Abstract
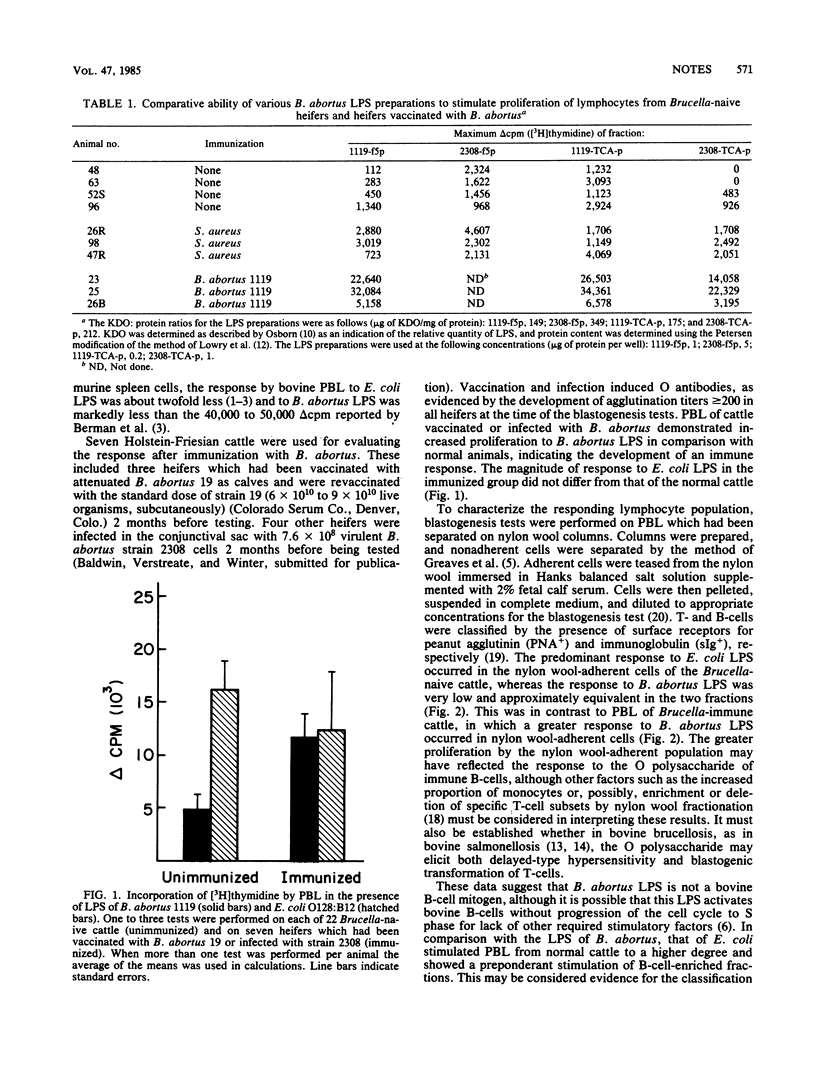
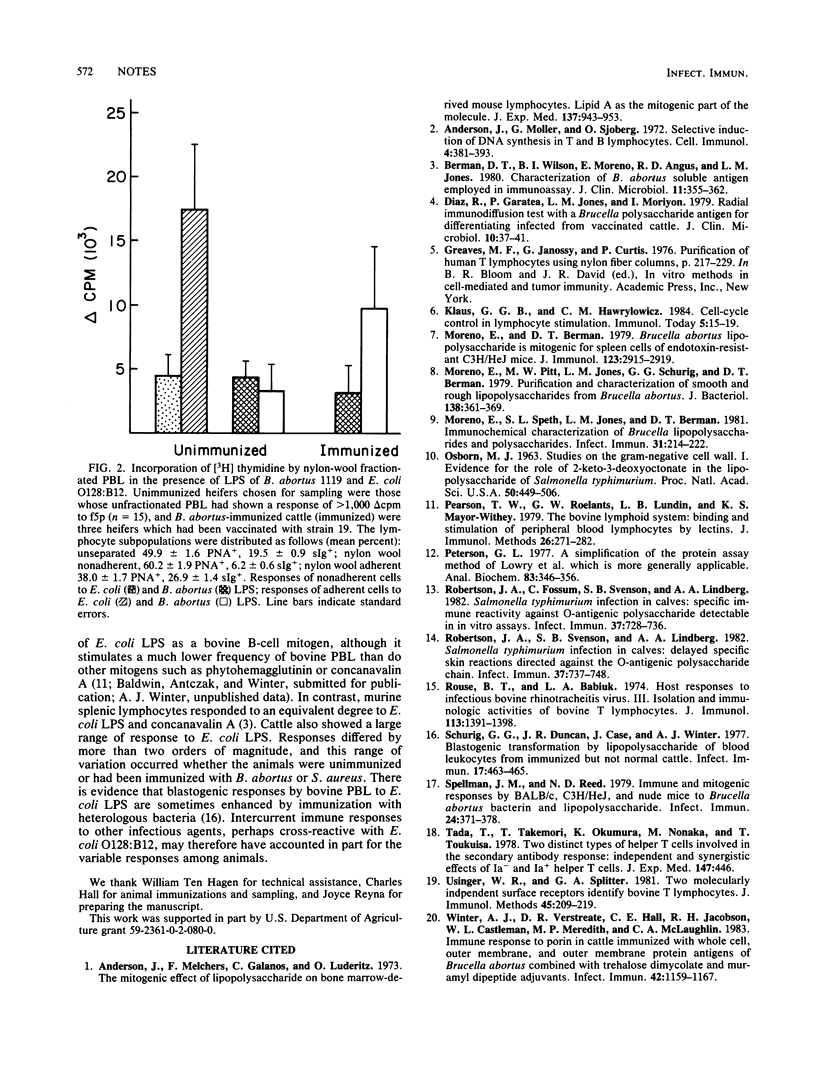
Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide was tested in a blastogenesis assay with unfractionated and nylon wool-separated peripheral blood lymphocytes of Brucella-naive cattle and cattle immunized with B. abortus. Our results indicated that in cattle the lipopolysaccharide of B. abortus is not a B-cell mitogen. In immunized animals it stimulated predominantly nylon wool-adherent cells. The lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli O128:B12, in contrast, induced a substantially greater proliferative response in circulating lymphocytes, predominantly those adherent to nylon wool, of the Brucella-naive cattle.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Melchers F., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. The mitogenic effect of lipopolysaccharide on bone marrow-derived mouse lymphocytes. Lipid A as the mitogenic part of the molecule. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):943–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Möller G., Sjöberg O. Selective induction of DNA synthesis in T and B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Aug;4(4):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman D. T., Wilson B. L., Moreno E., Angus R. D., Jones L. M. Characterization of Brucella abortus soluble antigen employed in immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):355–362. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.355-362.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Garatea P., Jones L. M., Moriyon I. Radial immunodiffusion test with a Brucella polysaccharide antigen for differentiating infected from vaccinated cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.37-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Berman D. T. Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide is mitogenic for spleen cells of endotoxin-resistant C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2915–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Pitt M. W., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Purification and characterization of smooth and rough lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.361-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Speth S. L., Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Immunochemical characterization of Brucella lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):214–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.214-222.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. W., Roelants G. E., Lundin L. B., Mayor-Withey K. S. The bovine lymphoid system: binding and stimulation of peripheral blood lymphocytes by lectins. J Immunol Methods. 