Abstract
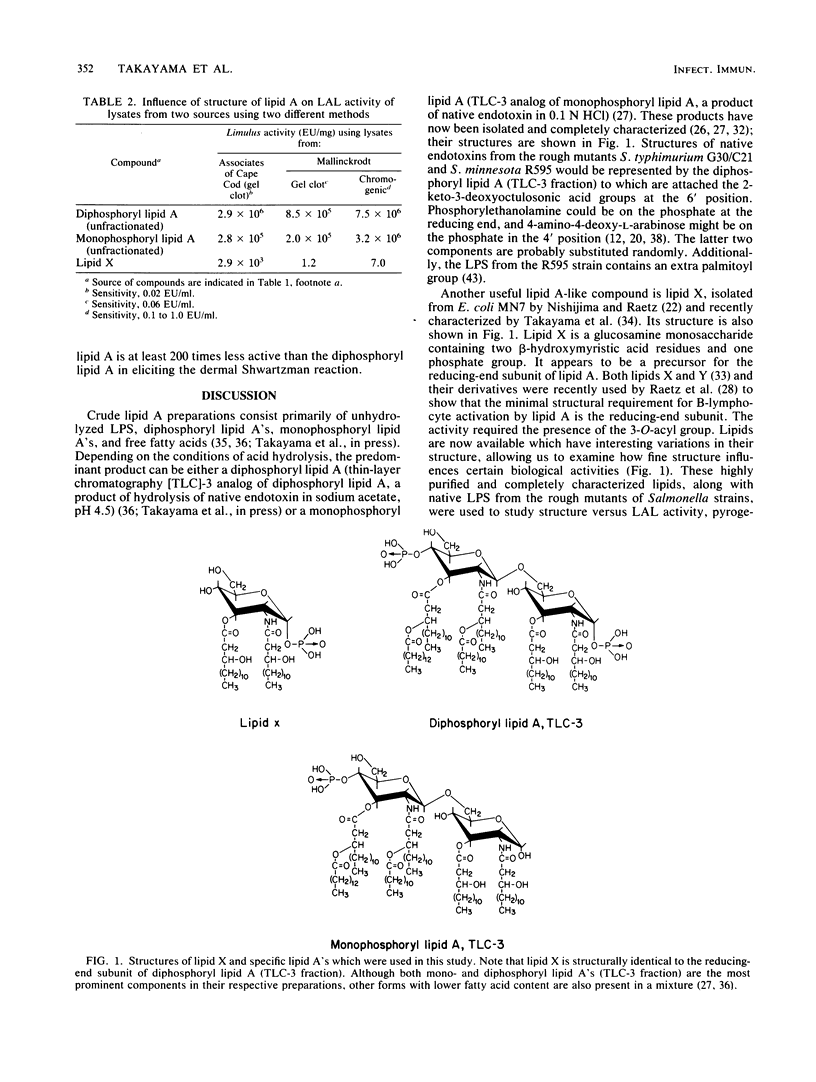
We examined the relationship between the fine structure of lipid A and the toxicity of endotoxin or lipopolysaccharides as measured by the Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL), rabbit pyrogenicity, chicken embryo lethal dose, and dermal Shwartzman reaction tests. Lipid A and lipid A-like compounds obtained from deep-rough mutants of Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli had a wide range of structural variations. These compounds included native lipopolysaccharides, diphosphoryl and monophosphoryl lipid A's, and lipid X (a monosaccharide). The LAL test was positive for all lipids tested with lysates from Travenol Laboratories and from Associates of Cape Cod (2.9 X 10(3) to 2.6 X 10(7) endotoxin units per mg), except for O-deacylated and dephosphorylated lipid X, which were negative. The Mallinckrodt lysate gave negative tests for lipid X. In the rabbit pyrogenicity and chicken embryo lethal dose tests, only native lipopolysaccharide and diphosphoryl lipid A's were judged toxic. The Shwartzman reaction was positive for a specific purified diphosphoryl lipid A (thin-layer chromatography-3 fraction) but negative for the purified monophosphoryl lipid A (also a thin-layer chromatography-3 fraction). These results show that the LAL test is not a valid measure of all parameters of toxicity of a lipid A or lipid A-like compound and can yield false-positive results. However, these findings are not in conflict with the widespread use of the LAL assay for pyrogens in the pharmaceutical industry since a good correlation exists between LAL results and pyrogenicity when undegraded endotoxin is evaluated in parallel assays.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANG F. B. A bacterial disease of Limulus polyphemus. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1956 May;98(5):325–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. F., Levin J., Wagner H. N., Jr Quantitative comparison of in vitro and in vivo methods for the detection of endotoxin. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jul;78(1):138–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S. Recognition coupled responses of the monocyte: activation of coagulation pathways. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1983;25(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Sandberg A. L., Rosentreich D. L. Comparison of the pyrogenicity, Limulus activity mitogenicity and complement reactivity of several bacterial endotoxins and related compounds. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1238–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Nonspecificity of the limulus amebocyte lysate test: positive reactions with polynucleotides and proteins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):349–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Jones P. M. Comparative evaluation of the Limulus assay and the direct Gram stain for detection of significant bacteriuria. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jan;63(1):142–148. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/63.3.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Lee J. C. Rapid diagnosis of gram-negative bacterial meningitis by the Limulus endotoxin assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):12–17. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.12-17.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiso M., Nishihori K., Hasegawa A., Okumura H., Azuma I. A new synthetic route to 2-(acylamino)-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl phosphates, and their endotoxic activity related to the Salmonella-type lipid A. Carbohydr Res. 1981 Sep 1;95(1):C5–C8. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN J., BANG F. B. A DESCRIPTION OF CELLULAR COAGULATION IN THE LIMULUS. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1964 Oct;115:337–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN J., BANG F. B. THE ROLE OF ENDOTOXIN IN THE EXTRACELLULAR COAGULATION OF LIMULUS BLOOD. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1964 Sep;115:265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Redmond J., Egan A., Minner I. The acceptor for polar head groups of the lipid A component of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):487–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Tomasulo P. A., Oser R. S. Detection of endotoxin in human blood and demonstration of an inhibitor. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jun;75(6):903–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough K. Z. The use of LAL as an alternative to the CFR rabbit pyrogen test for disodium ticarcillin. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;93:91–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner K. C., Finkelstein R. A. Bioassay of endotoxin: correlation between pyrogenicity for rabbits and lethality for chick embryos. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):529–536. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Cochrane C. G. Direct evidence for Hageman factor (factor XII) activation by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins). J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):797–811. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson T. E. FDA guideline for validation of the LAL test as an end-product endotoxin test for human and biological drugs. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;93:25–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F., Wray V., Lehmann V. A 31P-nuclear-magnetic-resonance study of the phosphate groups in lipopolysaccharide and lipid A from Salmonella. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 15;81(1):193–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima M., Raetz C. R. Membrane lipid biogenesis in Escherichia coli: identification of genetic loci for phosphatidylglycerophosphate synthetase and construction of mutants lacking phosphatidylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7837–7844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson F. C., 3rd, Weary M. E., Bohon J., Dabbah R. Relative potency of "environmental" endotoxin as measured by the Limulus amebocyte lysate test and the USP rabbit pyrogen test. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;93:65–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson F. C., 3rd, Weary M. E., Dabbah R. A corporate approach to in-process and end-product testing with the LAL assay for endotoxin. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;93:231–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Takayama K., Heller D., Fenselau C. Position of ester groups in the lipid A backbone of lipopolysaccharides obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12947–12951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Takayama K., Ribi E. Purification and structural determination of nontoxic lipid A obtained from the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11808–11815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R., Purcell S., Takayama K. Molecular requirements for B-lymphocyte activation by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4624–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribi E. Beneficial modification of the endotoxin molecule. J Biol Response Mod. 1984;3(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. R., Tang J., Barzilay I., Khorana H. G. Structure of the lipopolysaccharide from an Escherichia coli heptose-less mutant. I. Chemical degradations and identification of products. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5906–5917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Mikami T., Matsumoto T., Suzuki S. Gelation of Limulus lysate by synthetic dextran derivatives. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(8):419–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Mascagni P., Anderson L., Raetz C. R. Glucosamine-derived phospholipids in Escherichia coli. Structure and chemical modification of a triacyl glucosamine 1-phosphate found in a phosphatidylglycerol-deficient mutant. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14245–14252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Mascagni P. Complete structure of lipid A obtained from the lipopolysaccharides of the heptoseless mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12801–12803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Mascagni P., Nashed M. A., Anderson L., Raetz C. R. Fatty acyl derivatives of glucosamine 1-phosphate in Escherichia coli and their relation to lipid A. Complete structure of A diacyl GlcN-1-P found in a phosphatidylglycerol-deficient mutant. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7379–7385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Ribi E., Cantrell J. L. Isolation of a nontoxic lipid A fraction containing tumor regression activity. Cancer Res. 1981 Jul;41(7):2654–2657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk W. A., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. The occurrence of 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose as a constituent in Salmonella lipopolysaccharide preparations. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):223–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtel R. E., Tsuji K. Comparison of limulus amebocyte lysates and correlation with the United States Pharmacopeial pyrogen test. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jun;33(6):1265–1269. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.6.1265-1269.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weary M., Baker B. Utilization of the limulus amebocyte lysate test for pyrogen testing large volume parenterals, administration sets, and medical devices. Bull Parenter Drug Assoc. 1977 May-Jun;31(3):127–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weary M., Pearson F. C., 3rd, Bohon J., Donohue G. The activity of various endotoxins in the USP rabbit test and in three different LAL tests. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;93:365–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildfeuer A., Heymer B., Schleifer K. H., Haferkamp O. Investigations on the specificity of the Limulus test for the detection of endotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):867–871. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.867-871.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Broady K. W., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T. The chemical structure of lipid A. Demonstration of amide-linked 3-acyloxyacyl residues in Salmonella minnesota Re lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]