Abstract
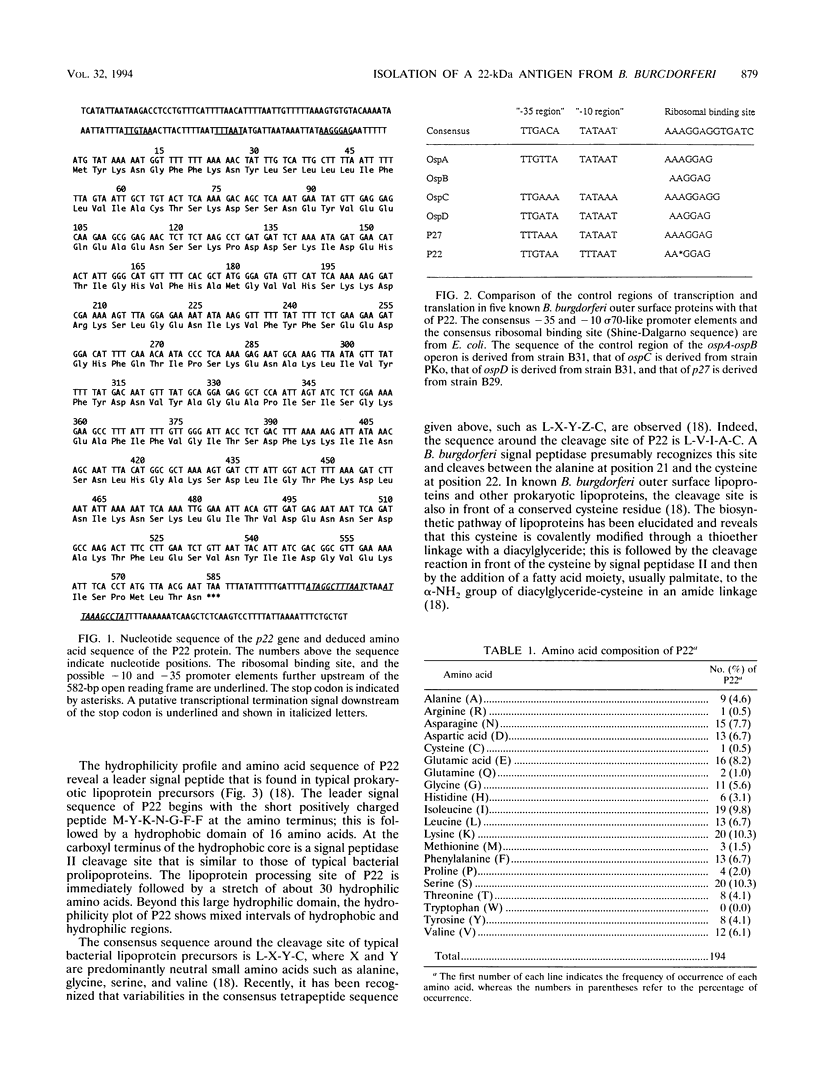
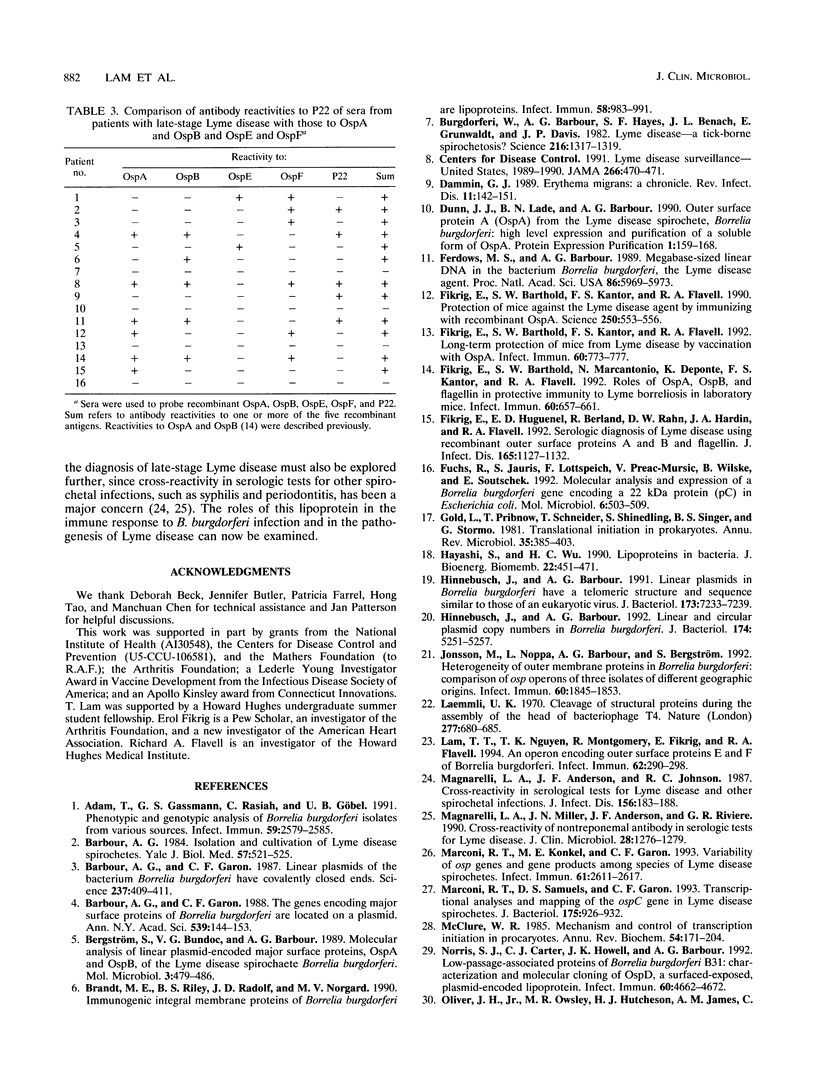
We describe the isolation of the gene encoding a 22-kDa antigen from Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiologic agent of Lyme disease. The p22 gene is 582 nucleotides in length and encodes a protein of 194 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 21.8 kDa. The leader signal sequence of P22 consists of a positively charged short amino terminus, a central hydrophobic domain, and at the carboxyl terminus, a cleavage site that is presumably recognized and cleaved by a B. burgdorferi signal peptidase. P22 has 98.5% homology with the recently described B. burgdorferi protein IpLA7. P22 is processed as a lipoprotein, as demonstrated by [3H]palmitate labeling. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis showed that p22, like LA7, is localized to the linear chromosome of B. burgdorferi. Examination of sera from patients with Lyme disease revealed that antibodies to P22 are rarely detected in patients with early-stage disease characterized by erythema migrans (2 of 20), and 35% of the patients with late-stage disease characterized by arthritis (9 of 26) developed antibodies to P22. Sera from patients with syphilis did not react with P22. When patients with late-stage disease were tested for their antibody reactivities to four other outer surface proteins (OspA), OspB, OspE, and OspF), 75% of these patients responded to P22 or to one or more outer surface proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam T., Gassmann G. S., Rasiah C., Göbel U. B. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates from various sources. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2579–2585. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2579-2585.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Garon C. F. Linear plasmids of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi have covalently closed ends. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):409–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3603026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Garon C. F. The genes encoding major surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi are located on a plasmid. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:144–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Molecular analysis of linear plasmid-encoded major surface proteins, OspA and OspB, of the Lyme disease spirochaete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt M. E., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Immunogenic integral membrane proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi are lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):983–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.983-991.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dammin G. J. Erythema migrans: a chronicle. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11(1):142–151. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Lade B. N., Barbour A. G. Outer surface protein A (OspA) from the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi: high level expression and purification of a soluble recombinant form of OspA. Protein Expr Purif. 1990 Nov;1(2):159–168. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(90)90011-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferdows M. S., Barbour A. G. Megabase-sized linear DNA in the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5969–5973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Long-term protection of mice from Lyme disease by vaccination with OspA. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):773–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.773-777.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Marcantonio N., Deponte K., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Roles of OspA, OspB, and flagellin in protective immunity to Lyme borreliosis in laboratory mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):657–661. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.657-661.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Huguenel E. D., Berland R., Rahn D. W., Hardin J. A., Flavell R. A. Serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease using recombinant outer surface proteins A and B and flagellin. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165(6):1127–1132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Jauris S., Lottspeich F., Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Soutschek E. Molecular analysis and expression of a Borrelia burgdorferi gene encoding a 22 kDa protein (pC) in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Wu H. C. Lipoproteins in bacteria. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):451–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00763177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch J., Barbour A. G. Linear plasmids of Borrelia burgdorferi have a telomeric structure and sequence similar to those of a eukaryotic virus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7233–7239. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7233-7239.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch J., Barbour A. G. Linear- and circular-plasmid copy numbers in Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5251–5257. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5251-5257.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson M., Noppa L., Barbour A. G., Bergström S. Heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins in Borrelia burgdorferi: comparison of osp operons of three isolates of different geographic origins. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1845–1853. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1845-1853.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam T. T., Nguyen T. P., Montgomery R. R., Kantor F. S., Fikrig E., Flavell R. A. Outer surface proteins E and F of Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme disease. Infect Immun. 1994 Jan;62(1):290–298. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.1.290-298.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C. Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Miller J. N., Anderson J. F., Riviere G. R. Cross-reactivity of nonspecific treponemal antibody in serologic tests for Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1276–1279. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1276-1279.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Konkel M. E., Garon C. F. Variability of osp genes and gene products among species of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2611–2617. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2611-2617.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Samuels D. S., Garon C. F. Transcriptional analyses and mapping of the ospC gene in Lyme disease spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):926–932. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.926-932.