Abstract
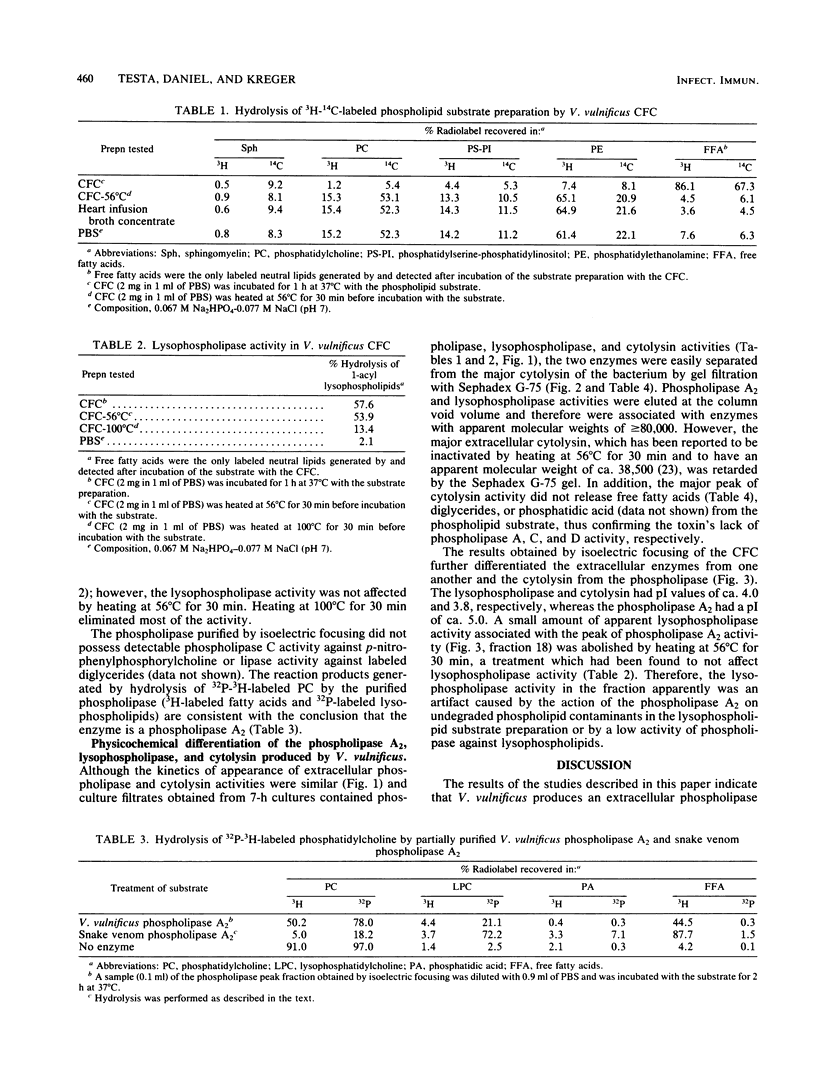
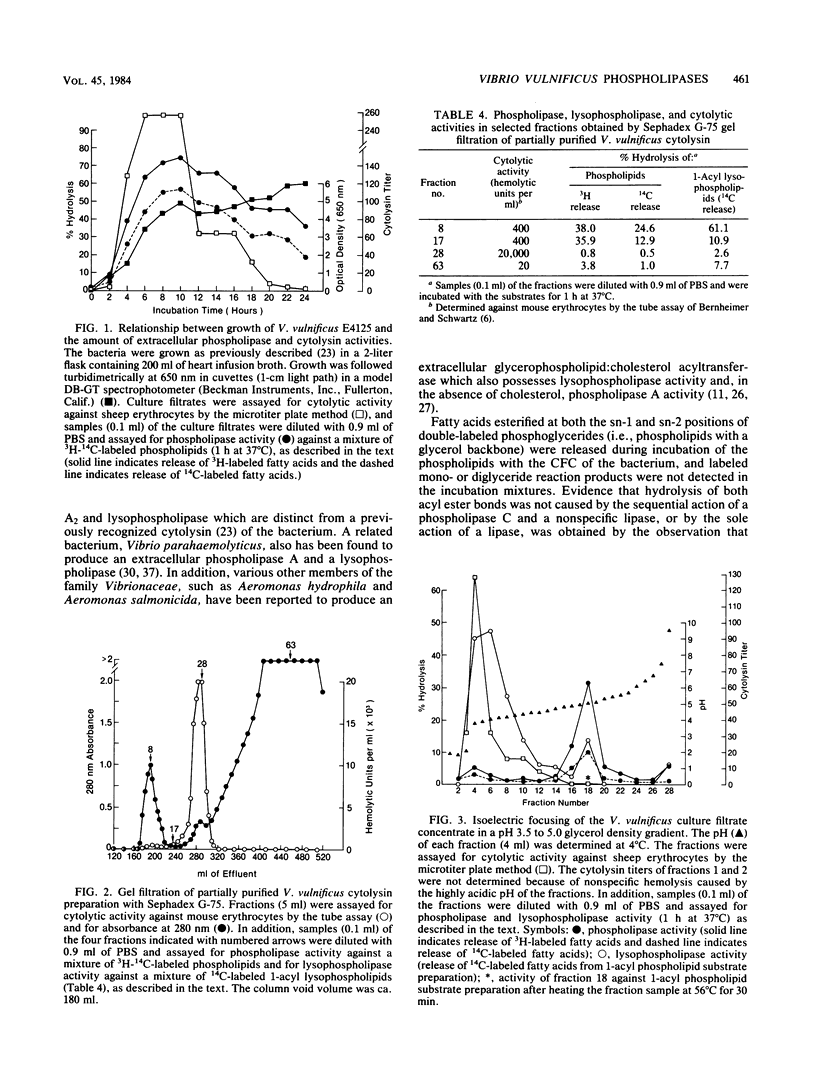
Phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipase activities were detected in the culture supernatant fluids of a virulent strain of Vibrio vulnificus. The phospholipase A2 was inactivated by heating at 56 degrees C for 30 min, had an apparent molecular weight of greater than or equal to 80,000 (estimated by gel filtration with Sephadex G-75), and a pI of ca. 5.0. Phospholipid hydrolysis was unaffected by Ca2+ or ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N-tetraacetic acid and was optimal at pH 5.0 to 5.5. The lysophospholipase was not affected by heating at 56 degrees C for 30 min but was inactivated at 100 degrees C and had an apparent molecular weight of greater than or equal to 80,000 and a pI of ca. 4.0. The enzymes were detected coincidentally with a previously described extracellular cytolysin of V. vulnificus; however, they were physically separable from the toxin (which did not possess phospholipase A, C, or D activity) by gel filtration with Sephadex G-75.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe P. M., Kendall C. J., Stauffer L. R., Holland J. W. Hemolytic activity of Fusobacterium necrophorum culture supernatants due to presence of phospholipase A and lysophospholipase. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Jan;40(1):92–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L. Biology of the marine enterobacteria: genera Beneckea and Photobacterium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:39–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman E. N., Leonard G. L., Castillo L. E., Genre C. F., Pankey G. A. Histopathology of marine vibrio wound infections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Dec;76(6):765–772. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/76.6.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Merson M. H., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G., Heublein P. C. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 4;300(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901043000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayton P. R., West P. A., Russek E., Colwell R. R. New selective plating medium for isolation of Vibrio vulnificus biogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1039–1044. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1039-1044.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley J. T., Halasa L. N., MacIntyre S. Purification and partial characterization of a bacterial phospholipid: cholesterol acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3320–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo L. E., Winslow D. L., Pankey G. A. Wound infection and septic shock due to Vibrio vulnificus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Jul;30(4):844–848. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig D. B., Stevens D. L. Halophilic Vibrio sepsis. South Med J. 1980 Sep;73(9):1285–1287. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198009000-00048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., King L., Waite M. Source of arachidonic acid for prostaglandin synthesis in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12830–12835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., Waite M., Kucera L. S., King L., Edwards I. Phospholipid synthesis in human embryo fibroblasts infected with herpes simplex virus type 2. Lipids. 1981 Sep;16(9):655–662. doi: 10.1007/BF02535060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington E. P., Wood J. G., Hill E. O. Disease caused by a marine vibrio--Vibrio vulnificus. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 23;307(26):1642–1642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212233072609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd Vibrio ("Beneckea") vulnificus, the bacterium associated with sepsis, septicaemia, and the sea. Lancet. 