Abstract
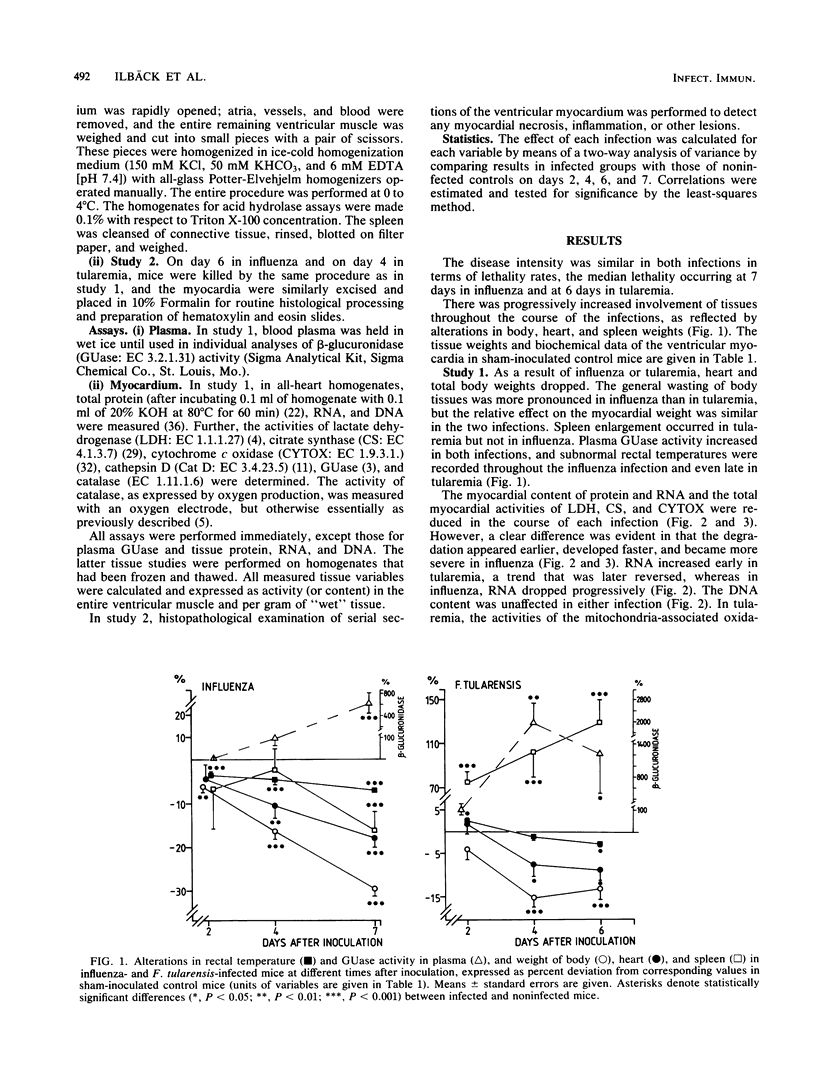
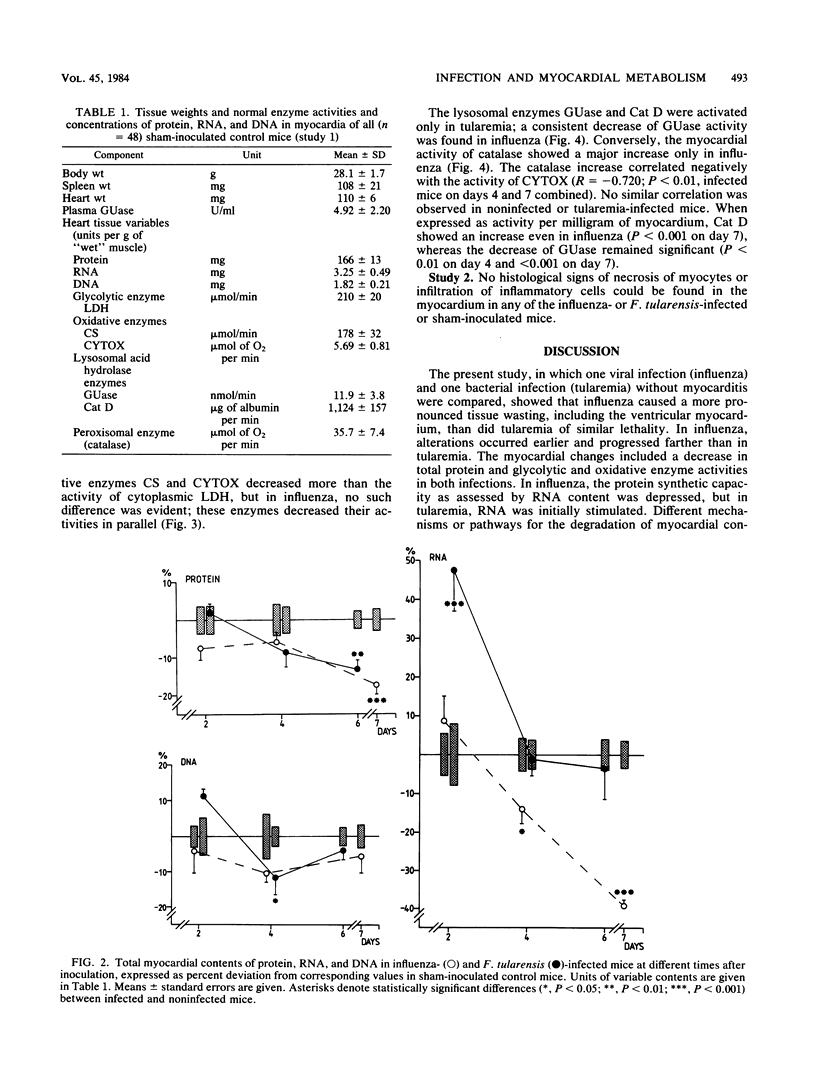
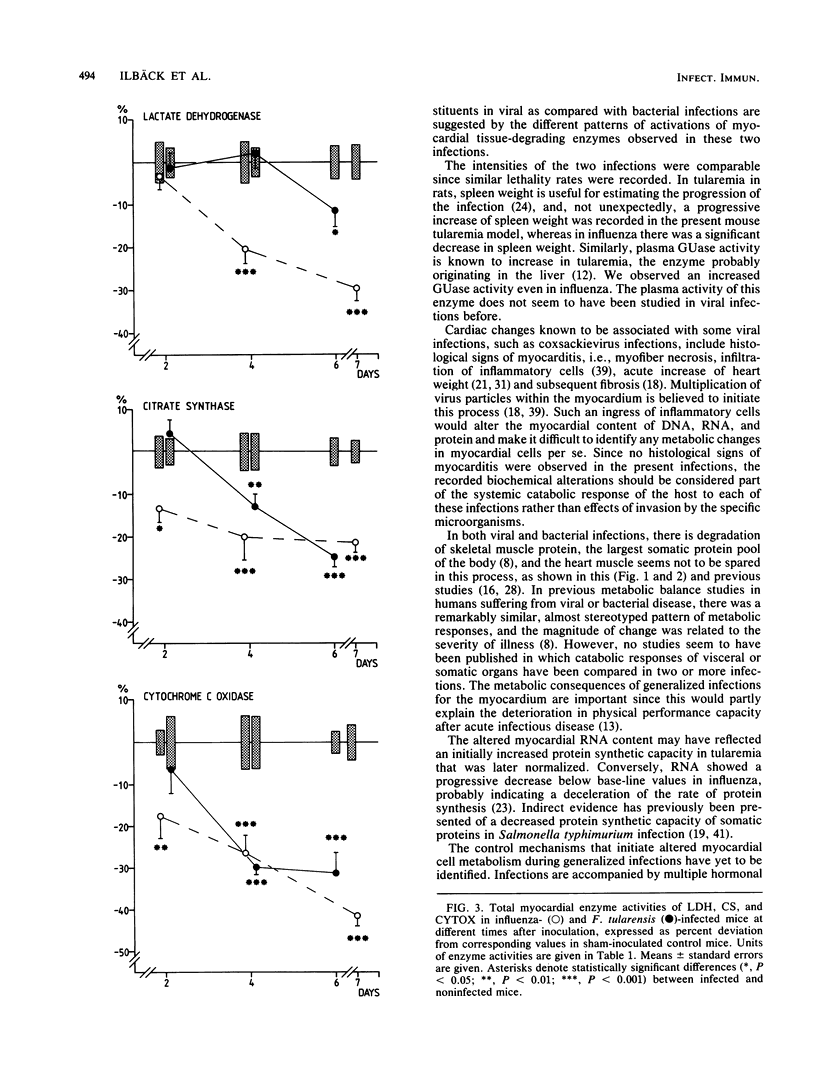
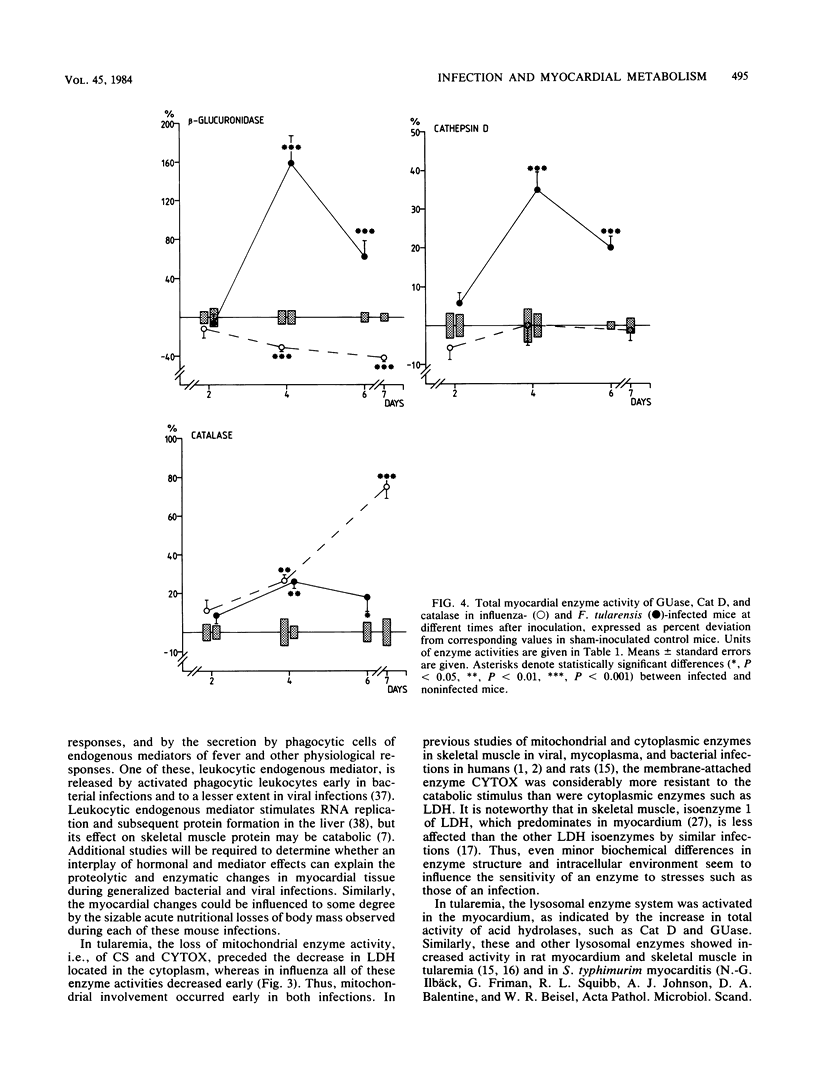
Mice with generalized influenza or tularemia of similar lethality were studied in an effort to compare biochemical responses of the myocardium during infections of viral and bacterial etiology. A progressive loss of body weight characterized the course of both infections. Accompanying this, the myocardial content of protein and the activities of lactate dehydrogenase, citrate synthase, and cytochrome c oxidase all decreased. However, myocardial protein degradation appeared earlier and was more pronounced in influenza, and the protein changes were accompanied by a rapid decline of myocardial RNA. Activation of acid hydrolases, such as cathepsin D and beta-glucuronidase, occurred in tularemia but not in influenza, whereas leakage of beta-glucuronidase into the plasma occurred in both infections. Conversely, there was a considerably greater activation of myocardial catalase in influenza. These findings suggested that different control mechanisms or metabolic pathways were operative in the degradation of myocardial constituents in influenza as compared with tularemia. The absence of histological signs of myocarditis in either infection appeared to exclude any direct local effects of an inflammatory process on myocardial cells. Since the infections were of comparable lethality (based upon the inoculated dose of organisms), the observed differences in pattern and extent of metabolic responses of the myocardium to these infections may be attributed to different pathophysiological mechanisms evoked by the different microorganisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aström E., Friman G., Pilström L. Effects of viral and mycoplasma infections on ultrastructure and enzyme activities in human skeletal muscle. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1976 Mar;84(2):113–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aström E., Friman G., Pilström L. Human skeletal muscle in bacterial infection: enzyme activities and their relationship to age. Scand J Infect Dis. 1977;9(3):193–195. doi: 10.3109/inf.1977.9.issue-3.07. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENGTSSON E. Working capacity and exercise electrocardiogram in convalescents after acute infectious diseases without cardiac complications. Acta Med Scand. 