Abstract
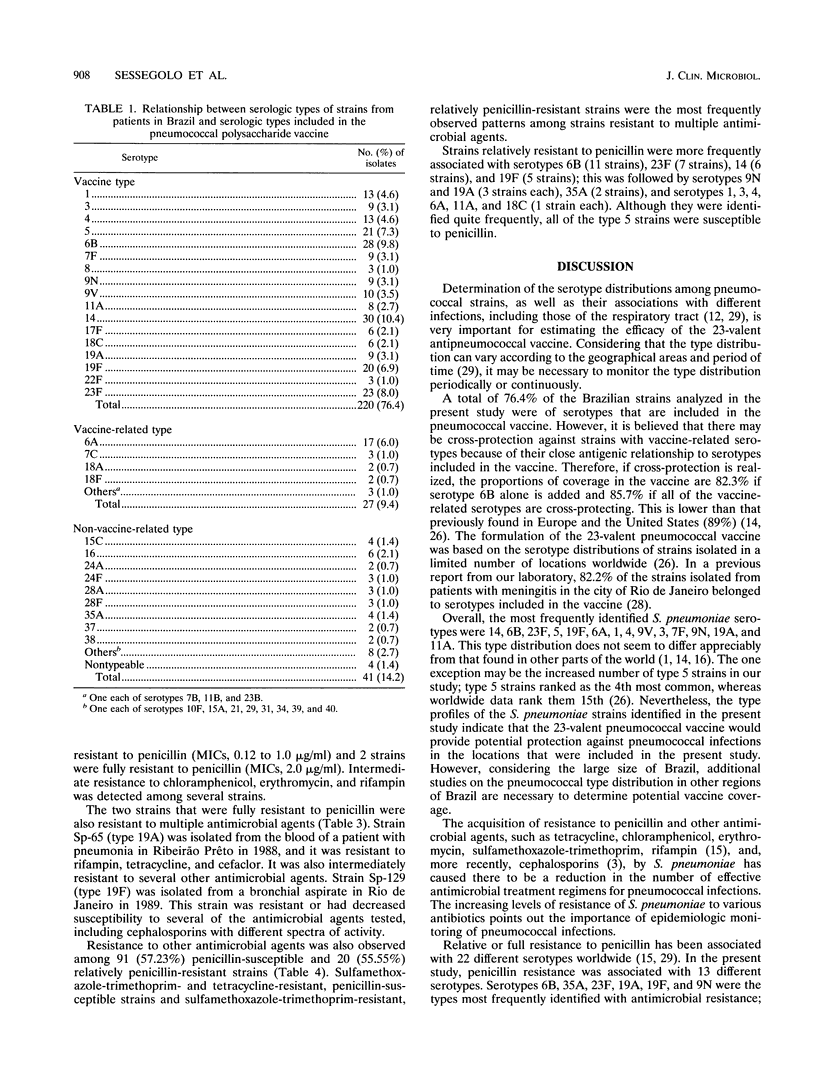
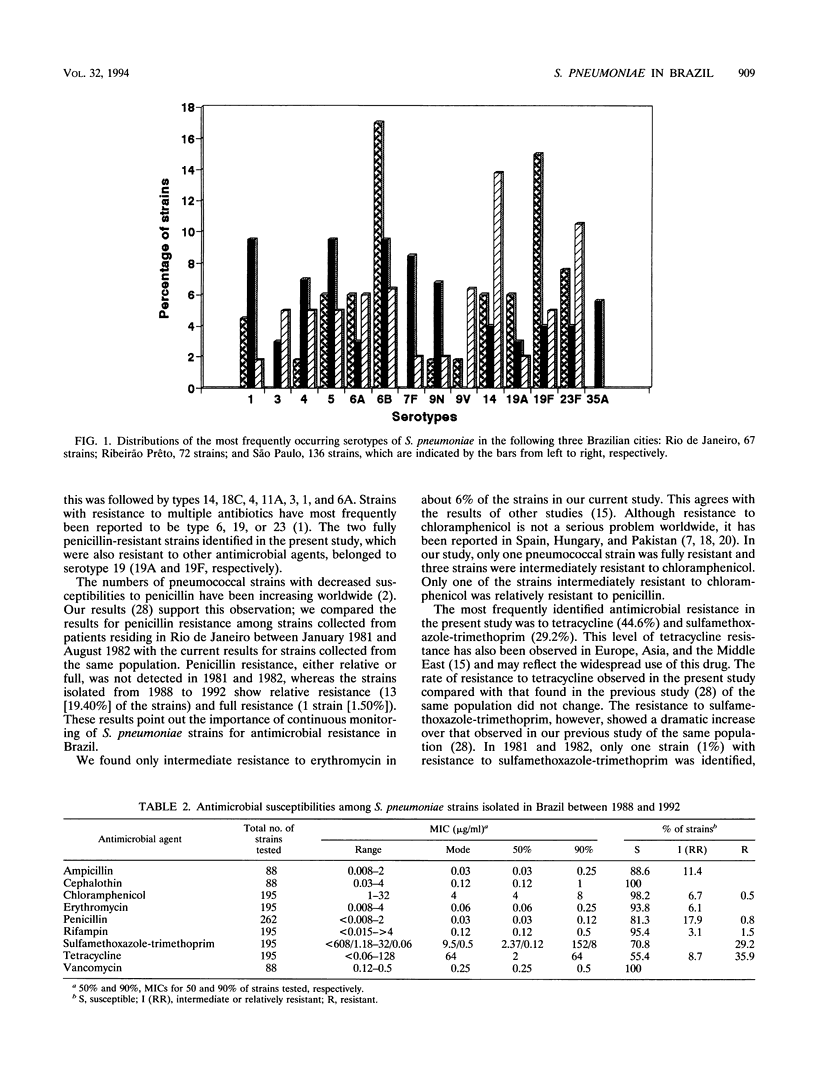
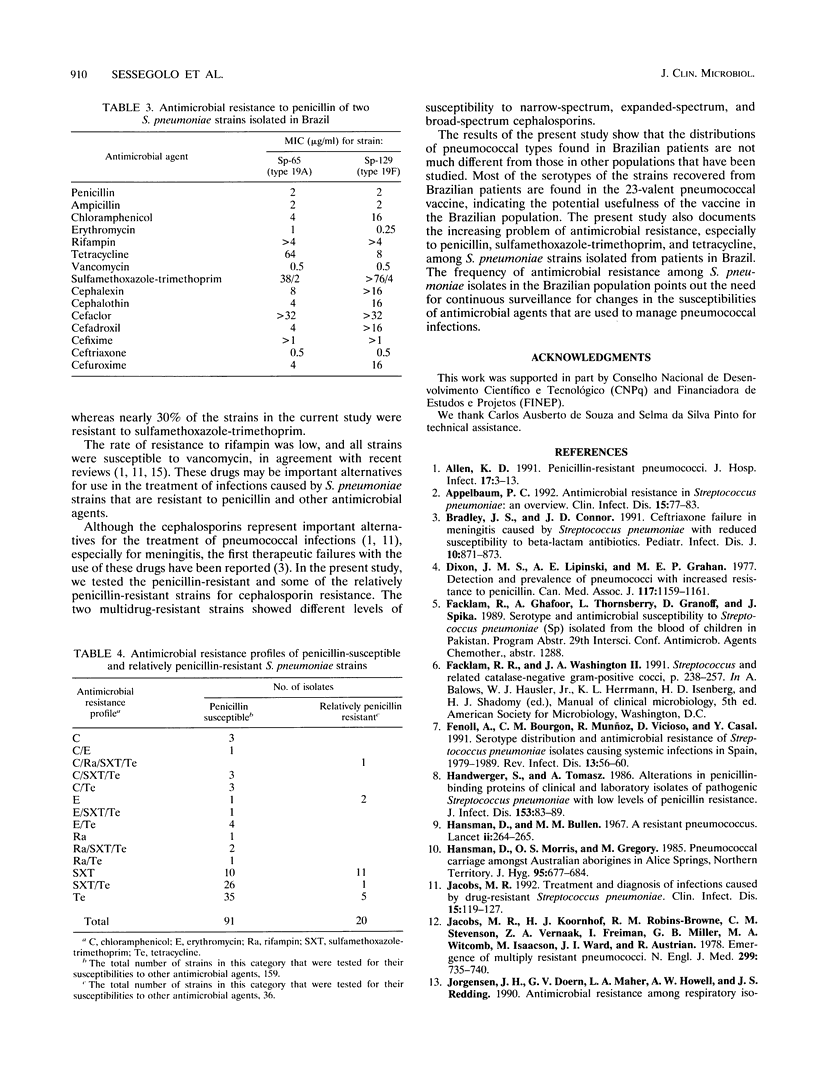
Forty-two serotypes were identified among 288 Streptococcus pneumoniae strains isolated from patients living in Brazil. Serotyping was determined by the capsular typing test (Quellung reaction). Types 14 (10.4%), 6B (9.8%), 23F (8.0%), 5 (7.3%), 19F (6.9%), 6A (6.0%), and 1 and 4 (4.6%) were the most commonly identified strains. Two hundred twenty (76.4%) of the strains were of serotypes that are included in the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. If vaccine-related serotypes are also considered, the proportions of coverage in the vaccine are 82.3% (if type 6B alone is added) and 85.7% (if all the vaccine-related types are considered to be cross-protecting). Decreased susceptibility to penicillin, which was identified by using the 1-microgram oxacillin disk method as a screening test, was detected in 70 (26.7%) strains. The MICs of nine antimicrobial agents were determined by using the procedures recommended by the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Seventy (35.9%) of the strains were resistant to tetracycline, 57 (29.2%) were resistant to sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, 3 (1.5%) were resistant to rifampin, 2 (0.80%) were resistant to penicillin, and 1 (0.5%) was resistant to chloramphenicol. The two penicillin-resistant strains were also resistant to or had decreased susceptibilities to cephalosporins. Forty-seven (17.9%) of the strains were intermediately resistant to penicillin, 17 (8.7%) were intermediately resistant to tetracycline, 13 (6.7%) were intermediately resistant to chloramphenicol, 12 (6.1%) were intermediately resistant to erythromycin, and 6 (3.1%) were intermediately resistant to rifampin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen K. D. Penicillin-resistant pneumococci. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Jan;17(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90072-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelbaum P. C. Antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae: an overview. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;15(1):77–83. doi: 10.1093/clinids/15.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J. S., Connor J. D. Ceftriaxone failure in meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae with reduced susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Nov;10(11):871–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. M., Lipinski A. E., Graham M. E. Detection and prevalence of pneumococci with increased resistance to penicillin. Can Med Assoc J. 1977 Nov 19;117(10):1159–1161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenoll A., Martín Bourgon C., Muñz R., Vicioso D., Casal J. Serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates causing systemic infections in Spain, 1979-1989. