Abstract
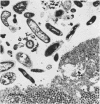
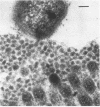
None of 74 strains of anaerobic bacteria cultured from the mucosal epithelial interface of the rabbit cecum adhered to isolated brush borders in experiments in which enteropathogenic Escherichia coli RDEC-1 was used as an adherent control. Scanning electron microscopy of the surfaces of the cecal epithelia confirmed that few organisms were in contact with the villus surface, but transmission electron microscopy revealed a layer of microvesicles up to 50 nm in diameter between the microvilli and mucous gel. The evidence indicates that there is no significant epithelium-adherent flora in the cecum but that a microvesicular layer could contribute significantly to prevention of adherence by both normal and potentially pathogenic bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooker B. E., Fuller R. Adhesion of Lactobacilli to the chicken crop epithelium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jul;52(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Boedeker E. C., Formal S. B. Quantitation of the adherence of an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to isolated rabbit intestinal brush borders. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):736–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.736-743.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Glagov S. Evaluation and publication of scanning electron micrographs. Science. 1976 Jun 25;192(4246):1360–1361. doi: 10.1126/science.1273599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Cleven D., Balish E., Yale C. E. Bacterial association in the gastrointestinal tract of beagle dogs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):194–206. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.194-206.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Savage D. C. Habitat, succession, attachment, and morphology of segmented, filamentous microbes indigenous to the murine gastrointestinal tract. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):948–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.948-956.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsdale D., Cheng K. J., Wallace R. J., Goodlad R. A. Digestion of epithelial tissue of the rumen wall by adherent bacteria in infused and conventionally fed sheep. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):1059–1066. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.1059-1066.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. Nature of the determinant responsible for the adhesion of lactobacilli to chicken crop epithelial cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):245–250. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J. Enteric pathogen--normal flora interactions. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Nov;23(11):1451–1456. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.11.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Abrams G. D., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: adhesion to isolated rabbit brush border membranes and hemagglutinating activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):232–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.232-239.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead L. J., Jones G. A. Isolation and presumptive identification of adherent epithelial bacteria ("epimural" bacteria) from the ovine rumen wall. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):1020–1028. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.1020-1028.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neutra M. R. Prokaryotic-eukaryotic cell junctions: attachment of spirochetes and flagellated bacteria to primate large intestinal cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 Feb;70(2):186–203. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)80005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozee K. R., Cooper D., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Microbial flora of the mouse ileum mucous layer and epithelial surface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1451–1463. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1451-1463.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Blumershine R. V. Surface-surface associations in microbial communities populating epithelial habitats in the murine gastrointestinal ecosystem: scanning electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):240–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.240-250.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., McAllister J. S., Davis C. P. Anaerobic bacteria on the mucosal epithelium of the murine large bowel. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):492–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.492-502.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Morphological diversity among members of the gastrointestinal microflora. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;82:305–334. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60827-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suegara N., Siegel J. E., Savage D. C. Ecological determinants in microbial colonization of the murine gastrointestinal tract: adherence of Torulopsis pintolopesii to epithelial surfaces. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.139-145.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]