Abstract
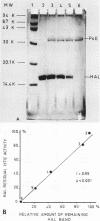
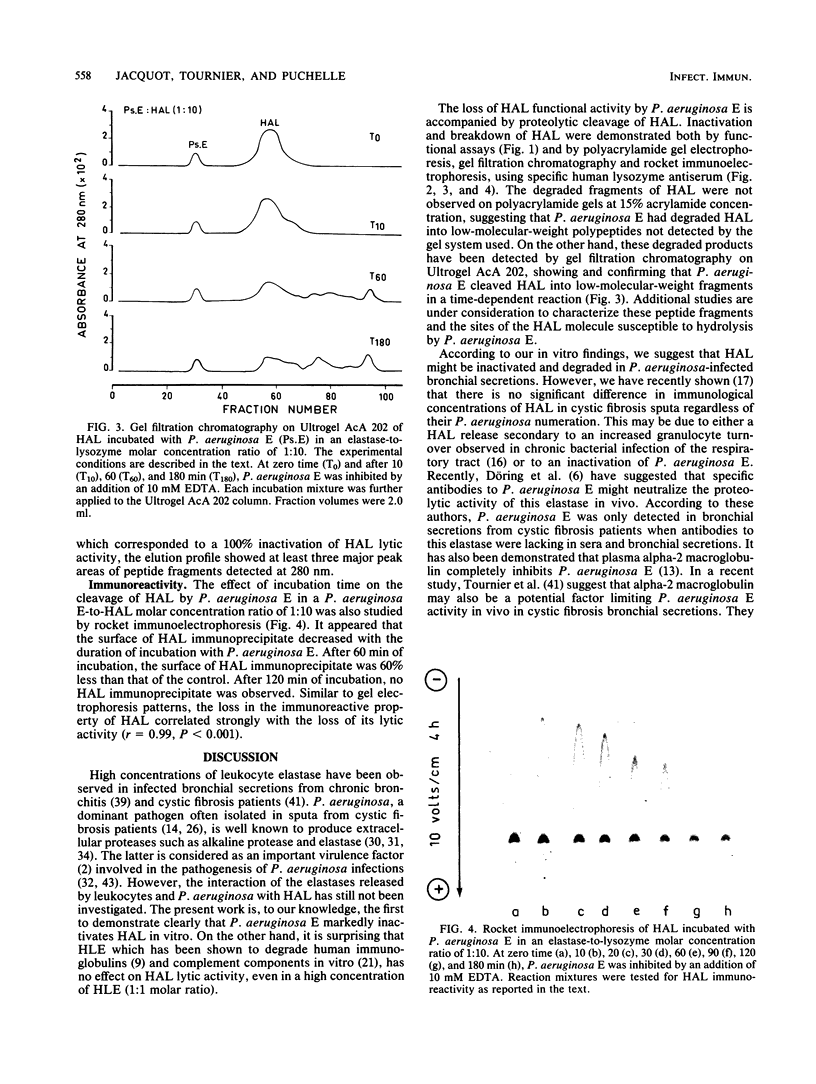
The in vitro effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase (P. aeruginosa E) and of human leukocyte elastase on human airway lysozyme (HAL) were investigated. P. aeruginosa E inactivated and cleaved HAL, whereas human leukocyte elastase had no effect. Total inactivation of HAL by P. aeruginosa E was observed after 120 min of incubation at 37 degrees C, for an elastase-to-lysozyme molar ratio of 1:5. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of reaction mixtures containing HAL and P. aeruginosa E in an elastase-to-lysozyme molar ratio of 1:10 showed a progressive disappearance of the HAL band upon increasing the incubation time with P. aeruginosa E. Gel filtration chromatography indicated that HAL was cleaved into at least three peptide fragments. The cleavage of HAL by P. aeruginosa E was accompanied by parallel losses of its bacteriolytic activity and its immunoreactive property.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baugh R. J., Travis J. Human leukocyte granule elastase: rapid isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):836–841. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood L. L., Stone R. M., Iglewski B. H., Pennington J. E. Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A and elastase as virulence factors in acute lung infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):198–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.198-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogan T. D., Ryley H. C., Neale L., Yassa J. Soluble proteins of bronchopulmonary secretions from patients with cystic fibrosis, asthma, and bronchitis. Thorax. 1975 Feb;30(1):72–79. doi: 10.1136/thx.30.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Obernesser H. J., Botzenhart K. Extrazelluläre Toxine von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Einwirkung zweier gereinigter Proteasen auf die menschlichen Immunoglobuline IgG, IgA und sekretorisches IgA. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1981 Mar;249(1):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Obernesser H. J., Botzenhart K., Flehmig B., Høiby N., Hofmann A. Proteases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):744–750. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Reynolds H. Y. Pseudomonas respiratory infection in cystic fibrosis: a possible defect in opsonic IgG antibody? Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983 Mar-Apr;19(2):151–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folds J. D., Prince H., Spitznagel J. K. Limited cleavage of human immunoglobulins by elastase of human neutrophil polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Possible modulator of immune complex disease. Lab Invest. 1978 Oct;39(4):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick A. D., Ranhand J. M., Cole R. M. Degradation of group A streptococcal cell walls by egg-white lysozyme and human lysosomal enzymes. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):403–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.403-413.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. I., Douglas S. D., Kay N. E., Yamada O., Osserman E. F., Jacob H. S. Modulation of neutrophil function by lysozyme. Potential negative feedback system of inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):226–232. doi: 10.1172/JCI109443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Todd J., Cohn Z. A. In vitro synthesis and secretion of lysozyme by mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1228–1248. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser K., Theopold H. M., Brandl O. Zur Hemmbarkeit der Proteinasen aus Pseudomonas aeruginosa durch alpha2-Makroglobulin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Aug;354(8):1013–1016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N. Epidemiological investigations of the respiratory tract bacteriology in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Aug;82(4):541–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Koblin B. A., Rosenstein B. J. Lysozyme activity in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Res. 1982 Oct;16(10):874–876. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198210000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquot J., Tournier J. M., Carmona T. G., Puchelle E., Chazalette J. P., Sadoul P. Protéines des sécrétions bronchiques dans la mucoviscidose. Role de l'infection. