Abstract
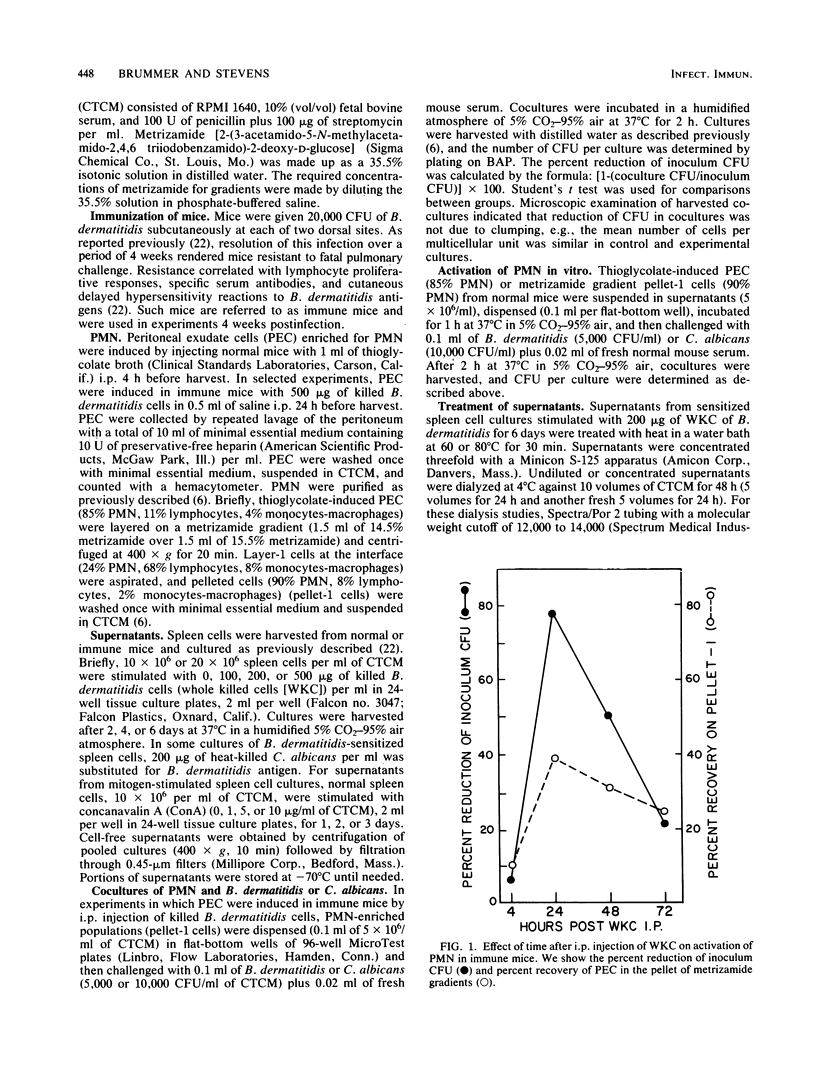
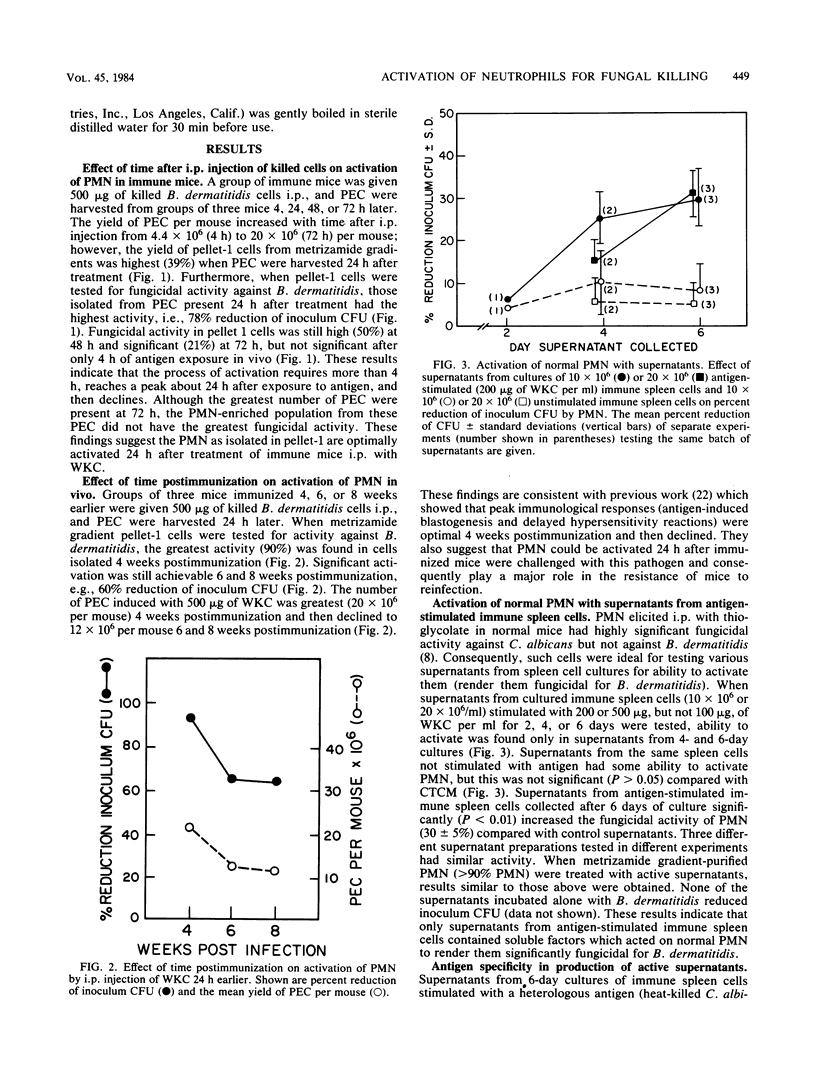
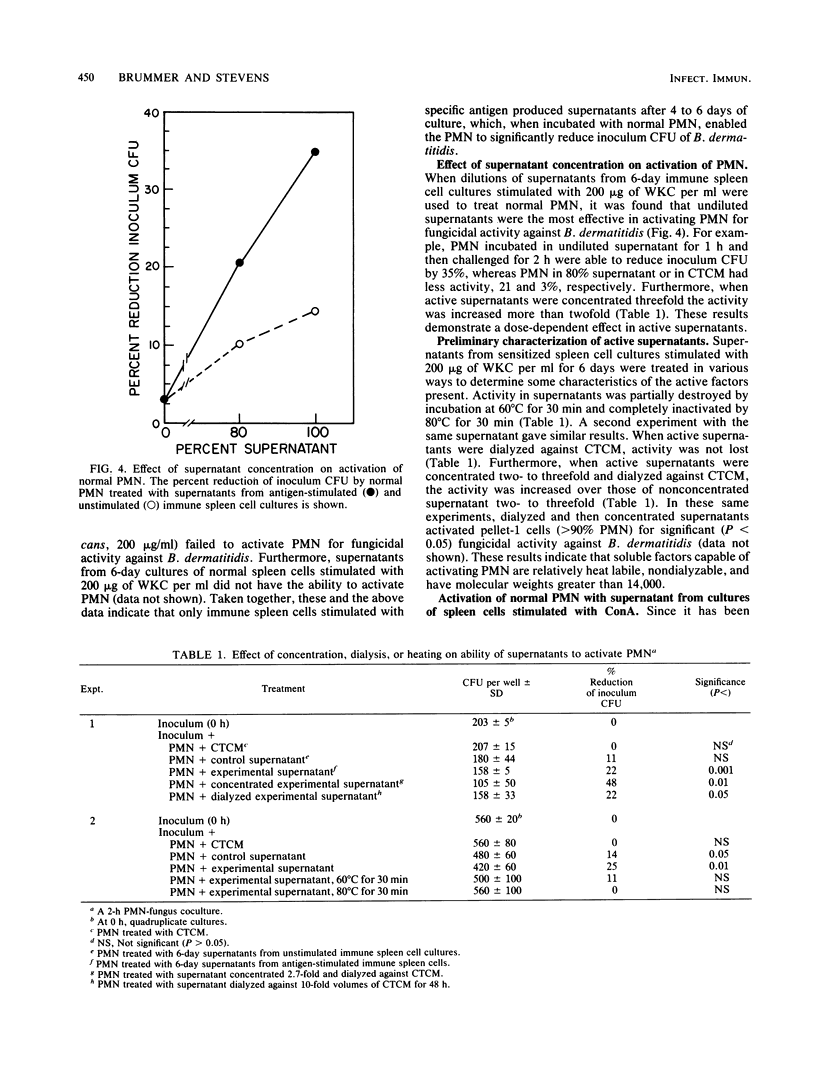
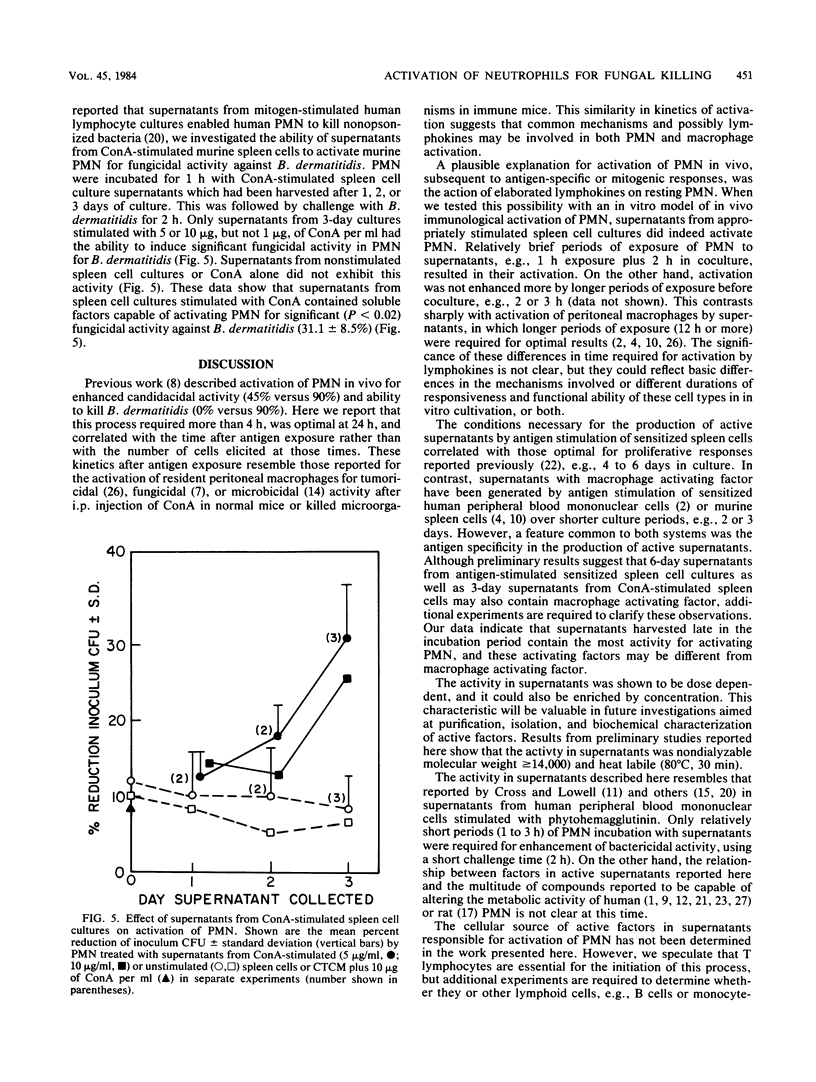
An in vitro model of in vivo immunological activation of murine polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) was developed. Culture supernatants of spleen cells from Blastomyces dermatitidis-immunized mice stimulated with B. dermatitidis antigens in vitro were studied. Incubation of the supernatants with thioglycolate-elicited PMN enabled the cells to significantly reduce (31 +/- 6%) B. dermatitidis inoculum CFU. Optimum production of active supernatants occurred after 4 to 6 days of stimulation in vitro and required 200 micrograms of nonviable B. dermatitidis cells per ml. Generation of activity by immune spleen cells was shown to be antigen specific in that stimulation with a heterologous antigen or stimulation of nonimmune spleen cells with B. dermatitidis antigen did not produce active supernatants. The activity in supernatants was dose dependent, nondialyzable (molecular weight greater than or equal to 14,000), and relatively heat labile (80 degrees C, 30 min). Activation of PMN by supernatants for fungicidal activity against B. dermatitidis required only a short incubation period (1 h) followed by a 2-h coculture (challenge) period. Stimulation of normal spleen cells with concanavalin A also resulted in the production of supernatants capable of activating PMN for significant fungicidal activity (31.1 +/- 8.5%). These findings demonstrate for the first time a link between soluble factors produced by antigen stimulation of sensitized lymphoid cells and activation of PMN for enhanced microbicidal activity. Such a process defines an additional immune defense mechanism whereby the immune host may clear specific microorganisms.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amoscato A. A., Davies P. J., Babcock G. F., Nishioka K. Receptor-mediated internalization of tuftsin by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Jul;34(1):53–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Bautista S., Remington J. S. Induction of resistance to Toxoplasma gondii in human macrophages by soluble lymphocyte products. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Benjamini E., Pappagianis D. Activation of macrophages by lymphokines: enhancement of phagosome-lysosome fusion and killing of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1201–1207. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1201-1207.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J. G., McPhail L. C., Van Epps D. E. Exposure of human neutrophils to chemotactic factors potentiates activation of the respiratory burst enzyme. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2316–2323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Stevens D. A. Enhancing effect of murine polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) on the multiplication of Blastomyces dermatitidis in vitro and in vivo. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Nov;54(2):587–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Sugar A. M., Stevens D. A. Activation of peritoneal macrophages by concanavalin A or Mycobacterium bovis BCG for fungicidal activity against Blastomyces dermatitidis and effect of specific antibody and complement. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):817–822. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.817-822.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E., Wilson M. K., Newburger P. E. Con-A-stimulated superoxide production by granulocytes: reversible activation of NADPH oxidase. Blood. 1982 Nov;60(5):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P. Activation of mouse peritoneal cells to kill Listeria monocytogenes by T-lymphocyte products. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.36-41.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Lowell G. H. Stimulation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte bactericidal activity by supernatants of activated human mononuclear cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):502–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.502-507.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Brindley L. L., Goldman D. W. Enhancement of human neutrophil adherence by synthetic leukotriene constituents of the slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis. Immunology. 