1956 Jun 9;154(5):359–373. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1956.tb14331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass A., Brdiczka D., Eyer P., Hofer S., Pette D. Metabolic differentiation of distinct muscle types at the level of enzymatic organization. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):198–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R. Mediators of fever and muscle proteolysis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 10;308(10):586–587. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303103081009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R., Sawyer W. D., Ryll E. D., Crozier D. Metabolic effects of intracellular infections in man. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Oct;67(4):744–779. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-4-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird J. W. Skeletal muscle lysosomes. Front Biol. 1975;43(4):75–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., Bird J. W. Lysosomes in skeletal muscle tissue. Zonal centrifugation evidence for multiple cellular sources. J Cell Biol. 1970 May;45(2):321–333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., Powanda M. C., Cockerell G. L., Moe J. B. Relationship of serum beta-glucuronidase and lysozyme to pathogenesis of tularemia in immune and nonimmune rats. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):42–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.42-47.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friman G. Effects of acute infectious disease on circulatory function. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1976;592:1–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friman G., Ilbäck N. G., Beisel W. R., Crawford D. J. The effects of strenuous exercise on infection with Francisella tularensis in rats. J Infect Dis. 1982 May;145(5):706–714. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friman G., Ilbäck N. G., Beisel W. R. Effects of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Salmonella typhimurium and Francisella tularensis infections on oxidative, glycolytic and lysosomal enzyme activity in red and white skeletal muscle in the rat. Scand J Infect Dis. 1984;16(1):111–119. doi: 10.3109/00365548409068416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friman G., Ilbäck N. G., Pilström L. Skeletal muscle lactate dehydrogenase isozymes and fibre composition in viral, mycoplasma and bacterial infections in young and old men. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1981 Oct;41(6):551–556. doi: 10.3109/00365518109090497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friman G. Serum creatine phosphokinase in epidemic influenza. Scand J Infect Dis. 1976;8(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatmaitan B. G., Chason J. L., Lerner A. M. Augmentation of the virulence of murine coxsackie-virus B-3 myocardiopathy by exercise. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1121–1136. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilbäck N. G., Friman G., Beisel W. R. Biochemical responses of the myocardium and red skeletal muscle to Salmonella typhimurium infection in the rat. Clin Physiol. 1983 Dec;3(6):551–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097x.1983.tb00864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson E. W., Dominik J. W., Rowberg A. H., Higbee G. A. Influenza virus population dynamics in the respiratory tract of experimentally infected mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):438–447. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.438-447.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Wilson F. M. Virus myocardiopathy. Prog Med Virol. 1973;15:63–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe J. B., Canonico P. G., Stookey J. L., Powanda M. C., Cockerell G. L. Pathogenesis of tularemia in immune and nonimmune rats. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Oct;36(10):1505–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld H. A., Pace J. A., White F. E. The effect of bacterial infections on ketone concentrations in rat liver and blood and on free fatty acid concentrations in rat blood. Metabolism. 1976 Aug;25(8):877–884. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohl H., Hegner D. Evidence for the existence of catalase in the matrix space of rat-heart mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 1;89(1):126–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80537-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb R. L., Lyons M. M., Beisel W. R. Virus involvement in the avian heart: effect on protein synthesis. J Nutr. 1968 Dec;96(4):509–512. doi: 10.1093/jn/96.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber W. T., Bird J. W., Schottelius B. A. Catalase: an enzymatic indicator of the degree of muscle wasting. Exp Neurol. 