Abstract
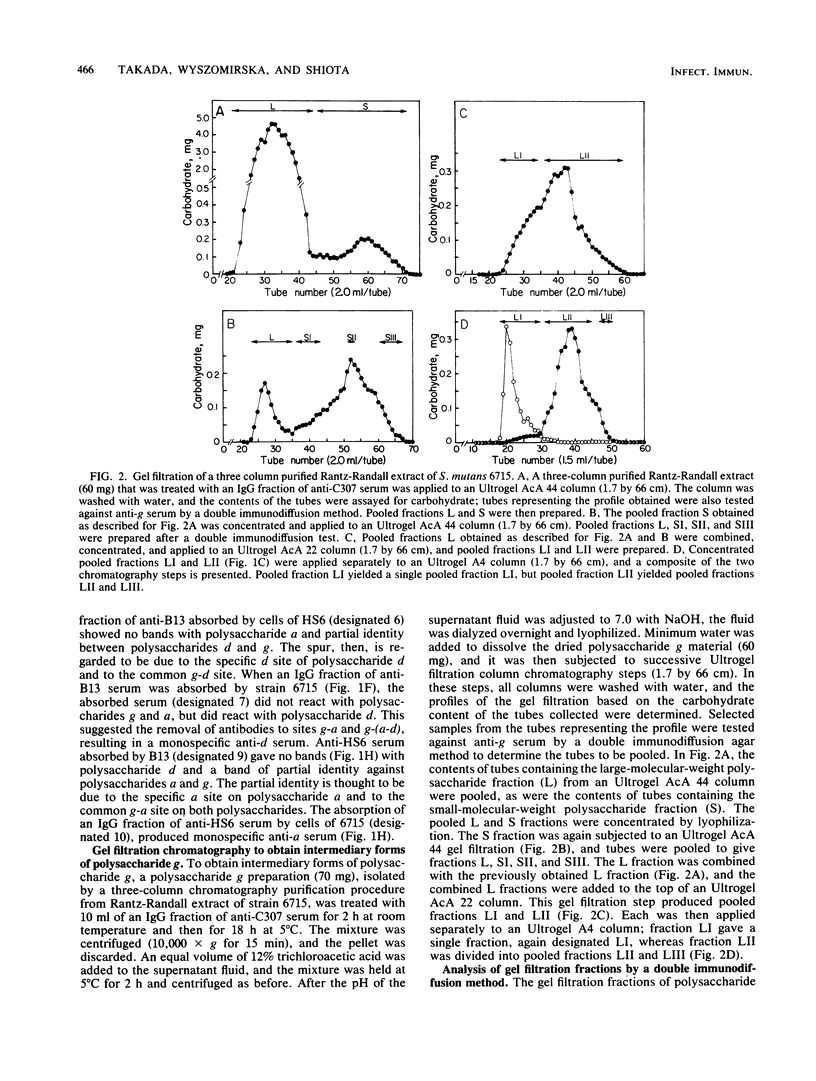
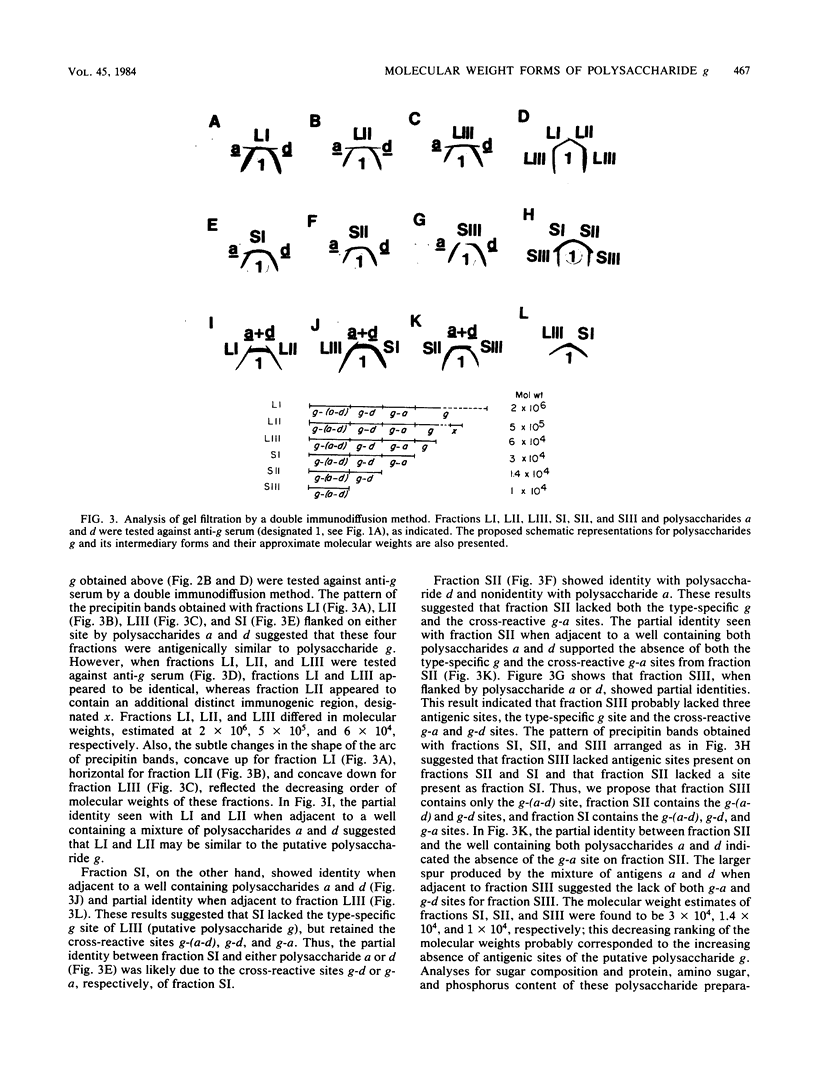
The serotype polysaccharide g from Streptococcus mutans 6715 was found to cross-react with serotype polysaccharide a from S. mutans HS6 and serotype polysaccharide d from S. mutans B13. Double immunodiffusion experiments indicated that the serotype polysaccharide g consisted of the following: (i) the type-specific g site; (ii) a cross-reactive site g-a that was in common with polysaccharide a; (iii) a cross-reactive site g-d that was in common with polysaccharide d; and (iv) a cross-reactive site g-(a-d) that was in common with both polysaccharides a and d. Moreover, by a procedure involving several column chromatography steps, six polysaccharide-containing fractions showing reactivity with anti-g serum were found. By gel filtration, the molecular weight estimates of fractions LI, LII, LIII, SI, SII, and SIII were 2 X 10(6), 5 X 10(5), 6 X 10(4), 3 X 10(4), 1.4 X 10(4), and 1 X 10(4), respectively. Double immunodiffusion analysis indicated that LI, LII, and LIII contained the four antigenic sites of the putative polysaccharide g. LII also contained another additional immunodominant region, designated site x. The analysis also suggested that fraction SI lacked the type-specific site g, fraction SII lacked sites g and g-a, and fraction SIII lacked sites g, g-a, and g-d.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Bleiweis A. S. Chemical, immunochemical, and structural studies of the cross-reactive antigens of Streptococcus mutans AHT and B13. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):326–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.326-336.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser L. Bacterial cell surface polysaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:91–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Masuda N., Kotani S. Demonstration of serotype d and g specificities of Streptococcus mutans by immunodiffusion. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(6):495–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Adherence of serotype e Streptococcus mutans and the inhibitory effect of Lancefield group E and S mutans type e antiserum. J Dent Res. 1976 Apr;55(Spec No):C65–C74. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500328011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Purification and immunochemical characterization of type e polysaccharide antigen of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):68–76. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.68-76.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa M., Kiyono H., Shiota T., Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R. Virulence of Streptococcus mutans: immunochemical characterization of a serotype g-defective mutant (C307). Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):697–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.697-699.