1979;26(3):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertsson J. A., Fossum C., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: specific immune reactivity against O-antigenic polysaccharide detectable in in vitro assays. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):728–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.728-736.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertsson J. A., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: delayed specific skin reactions directed against the O-antigenic polysaccharide chain. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):737–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.737-748.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Host responses to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. III. Isolation and immunologic activities of bovine T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1391–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Duncan J. R., Case J., Winter A. J. Blastogenic transformation by lipopolysaccharide of blood leukocytes from immunized but not normal cattle. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):463–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.463-465.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spellman J. M., Reed N. D. Immune and mitogenic responses by BALB/c, C3H/HeJ, and nude mice to Brucella abortus bacterin and lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):371–378. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.371-378.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Takemori T., Okumura K., Nonaka M., Tokuhisa T. Two distinct types of helper T cells involved in the secondary antibody response: independent and synergistic effects of Ia- and Ia+ helper T cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):446–458. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usinger W. R., Splitter G. A. Two molecularly independent surface receptors identify bovine T lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1981;45(3):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J., Verstreate D. R., Hall C. E., Jacobson R. H., Castleman W. L., Meredith M. P., McLaughlin C. A. Immune response to porin in cattle immunized with whole cell, outer membrane, and outer membrane protein antigens of Brucella abortus combined with trehalose dimycolate and muramyl dipeptide adjuvants. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1159–1167. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1159-1167.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