1977 May;55(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(77)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TILLES J. G., ELSON S. H., SHAKA J. A., ABELMANN W. H., LERNER A. M., FINLAND M. EFFECTS OF EXERCISE ON COXSACKIE A9 MYOCARDITIS IN ADULT MICE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:777–782. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tottmar S. O., Pettersson H., Kiessling K. H. The subcellular distribution and properties of aldehyde dehydrogenases in rat liver. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):577–586. doi: 10.1042/bj1350577a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihko V., Salminen A., Rantamäki J. Exhaustive exercise, endurance training, and acid hydrolase activity in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Jul;47(1):43–50. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladimirov Y. A., Olenev V. I., Suslova T. B., Cheremisina Z. P. Lipid peroxidation in mitochondrial membrane. Adv Lipid Res. 1980;17:173–249. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024917-6.50011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Banks W. L., Jr, Wunner W. H. Use of a single tissue extract to determine cellular protein and nucleic acid concentrations and rate of amino acid incorporation. Anal Biochem. 1965 May;11(2):320–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Pekarek R. S., Klainer A. S., Bartelloni P. J., Dupont H. L., Hornick R. B., Beisel W. R. Detection of a leukocytic endogenous mediator-like mediator of serum amino acid and zinc depression during various infectious illnesses. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):873–875. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.873-875.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Pekarek R. S., Thompson W. L., Curnow R. T., Beall F. A., Zenser T. V., DeRubertis F. R., Beisel W. R. A protein from polymorphonuclear leukocytes (LEM) which affects the rate of hepatic amino acid transport and synthesis of acute-phase globulins. Endocrinology. 1975 Mar;96(3):651–661. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-3-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young V. R., Chen S. C., Newberne P. M. Effect of infection on skeletal muscle ribosomes in rats fed adequate or low protein. J Nutr. 1968 Mar;94(3):361–368. doi: 10.1093/jn/94.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



