Abstract
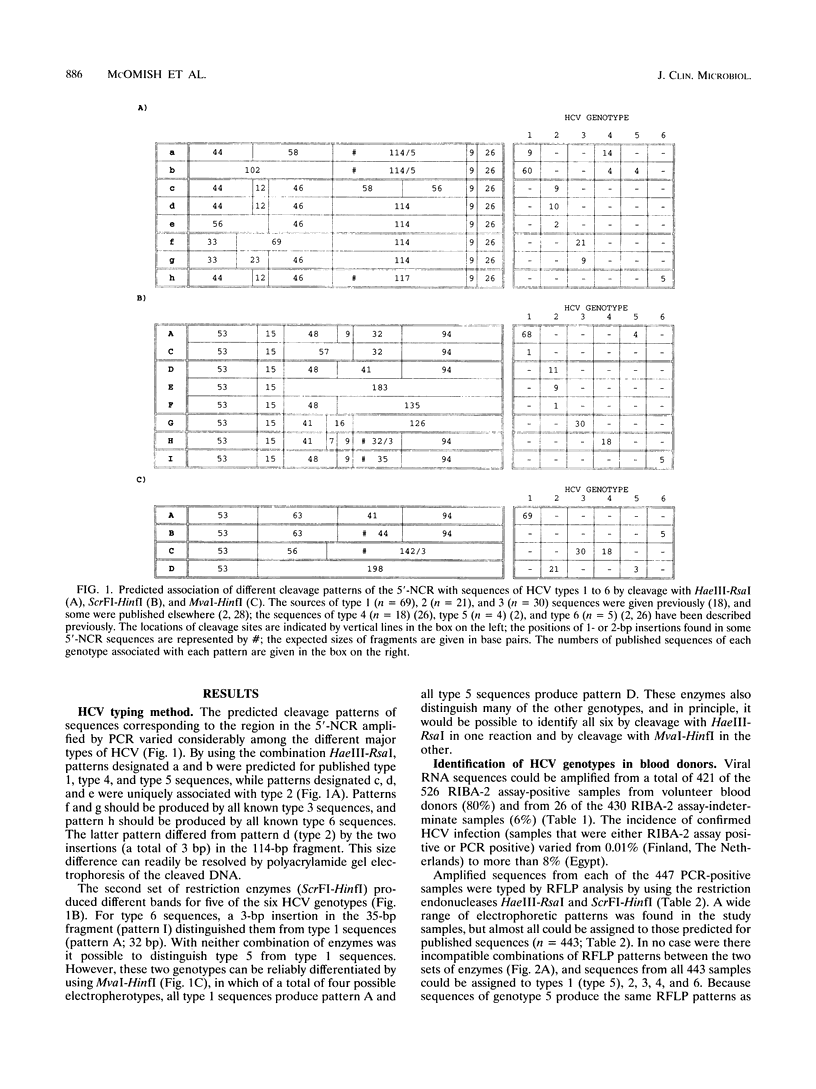
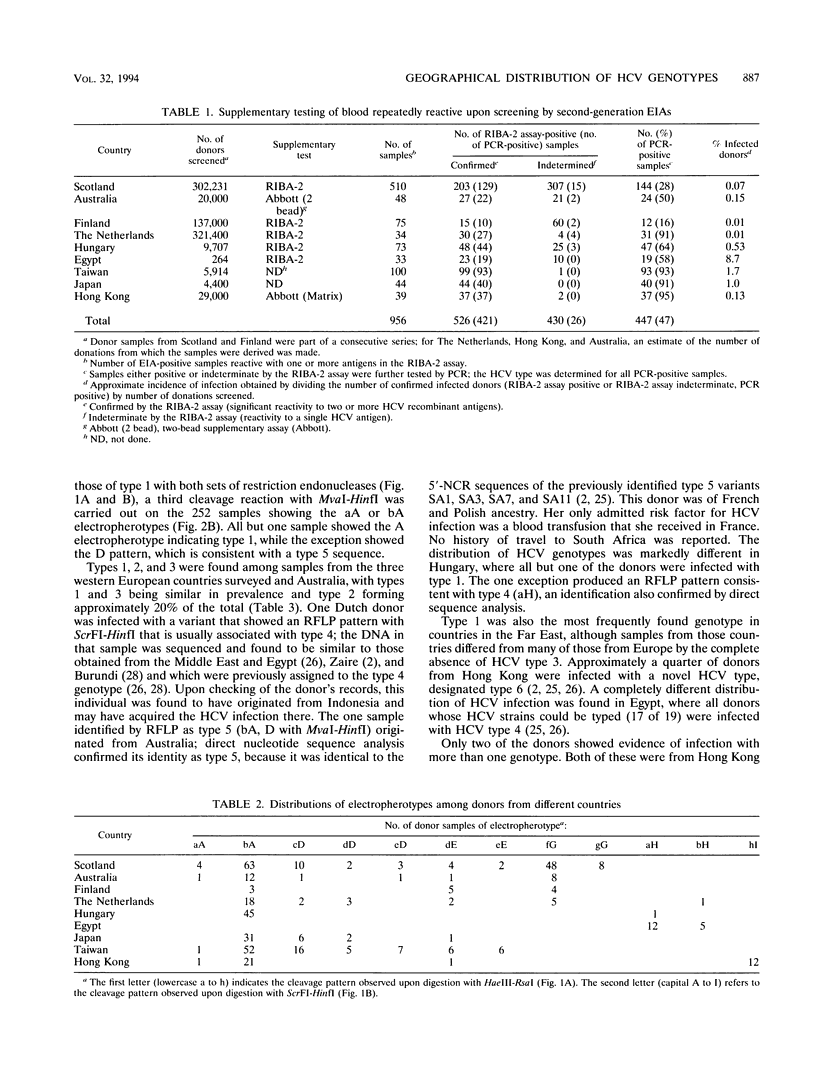
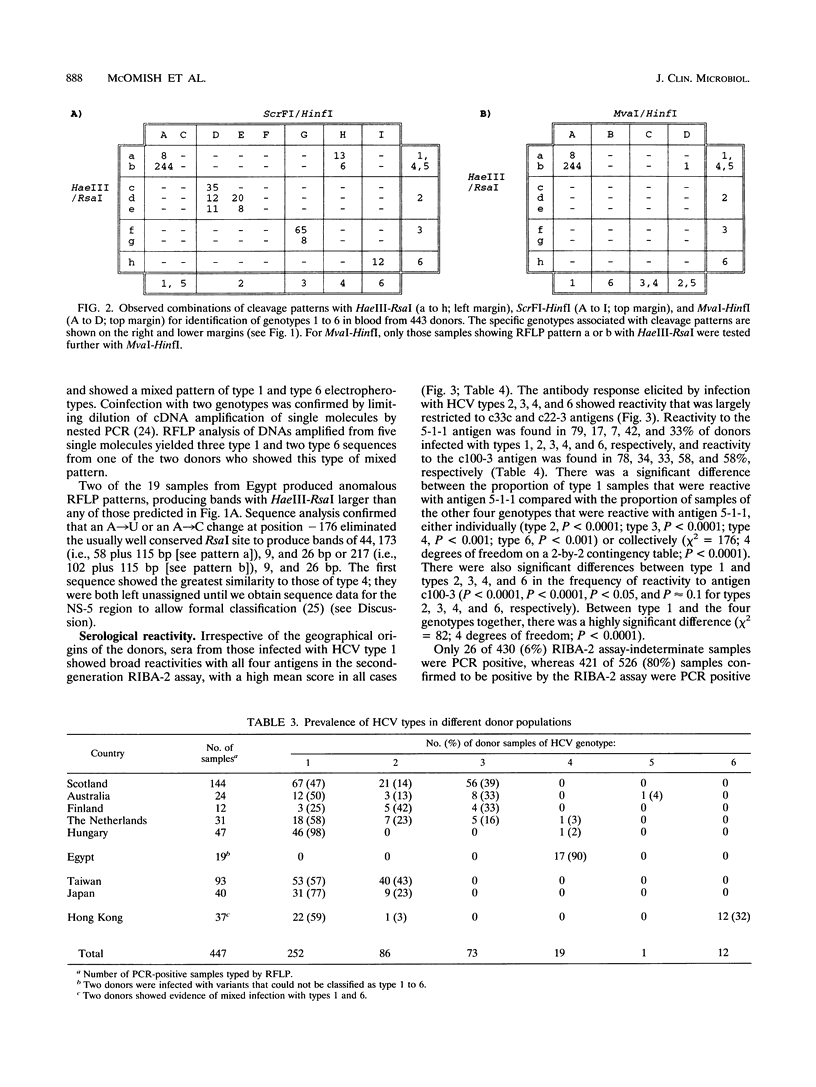
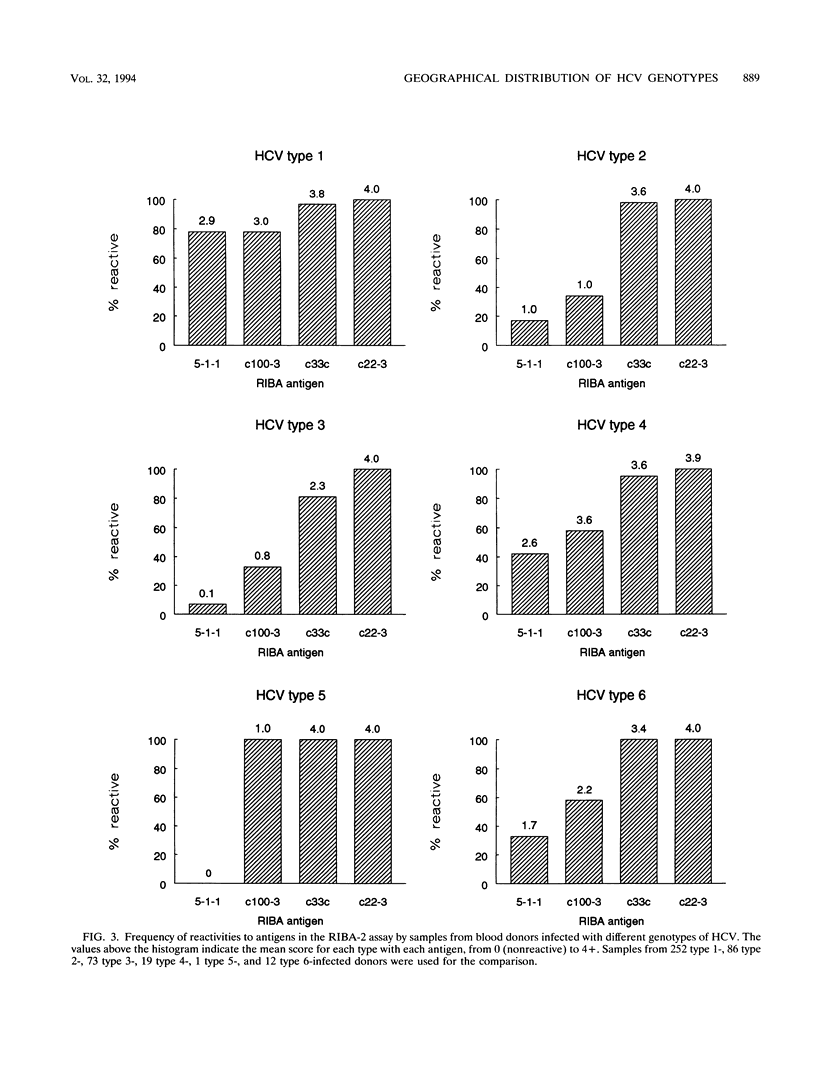
The frequency of infection with the six classified major genotypes of hepatitis C virus (HCV) was investigated in 447 infected volunteer blood donors from the following nine countries: Scotland, Finland, The Netherlands, Hungary, Australia, Egypt, Japan, Hong Kong, and Taiwan. Viral sequences in plasma from blood donors infected with HCV were amplified in the 5'-noncoding region and were typed by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Electrophoresis of DNA fragments produced by cleavage with HaeIII-RsaI and ScrFI-HinfI allowed HCV types 1 (or 5), 2, 3, 4, and 6 to be identified. Further analysis with MvaI-HinfI allowed sequences of the type 5 genotype to be distinguished from sequences of the type 1 genotype. Types 1, 2, and 3 accounted for almost all infections in donors from Scotland, Finland, The Netherlands, and Australia. Types 2 and 3 were not found in the eastern European country (Hungary), where all but one of the donors were infected with type 1. Donors from Japan and Taiwan were infected only with type 1 or 2, while types 1, 2, and 6 were found in those from Hong Kong. HCV infection among Egyptians was almost always by type 4. Donors infected with HCV type 1 showed broad serological reactivity with all four antigens of the second generation Chiron RIBA-2 assay (Chiron Corporation, Emeryville, Calif.), while infection with divergent HCV genotypes elicited antibodies mainly reactive to c22-3 and c33c. Reactivities with antibodies 5-1-1 and c100-3 were infrequent and were generally weak, irrespective of the geographical origin of the donor. Because the envelope region of HCV is even more variable than the NS-4 region, it is likely that vaccines based on these proteins need to be multivalent and perhaps specifically adapted for different geographical regions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bresters D., Cuypers H. T., Reesink H. W., Schaasberg W. P., van der Poel C. L., Mauser-Bunschoten E. P., Houghton M., Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Lesniewski R. Enhanced sensitivity of a second generation ELISA for