Abstract
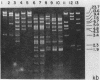
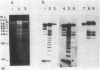
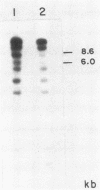
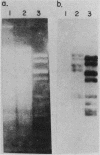
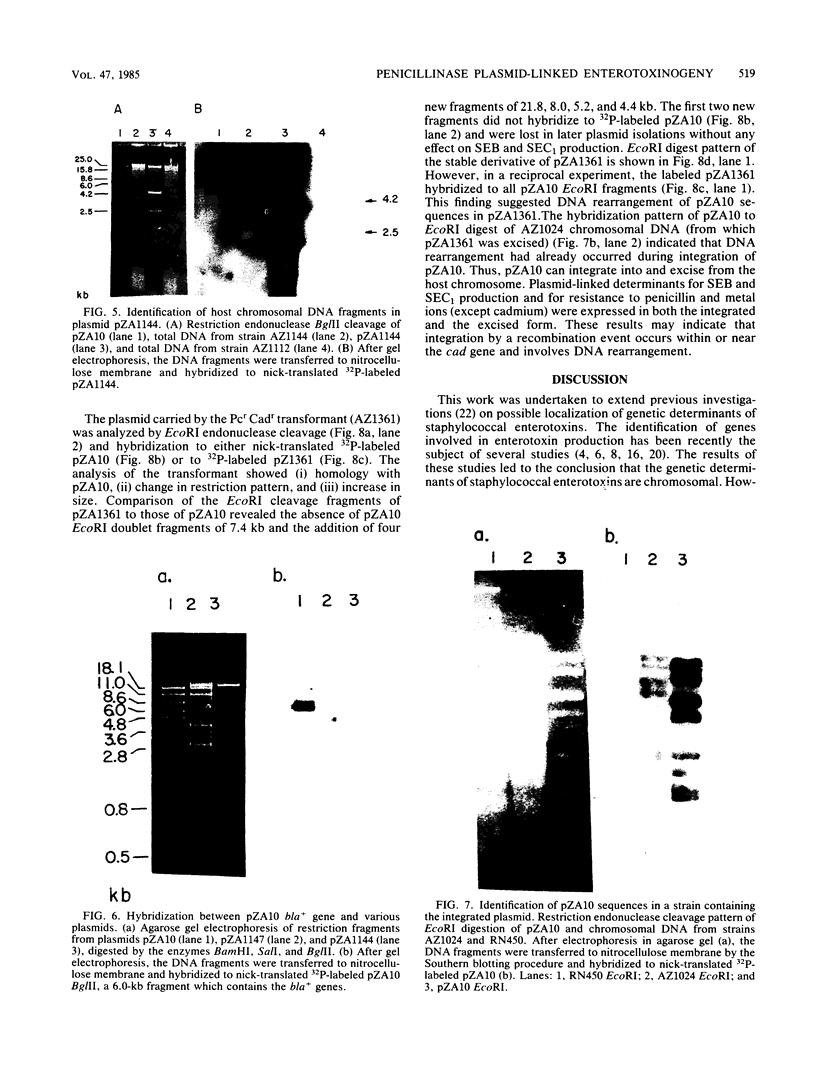
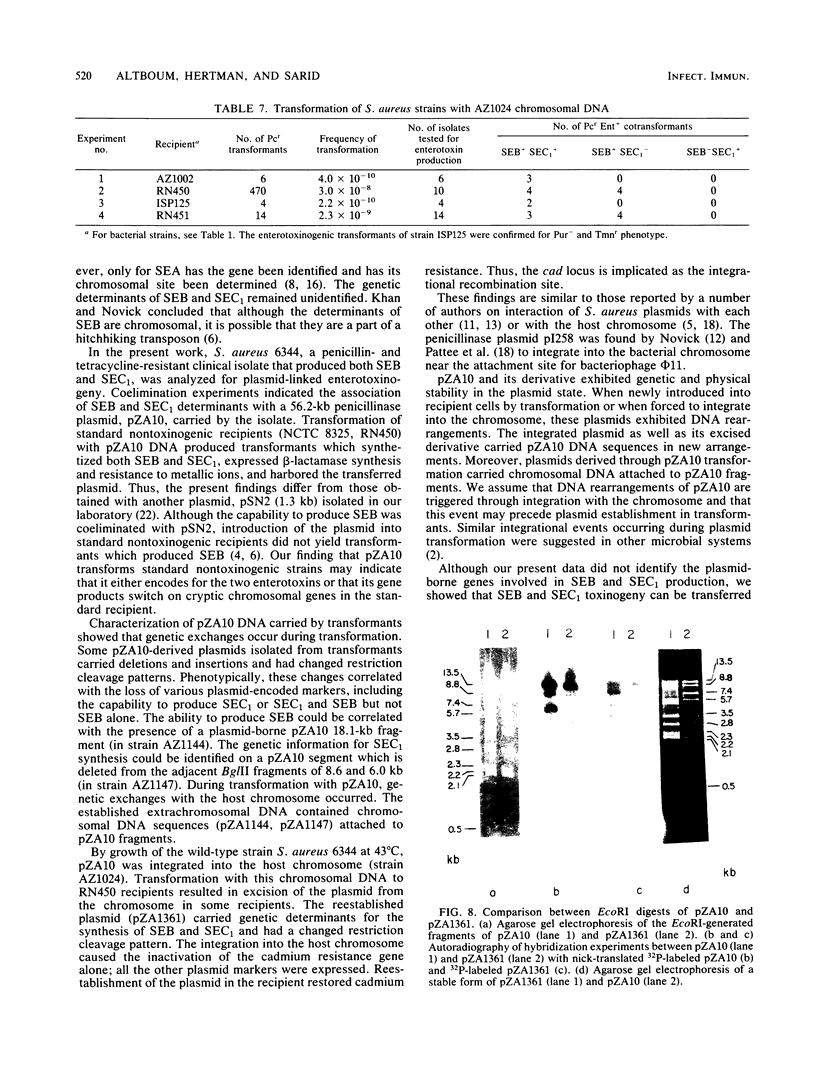
The genes encoding for beta-lactamase (bla+) and resistance to metallic ions (cadmium, mercury, lead, arsenate, and arsenite) were located in a 56.2-kilobase plasmid, pZA10, isolated from a clinical strain, Staphylococcus aureus 6344. This strain produced enterotoxin B and enterotoxin C1. Elimination of pZA10 by either sodium dodecyl sulfate or heat treatment (43 degrees C) resulted in the loss of the capability of the bacteria to produce both enterotoxin B and enterotoxin C1. A physical map of pZA10 was constructed with BamHI, SalI and BglII restriction endonucleases. Penicillin-resistant, enterotoxin B- and C1-producing cotransformants were isolated by transformation with pZA10 DNA with either S. aureus RN450 or cured S. aureus 6344 as recipients. The transferred plasmids exhibited genetic instability shown by changes in restriction pattern and molecular size, loss of plasmid DNA, and addition of chromosomal DNA. Enterotoxin B production was related to a 18.1-kilobase pZA10 fragment carried by such a rearranged plasmid. Chromosomal cointegration of bla+ with genetic determinants for metallic ion resistance and enterotoxin B and C1 production were detected in heat-treated S. aureus 6344. Transformation employing chromosomal DNA containing the integrated plasmid resulted in excision and reestablishment of pZA10-related plasmids in the transformants. pZA10-linked resistance to cadmium, which was lost upon the integration of pZA10 into the host chromosome, reappeared in transformants carrying the excised plasmid.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry J. O., Atherly A. G. Induced plasmid-genome rearrangements in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):218–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.218-224.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Bennett R. W., Dorsey A. E., Stone J. E. The micro-slide gel double diffusion test for the detection and assay of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Health Lab Sci. 1969 Oct;6(4):185–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., Iandolo J. J. Plasmid-chromosomal transition of genes important in staphylococcal enterotoxin B expression. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):450–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.450-458.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. A., Novick R. P. Structural analysis of plasmid pSN2 in Staphylococcus aureus: no involvement in enterotoxin B production. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):642–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.642-649.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg M., Sjöström J. E., Johansson T. Transformation of chromosomal and plasmid characters in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):844–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.844-847.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallonee D. H., Glatz B. A., Pattee P. A. Chromosomal mapping of a gene affecting enterotoxin A production in Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):397–402. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.397-402.