, New York State, and North Carolina. J Wildl Dis. 1986 Apr;22(2):178–188. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-22.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Meegan J. M., Anderson J. F., Chappell W. A. Comparison of an indirect fluorescent-antibody test with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serological studies of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.181-184.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Oliver J. H., Jr, Hutcheson H. J., Boone J. L., Anderson J. F. Antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in rodents in the eastern and southern United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1449–1452. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1449-1452.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers W., Meis J., Rosa P., Claas E., Nohlmans L., Koopman R., Horrevorts A., Galama J. Amplification of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in skin biopsies from patients with Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2401–2406. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2401-2406.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. H., Jr, Owsley M. R., Hutcheson H. J., James A. M., Chen C., Irby W. S., Dotson E. M., McLain D. K. Conspecificity of the ticks Ixodes scapularis and I. dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1993 Jan;30(1):54–63. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachner A. R., Ricalton N., Delaney E. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction with culture and serology for diagnosis of murine experimental Lyme borreliosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):208–214. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.208-214.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N. Polymerase chain reaction primers and probes derived from flagellin gene sequences for specific detection of the agents of Lyme disease and North American relapsing fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):99–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.99-114.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha M., Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Diagnosing early Lyme disease. Am J Med. 1985 Feb;78(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90432-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