antibody to hepatitis C virus. Vox Sang. 1992;62(4):213–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1992.tb01201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukh J., Purcell R. H., Miller R. H. Sequence analysis of the 5' noncoding region of hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha T. A., Beall E., Irvine B., Kolberg J., Chien D., Kuo G., Urdea M. S. At least five related, but distinct, hepatitis C viral genotypes exist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7144–7148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. W., McOmish F., Holmes E. C., Dow B., Peutherer J. F., Follett E., Yap P. L., Simmonds P. Analysis of a new hepatitis C virus type and its phylogenetic relationship to existing variants. J Gen Virol. 1992 May;73(Pt 5):1131–1141. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-5-1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. W., Simmonds P., McOmish F., Yap P. L., Mitchell R., Dow B., Follett E. Serological responses to infection with three different types of hepatitis C virus. Lancet. 1991 Nov 30;338(8779):1391–1391. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Richman K. H., Han J. H., Berger K., Lee C., Dong C., Gallegos C., Coit D., Medina-Selby R., Barr P. J. Genetic organization and diversity of the hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2451–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dow B. C., Coote I., Munro H., McOmish F., Yap P. L., Simmonds P., Follett E. A. Confirmation of hepatitis C virus antibody in blood donors. J Med Virol. 1993 Nov;41(3):215–220. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890410309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto N., Takada A., Nakao T., Date T. There are two major types of hepatitis C virus in Japan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 16;170(3):1021–1025. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90494-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban J. I., González A., Hernández J. M., Viladomiu L., Sánchez C., López-Talavera J. C., Lucea D., Martin-Vega C., Vidal X., Esteban R. Evaluation of antibodies to hepatitis C virus in a study of transfusion-associated hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 18;323(16):1107–1112. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010183231605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton M., Weiner A., Han J., Kuo G., Choo Q. L. Molecular biology of the hepatitis C viruses: implications for diagnosis, development and control of viral disease. Hepatology. 1991 Aug;14(2):381–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai K., Kako M., Okamoto H. HCV genotypes in chronic hepatitis C and response to interferon. Lancet. 1992 Jun 20;339(8808):1543–1543. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91311-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Ootsuyama Y., Ohkoshi S., Nakazawa T., Mori S., Hijikata M., Shimotohno K. Distribution of plural HCV types in Japan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 27;181(1):279–285. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelie P. N., Cuypers H. T., Reesink H. W., van der Poel C. L., Winkel I., Bakker E., van Exel-Oehlers P. J., Vallari D., Allain J. P., Mimms L. Patterns of serological markers in transfusion-transmitted hepatitis C virus infection using second-generation HCV assays. J Med Virol. 1992 Jul;37(3):203–209. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McOmish F., Chan S. W., Dow B. C., Gillon J., Frame W. D., Crawford R. J., Yap P. L., Follett E. A., Simmonds P. Detection of three types of hepatitis C virus in blood donors: investigation of type-specific differences in serologic reactivity and rate of alanine aminotransferase abnormalities. Transfusion. 1993 Jan;33(1):7–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1993.33193142314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Kato N., Yagyu A., Tanaka T., Ikeda Y., Petchclai B., Chiewsilp P., Kurimura T., Shimotohno K. A new type of hepatitis C virus in patients in Thailand. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):334–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91648-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao T., Enomoto N., Takada N., Takada A., Date T. Typing of hepatitis C virus genomes by restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2105–2112. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Kurai K., Okada S., Yamamoto K., Lizuka H., Tanaka T., Fukuda S., Tsuda F., Mishiro S. Full-length sequence of a hepatitis C virus genome having poor homology to reported isolates: comparative study of four distinct genotypes. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90762-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Okada S., Sugiyama Y., Kurai K., Iizuka H., Machida A., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of hepatitis C virus isolated from a human carrier: comparison with reported isolates for conserved and divergent regions. J Gen Virol. 1991 Nov;72(Pt 11):2697–2704. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-11-2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Sugiyama Y., Okada S., Kurai K., Akahane Y., Sugai Y., Tanaka T., Sato K., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y. Typing hepatitis C virus by polymerase chain reaction with type-specific primers: application to clinical surveys and tracing infectious sources. J Gen Virol. 1992 Mar;73(Pt 3):673–679. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-3-673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Balfe P., Peutherer J. F., Ludlam C. A., Bishop J. O., Brown A. J. Human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals contain provirus in small numbers of peripheral mononuclear cells and at low copy numbers. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):864–872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.864-872.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Holmes E. C., Cha T. A., Chan S. W., McOmish F., Irvine B., Beall E., Yap P. L., Kolberg J., Urdea M. S. Classification of hepatitis C virus into six major genotypes and a series of subtypes by phylogenetic analysis of the NS-5 region. J Gen Virol. 1993 Nov;74(Pt 11):2391–2399. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-11-2391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., McOmish F., Yap P. L., Chan S. W., Lin C. K., Dusheiko G., Saeed A. A., Holmes E. C. Sequence variability in the 5' non-coding region of hepatitis C virus: identification of a new virus type and restrictions on sequence diversity. J Gen Virol. 1993 Apr;74(Pt 4):661–668. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-4-661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Rose K. A., Graham S., Chan S. W., McOmish F., Dow B. C., Follett E. A., Yap P. L., Marsden H. Mapping of serotype-specific, immunodominant epitopes in the NS-4 region of hepatitis C virus (HCV): use of type-specific peptides to serologically differentiate infections with HCV types 1, 2, and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jun;31(6):1493–1503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.6.1493-1503.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuyver L., Rossau R., Wyseur A., Duhamel M., Vanderborght B., Van Heuverswyn H., Maertens G. Typing of hepatitis C virus isolates and characterization of new subtypes using a line probe assay. J Gen Virol. 1993 Jun;74(Pt 6):1093–1102. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-6-1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada N., Takase S., Enomoto N., Takada A., Date T. Clinical backgrounds of the patients having different types of hepatitis C virus genomes. J Hepatol. 1992 Jan;14(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90128-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada N., Takase S., Takada A., Date T. Differences in the hepatitis C virus genotypes in different countries. J Hepatol. 1993 Mar;17(3):277–283. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80205-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada N., Takase S., Takada A., Date T. HCV genotypes in different countries. Lancet. 1992 Mar 28;339(8796):808–808. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91933-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Kakumu S., Wakita T., Ishikawa T., Itoh Y., Takayanagi M., Higashi Y., Shibata M., Morishima T. Detection of hepatitis C virus by polymerase chain reaction and response to interferon-alpha therapy: relationship to genotypes of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 1992 Aug;16(2):293–299. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poel C. L., Bresters D., Reesink H. W., Plaisier A. A., Schaasberg W., Leentvaar-Kuypers A., Choo Q. L., Quan S., Polito A., Houghton M. Early antihepatitis C virus response with second-generation C200/C22 ELISA. Vox Sang. 1992;62(4):208–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1992.tb01200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