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Carter C. J., Howell J. K., Barbour A. G. Low-passage-associated proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi B31: characterization and molecular cloning of OspD, a surface-exposed, plasmid-encoded lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4662–4672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4662-4672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. H., Jr, Owsley M. R., Hutcheson H. J., James A. M., Chen C., Irby W. S., Dotson E. M., McLain D. K. Conspecificity of the ticks Ixodes scapularis and I. dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1993 Jan;30(1):54–63. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reindl M., Redl B., Stöffler G. Isolation and analysis of a linear plasmid-located gene of Borrelia burgdorferi B29 encoding a 27 kDa surface lipoprotein (P27) and its overexpression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jun;8(6):1115–1124. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadziene A., Wilske B., Ferdows M. S., Barbour A. G. The cryptic ospC gene of Borrelia burgdorferi B31 is located on a circular plasmid. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2192–2195. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2192-2195.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eichmann K., Modolell M., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi prevent Lyme borreliosis in severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3768–3772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P. The global distribution of Lyme disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):41–50. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears J. E., Fikrig E., Nakagawa T. Y., Deponte K., Marcantonio N., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Molecular mapping of Osp-A mediated immunity against Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme disease. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1995–2000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal L. H., Curran A. S. Lyme disease: a multifocal worldwide epidemic. Annu Rev Public Health. 1991;12:85–109. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pu.12.050191.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eckerskorn C., Museteanu C., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Wallich R. Recombinant outer surface protein a from Borrelia burgdorferi induces antibodies protective against spirochetal infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):123–132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Craft J. E., Hutchinson G. J., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Spieler P. N., Stenn K. S., Malawista S. E. The early clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):76–82. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sădziene A., Rosa P. A., Thompson P. A., Hogan D. M., Barbour A. G. Antibody-resistant mutants of Borrelia burgdorferi: in vitro selection and characterization. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):799–809. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Helmes C., Schaible U. E., Lobet Y., Moter S. E., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. Evaluation of genetic divergence among Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by use of OspA, fla, HSP60, and HSP70 gene probes. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4856–4866. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4856-4866.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Simon M. M., Hofmann H., Moter S. E., Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D. Molecular and immunological characterization of a novel polymorphic lipoprotein of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4158–4166. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4158-4166.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