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983 Sep-Oct;19(5):453–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenssen A. O., Smidsrød O., Harbitz O. The importance of lysozyme for the viscosity of sputum from patients with chronic obstructive lung disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1980;40(8):727–731. doi: 10.3109/00365518009095588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. G., Malmquist J. Quantitative immunochemical determination of lysoqyme (muramidase) in serum and urine. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 May;27(3):255–261. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Carter-Hamm B., Dralle W. M. Inactivation of human bronchial mucosal proteinase inhibitor by Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Dec;126(6):1070–1073. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.6.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson U., Ohlsson K., Olsson I. Effects of granulocyte neutral proteases on complement components. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):421–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockars M., Reitamo S. Tissue distribution of lysozyme in man. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Dec;23(12):932–940. doi: 10.1177/23.12.1104708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlar H. K., Harbitz O., Jenssen A. O., Smidsrød O. Quantitation of proteins in sputum from patients with chronic obstructive lung disease. II. Determination of albumin, transferrin, alpha1-acid glycoprotein, IgG, IgM, lysozyme and C3-complement factor. Eur J Respir Dis. 1980 Aug;61(4):233–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki L. L., Murphy T. M., Bellanti J. A. Pseudomonas colonization in cystic fibrosis. A study of 160 patients. JAMA. 1978 Jul 7;240(1):30–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K. PRODUCTION OF ELASTASE AND PROTEINASE BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:745–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.745-757.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H., OKA T., INOUE H., EBATA M. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ELASTASE. ISOLATION, CRYSTALLIZATION, AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martodam R. R., Baugh R. J., Twumasi D. Y., Liener I. E. A rapid procedure for the large scale purification of elastase and cathepsin G from human sputum. Prep Biochem. 1979;9(1):15–31. doi: 10.1080/00327487908061669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H., Oda K. Protease and elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: inactivation of human plasma alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):188–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.188-193.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H. Production of protease and elastase by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):679–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.679-685.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKINS H. R. The structure of a disaccharide liberated by lysozyme from the cell walls of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:182–186. doi: 10.1042/bj0740182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUGAR D. The measurement of lysozyme activity and the ultra-violet inactivation of lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Mar;8(3):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz D. R., Miller K. D. Elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: inactivation of complement components and complement-derived chemotactic and phagocytic factors. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):128–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.128-135.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockley R. A., Burnett D. Alpha,-antitrypsin and leukocyte elastase in infected and noninfected sputum. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Nov;120(5):1081–1086. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.5.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winninger C., Lestienne P., Dimicoli J. L., Bieth J. G. NMR and enzymatic investigation of the interaction between elastase and sodium trifluoroacetate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 11;526(1):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Cryz S. J., Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Contribution of toxin A and elastase to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infections of rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1223–1228. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1223-1228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Sant'Agnese P. A., Davis P. B. Research in cystic fibrosis (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 9;295(11):597–602. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609092951105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]