Abstract
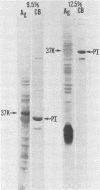
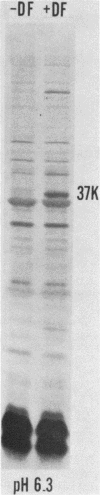
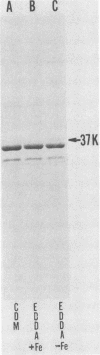
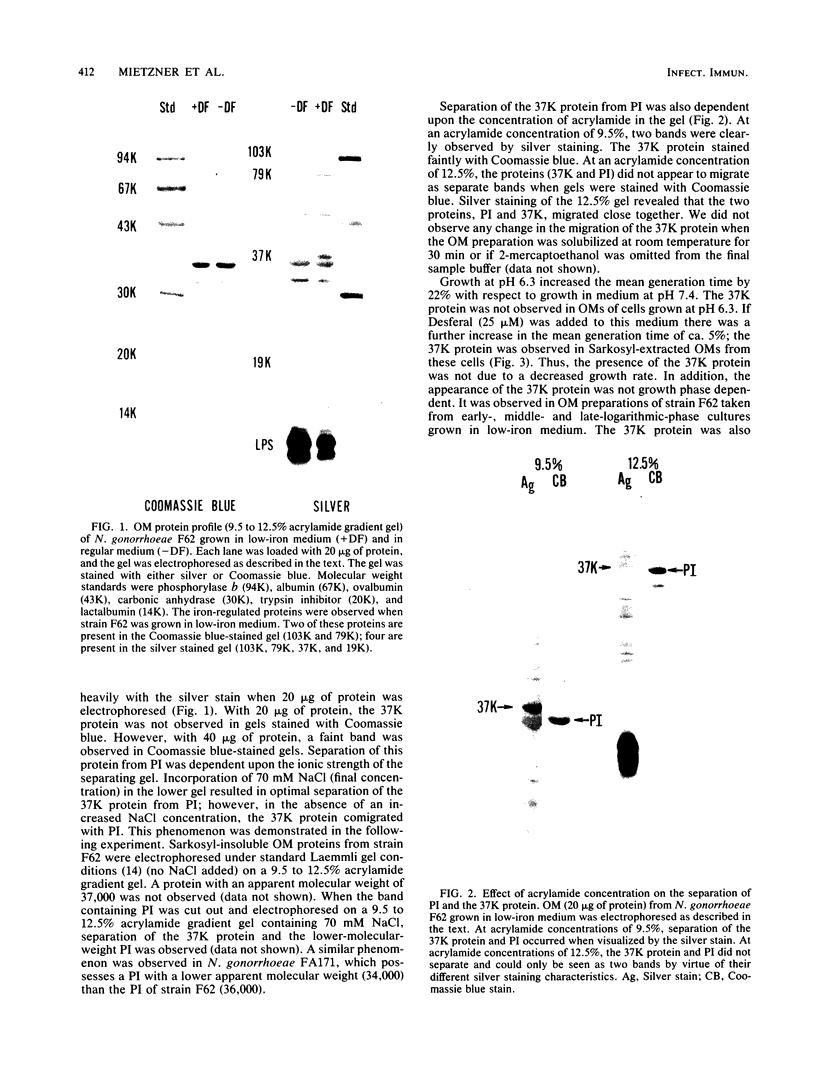
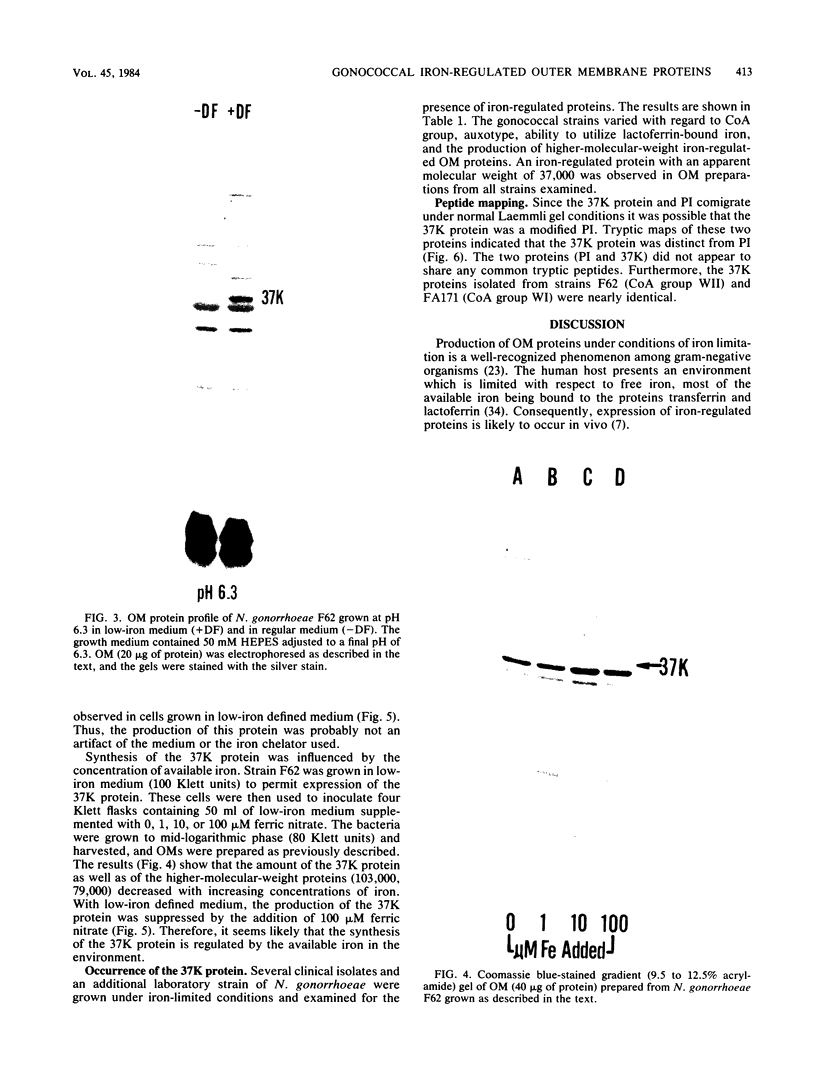
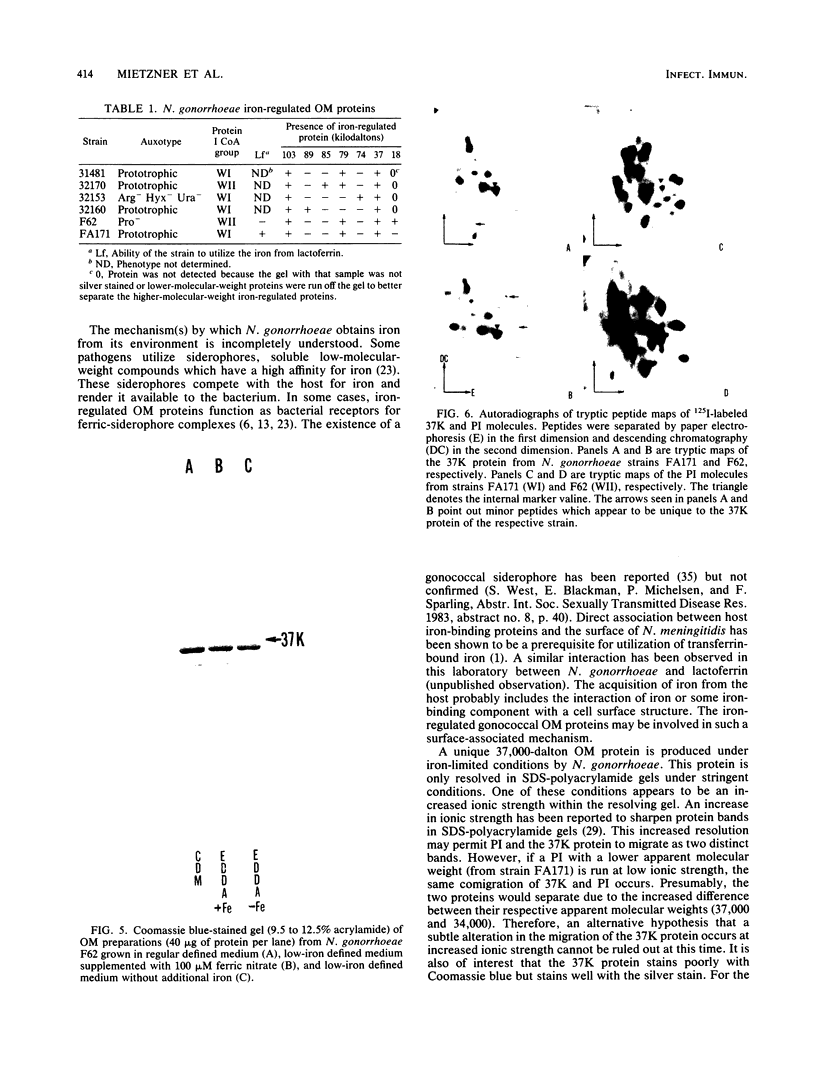
We examined the outer membrane proteins which appear during the growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae F62 in complex medium supplemented with 25 microM Desferal mesylate, a potent iron chelator. Outer membranes were prepared by Sarkosyl extraction and analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Several higher-molecular-weight (74,000 to greater than 94,000) proteins increased under iron-limiting conditions. In addition we observed the appearance of an iron-regulated protein with an apparent molecular weight of 37,000. This protein comigrated with the gonococcal protein I under normal Laemmli gel conditions. By increasing the ionic strength of the lower gel buffer, separation of protein I and the 37,000-dalton iron-regulated protein occurred. The 37,000-dalton protein stained poorly with Coomassie blue. However, when a silver stain was used, the protein appeared as a major component of the gonococcal outer membrane. Production of this 37,000-dalton protein was suppressed by the addition of iron to the medium. An iron-regulated protein with a similar molecular weight was observed in four clinical isolates and in an additional laboratory strain. Peptide mapping indicated that the 37,000-dalton protein was distinct from protein I and was identical between strains of the WI and WII serogroups.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Hodges L. L. Outer membrane proteins induced under conditions of iron limitation in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum 775. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):223–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.223-227.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal K. K., Warner P. J., Williams P. H. An inducible outer membrane protein involved in aerobactin-mediated iron transport by co1V strains of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 5;140(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80513-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. The surface of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: isolation of the major components of the outer membrane. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):333–341. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Gotschlich E. C. Isolation and characterization of the outer membrane of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.250-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebba P. E., McIntosh M. A., Neilands J. B. Kinetics of biosynthesis of iron-regulated membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):880–888. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.880-888.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., James L. T., Watt P. J. Variations in surface protein composition associated with virulence properties in opacity types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leith D. K., Morse S. A. Cross-linking analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):182–187. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.182-187.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong S. A., Neilands J. B. Relationship of siderophore-mediated iron assimilation to virulence in crown gall disease. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):482–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.482-491.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Kihlstrom E., Norqvist A., Davies J., Normark S. Effect of iron on surface charge and hydrophobicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):402–407. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.402-407.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Characterization of serologically dominant outer membrane proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1183-1191.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh M. A., Earhart C. F. Coordinate regulation by iron of the synthesis of phenolate compounds and three outer membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):331–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.331-339.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from lactoferrin. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):915–920. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.915-920.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Bartenstein L. Purine metabolism in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: the requirement for hypoxanthine. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Jan;26(1):13–20. doi: 10.1139/m80-003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Sawyer W. D., Haak R. A. Cross-linking analysis of the outer membrane proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.785-791.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstrom E. G., Chen K. C., Buchanan T. M. Serology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: coagglutination serogroups WI and WII/III correspond to different outer membrane protein I molecules. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):462–470. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.462-470.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel S. P., Payne S. M. Effect of iron limitation on growth, siderophore production, and expression of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.148-155.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Brener D., DeVoe I. W. Expression of a high-affinity mechanism for acquisition of transferrin iron by Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.107-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Mayer L. W., Tam M. R. Antigenicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane protein(s) III detected by immunoprecipitation and Western blot transfer with a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):668–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.668-672.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagegg W., Braun V. Ferric citrate transport in Escherichia coli requires outer membrane receptor protein fecA. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):156–163. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.156-163.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Finkelstein R. A. Siderophore production by pathogenic Neisseria spp. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):600–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.600-608.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]