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Novick R. P. Site-specific recombination between plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):316–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.316-326.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Iordanescu S., Surdeanu M., Edelman I. Transduction-related cointegrate formation between Staphylococcal plasmids: a new type of site-specific recombination. Plasmid. 1981 Sep;6(2):159–172. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Murphy E., Gryczan T. J., Baron E., Edelman I. Penicillinase plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus: restriction-deletion maps. Plasmid. 1979 Jan;2(1):109–129. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Roth C. Plasmid-linked resistance to inorganic salts in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1335-1342.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. Properties of a cryptic high-frequency transducing phage in Staphylococcus aureus. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Glatz B. A. Identification of a chromosomal determinant of enterotoxin A production in Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):186–193. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.186-193.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Neveln D. S. Transformation analysis of three linkage groups in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):201–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.201-211.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Thompson N. E., Haubrich D., Novick R. P. Chromosomal map locations of integrated plasmids and related elements in Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1977 Nov;1(1):38–51. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(77)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R., Gould S., Bergdoll M. Detecting the enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):946–950. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.946-950.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN S. J. SEROLOGICAL ASSAY OF CULTURE FILTRATES FOR STAPHYLOCOCCUS ENTEROTOXIN. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:955–956. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.955-956.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Iandolo J. J. Genetics of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in methicillin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):902–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.902-911.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafferman A., Shalita Z., Hertman I. Cleavage maps of a tetracycline plasmid from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):345–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.345-348.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalita Z., Hertman I., Sarid S. Isolation and characterization of a plasmid involved with enterotoxin B production in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):317–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.317-325.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weirether F. J., Lewis E. E., Rosenwald A. J., Lincoln R. E. Rapid quantitative serological assay of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.284-291.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]