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):56–60. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerger S., Tomasz A. Alterations in penicillin-binding proteins of clinical and laboratory isolates of pathogenic Streptococcus pneumoniae with low levels of penicillin resistance. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):83–89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansman D., Morris S., Gregory M., McDonald B. Pneumococcal carriage amongst Australian aborigines in Alice Springs, Northern Territory. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Dec;95(3):677–684. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Koornhof H. J., Robins-Browne R. M., Stevenson C. M., Vermaak Z. A., Freiman I., Miller G. B., Witcomb M. A., Isaäcson M., Ward J. I. Emergence of multiply resistant pneumococci. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 5;299(14):735–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810052991402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R. Treatment and diagnosis of infections caused by drug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;15(1):119–127. doi: 10.1093/clinids/15.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Doern G. V., Maher L. A., Howell A. W., Redding J. S. Antimicrobial resistance among respiratory isolates of Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2075–2080. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgenson J. H., Howell A. W., Maher L. A., Facklam R. R. Serotypes of respiratory isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae compared with the capsular types included in the current pneumococcal vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):644–646. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugman K. P. Pneumococcal resistance to antibiotics. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Apr;3(2):171–196. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koornhof H. J., Wasas A., Klugman K. Antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae: a South African perspective. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;15(1):84–94. doi: 10.1093/clinids/15.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liñares J., Pallares R., Alonso T., Perez J. L., Ayats J., Gudiol F., Viladrich P. F., Martin R. Trends in antimicrobial resistance of clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Bellvitge Hospital, Barcelona, Spain (1979-1990). Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;15(1):99–105. doi: 10.1093/clinids/15.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton A., Gulyas M., Munoz R., Tomasz A. Extremely high incidence of antibiotic resistance in clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Hungary. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):542–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton A. Pneumococcal antimicrobial resistance: the problem in Hungary. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;15(1):106–111. doi: 10.1093/clinids/15.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastro T. D., Ghafoor A., Nomani N. K., Ishaq Z., Anwar F., Granoff D. M., Spika J. S., Thornsberry C., Facklam R. R. Antimicrobial resistance of pneumococci in children with acute lower respiratory tract infection in Pakistan. Lancet. 1991 Jan 19;337(8734):156–159. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90813-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson M. A. Pneumococcal infections. JAMA. 1981 Oct 23;246(17):1942–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell E. D., Alter K. E., Frenkel L. D. Postoperative infection caused by an unusual serotype of Streptococcus pneumoniae associated with multiple drug resistance. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):967–968. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.967-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paredes A., Taber L. H., Yow M. D., Clark D., Nathan W. Prolonged pneumococcal meningitis due to an organism with increased resistance to penicillin. Pediatrics. 1976 Sep;58(3):378–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Austrian R., Lee C. J., Rastogi S. C., Schiffman G., Henrichsen J., Mäkelä P. H., Broome C. V., Facklam R. R., Tiesjema R. H. Considerations for formulating the second-generation pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide vaccine with emphasis on the cross-reactive types within groups. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1136–1159. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spika J. S., Facklam R. R., Plikaytis B. D., Oxtoby M. J. Antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae in the United States, 1979-1987. The Pneumococcal Surveillance Working Group. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1273–1278. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. Antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae: clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3(2):254–266. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.2.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



