Abstract
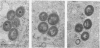
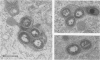
Data obtained in this study reaffirm that virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv has a potent phagosome-destroying capacity when ingested by normal alveolar macrophages. In contrast, Mycobacterium bovis BCG-immune alveolar macrophages are highly resistant to this virulence mechanism. BCG-immune sera incubated with BCG-immune alveolar macrophages did not increase resistance of BCG-immune alveolar macrophages as compared with the data obtained from experiments with normal sera. BCG-immune sera failed to confer resistance to normal alveolar macrophages against the phagosomal membrane-destroying H37Rv virulence mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hirsch J. G., Fedorko M. E. Ultrastructure of human leukocytes after simultaneous fixation with glutaraldehyde and osmium tetroxide and "postfixation" in uranyl acetate. J Cell Biol. 1968 Sep;38(3):615–627. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrvik Q. N., Leake E. S., Tenner-Racz K. Interaction of mycobacteria with normal and immunologically activated alveolar macrophages. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;162:83–98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4481-0_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrvik Q. N., Leake E. S., Wright M. J. Disruption of phagosomal membranes of normal alveolar macrophages by the H37Rv strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A correlate of virulence. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Feb;129(2):322–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]