1979 Oct 27;2(8148):903–903. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92715-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. K., Bowen T. E. Halophilic vibrios from human tissue infections on the pacific coast of Australia. Pathology. 1980 Jul;12(3):397–402. doi: 10.3109/00313028009077102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Halophilic Vibrio species isolated from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Apr;3(4):425–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.4.425-431.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. M., Andes W. A., Glasser G. Vibrio vulnificus. A gastronomic hazard. JAMA. 1983 Apr 1;249(13):1756–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Avery D. M. Lactose-positive Vibrio in seawater: a cause of pneumonia and septicemia in a drowning victim. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):278–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.278-280.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., McCormick W. F. Acute bacterial myositis caused by Vibrio vulnificus. JAMA. 1981 Jul 3;246(1):72–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A., Lockwood D. Detection of extracellular toxin(s) produced by Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.583-590.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Matsuda M. Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre S., Buckley J. T. Presence of glycerophospholipid: cholesterol acyltransferase and phospholipase in culture supernatant of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):402–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.402-407.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre S., Trust T. J., Buckley J. T. Distribution of glycerophospholipid-cholesterol acyltransferase in selected bacterial species. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):132–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.132-136.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Kohno S., Ikeda T., Saruwatari K., Ninomiya H. Fulminating lactose-positive Vibrio septicemia. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1978 Nov;28(6):937–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1978.tb01282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens A., Nagler J., Hansen W., Gepts-Friedenreich E. Halophilic, lactose-positive Vibrio in a case of fatal septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):233–235. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.233-235.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misaki H., Matsumoto M. Purification of lysophospholipase of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its properties. J Biochem. 1978 May;83(5):1395–1405. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura T., Kimura S., Saito K. A novel purification procedure for Penicillium notatum phospholipase B and evidence for a modification of phospholipase B activity by the action of an endogenous protease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 22;617(2):264–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollak S. J., Parrish E. F., 3rd, Barrett T. J., Dretler R., Morris J. G., Jr Vibrio vulnificus septicemia. Isolation of organism from stool and demonstration of antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Apr;143(4):837–838. doi: 10.1001/archinte.143.4.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Siakotos A. N., Fleischer S. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography and phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1966 Jan;1(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02668129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagase Y., Inoue K., Ozaki M., Ochi T., Amano T. Hemolysins and related enzymes of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. I. Identification and partial purification of enzymes. Biken J. 1970 Jun;13(2):77–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