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacono V. J., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J., Levine M. J. Isolation and immunochemical characterization of the group-specific antigen of Streptococcus mutants 6715. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):117–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.117-128.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Shiota T., McGhee J. R., Otake S., Michalek S. M., Ochiai K., Hirasawa M., Sugimoto K. Virulence of Streptococcus mutans: comparison of the effects of a coupling sugar and sucrose on certain metabolic activities and cariogenicity. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):477–480. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.477-480.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer R., Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Serological purification of polysaccharide antigens from Streptococcus mutans serotypes a and d: characterization of multiple antigenic determinants. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):791–798. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.791-798.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer R., Slade H. D. Purification and characterization of Streptococcus mutans group d cell wall polysaccharide antigen. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):361–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.361-368.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Extraction, purification, and chemical and immunological properties of the Streptococcus mutans group "a" polysaccharide cell wall antigen. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):190–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.190-198.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. I. Roles of insoluble dextran-levan synthetase enzymes and cell wall polysaccharide antigen in plaque formation. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):555–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.555-562.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. II. Nature of the binding site and the adsorption of dextran-levan synthetase enzymes on the cell-wall surface of the streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):419–429. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.419-429.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otake S., Hirasawa M., Brown T. A., Kawabata Y., Kiyono H., Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R., Shiota T. Virulence of Streptococcus mutans: characterization of a serotype g antigen-defective mutants and its revertants. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):151–159. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.151-159.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Kjems E., Ravn T. Biochemical and serological properties of Streptococcus mutans from various human and animal sources. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):357–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]