1983 Sep;50(1):35–41. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Feit F., Weissmann G. Enhancement of nitroblue tetrazolium dye reduction by leukocytes exposed to a component of complement in the absence of phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):516–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington-Fowler L., Henson P. M., Wilder M. S. Fate of Listeria monocytogenes in resident and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):11–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.11-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harthus H. P., Hannig K. Partial characterization of lymphokines that change the surface charge density of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Immunobiology. 1982;162(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Schmid E. S., Carrington C. C., Stevens D. A. Mouse model of pulmonary blastomycosis: utility, simplicity, and quantitative parameters. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Apr;117(4):695–703. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.4.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sendo F. In vitro induction of cytotoxic polymorphonuclear leukocytes by supernatant from a concanavalin A-stimulated spleen cell culture. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2508–2514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Lee K. Y., Biggar W. D. Enhancement of human neutrophil bactericidal activity by chemotactic factors. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):295–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.295-301.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lace J. K., Tan J. S., Watanakunakorn C. An appraisal of the nitroblue tetrazolium reduction test. Am J Med. 1975 May;58(5):685–694. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90505-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomnitzer R., Glover A., Rabson A. R. The effect of PHA-activated MN-cell supernatants on polymorphonuclear leucocyte function. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Sep;29(3):501–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moqbel R., Sass-Kuhn S. P., Goetzl E. J., Kay A. B. Enhancement of neutrophil- and eosinophil-mediated complement-dependent killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni in vitro by leukotriene B4. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jun;52(3):519–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi P. A., Brummer E., Stevens D. A. Protection against pulmonary blastomycosis: correlation with cellular and humoral immunity in mice after subcutaneous nonlethal infection. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):670–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.670-678.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Salmon J. A. Release of leukotriene B4 from human neutrophils and its relationship to degranulation induced by N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, serum-treated zymosan and the ionophore A23187. Immunology. 1983 Sep;50(1):65–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. H., Fikrig S. M., Smithwick E. M. Infection and nitroblue-tetrazolium reduction by neutrophils. A diagnostic acid. Lancet. 1968 Sep 7;2(7567):532–534. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H. H., Good R. A. N.B.T. test stimulated. Lancet. 1970 Sep 19;2(7673):616–616. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: induction of tumoricidal macrophages by supernatants of PPD-stimulated Bacillus Calmette-Guérin-immune spleen cell cultures. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):889–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Bowman B. J. Generation of hydrogen peroxide by human neutrophils: effects of soluble stimuli and requirements for divalent cations. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Aug;24(2):194–203. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Garcia M. L. Enhancement of neutrophils function as a result of prior exposure to chemotactic factor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):167–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI109841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


