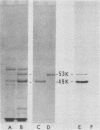
Abstract
Exoenzyme S is an extracellular product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This enzyme catalyzes the transfer of ADP-ribose from NAD to a number of as yet unidentified eucaryotic proteins, but it is distinct from toxin A. To evaluate the role of exoenzyme S in the pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa, we isolated transposon-induced mutants of strain 388, a clinical isolate that produces exoenzyme S but no toxin A. The transposon Tn1 was introduced by using a temperature-sensitive derivative of plasmid RP1. A Tn1-induced mutant was found which had no detectable exoenzyme S activity or antigen in culture supernatants or in cell lysates. Except for its lack of exoenzyme S and resistance to carbenicillin, this mutant was indistinguishable from the parent strain. When tested in an experimental mouse burn infection model, this Tn1-induced mutant was reduced in virulence by at least 2,000-fold, suggesting a role for exoenzyme S in the virulence of this strain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorn M. J., Pavlovskis O. R., Thompson M. R., Iglewski B. H. Production of exoenzyme S during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections of burned mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):837–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.837-842.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadesús J., Iáez E., Olivares J. Transposition of Tn 1 to the Rhizobium meliloti genome. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(2):405–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00425855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Ingram J. M., Costerton J. W. Release of alkaline phosphatase from cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by manipulation of cation concentration and of pH. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):748–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.748-753.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant producing a nontoxic, immunologically crossreactive toxin A protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7199–7203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Watson J., Krieg R., Leisinger T. Isolation of an Hfr donor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO by insertion of the plasmid RP1 into the tryptophan synthase gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):240–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00269664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Poole K., Benz R. Outer membrane protein P of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: regulation by phosphate deficiency and formation of small anion-specific channels in lipid bilayer membranes. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):730–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.730-738.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Tsuda M., Iino T. Tn1 insertion mutagenesis in Escherichia coli K-12 using a temperature-sensitive mutant of plasmid RP4. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):52–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00271194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt R. J. The detection of bacterial esterases and lipases. Med Lab Technol. 1971 Apr;28(2):208–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of alkaline protease-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro and in a mouse eye model. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1058–1063. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1058-1063.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J. C. Toxin inhibitors of protein synthesis: production, purification, and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:780–793. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J., Bjorn M. J., Maxwell E. S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S: an adenosine diphosphate ribosyltransferase distinct from toxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3211–3215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Roth J., Botstein D. Genetic engineering in vivo using translocatable drug-resistance elements. New methods in bacterial genetics. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):125–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V., Royle P., Lehrer J. Insertions of the transposon Tn1 into the Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosome. Genetics. 1981 Mar-Apr;97(3-4):495–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/97.3-4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Matsuda M. Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Toxin A-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):899–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.899-908.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A., Iglewski B. H., Hager T. A., Sadoff J. C., Cross A. S., McManus A., Farber B. F., Iglewski W. J. Production of exoenzyme S by clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):147–153. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.147-153.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A., Holloway B. W. A mutant sex factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1972 Feb;19(1):91–108. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieritz D. D., Holder I. A. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: description of a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):688–691. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]