Abstract
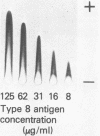
Clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus have been previously classified into eight types on the basis of their capsular polysaccharide. The high prevalence of the type 8 capsular polysaccharide among bacteremic isolates suggests the importance of this capsular antigen in staphylococcal disease. The capsular polysaccharide was purified from extracts of three clinical isolates of S. aureus type 8 of different geographic and temperal origin by ion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration. Gas chromatography, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, and 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance showed that the type 8 capsular polysaccharide is composed of O-acetyl groups, N-acetylfucosamine, and an aminouronic acid similar to N-acetylgalactosaminouronic acid. The purified polysaccharide reacted only with type 8 antiserum in double diffusion experiments. Our analysis shows that the type 8 polysaccharide is both chemically and serologically distinct from teichoic acid and previously characterized polysaccharides of S. aureus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asheshov E. H., Winkler K. C. Staphylococcus aureus strains in the "52, 52A, 80, 81 complex". Nature. 1966 Feb 5;209(5023):638–639. doi: 10.1038/209638b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bietz J. A., Sandford P. A. Reaction of sodium hypochlorite with amines and amides: automation of the method. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):122–133. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90353-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputy G. G., Costerton J. W. Morphological examination of the glycocalyces of Staphylococcus aureus strains Wiley and Smith. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):759–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.759-767.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt R. D. Mechanisms of resistance to staphylococcal infection: natural and acquired. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):301–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. D., Tai J. Y. The type-specific polysaccharides of Streptococcus suis. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1699–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Rey M., Etienne J., Sanborn W. R., Triau R., Cvjetanović B. The immunological responses observed in field studies in Africa with group A meningococcal vaccines. Prog Immunobiol Stand. 1971;5:485–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANESSIAN S., HASKELL T. H. STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON STAPHYLOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGEN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2758–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASKELL T. H., HANESSIAN S. THE PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF A NEW ACTIVE IMMUNIZING POLYSACCHARIDE PREPARED FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 2;83:35–41. doi: 10.1016/0926-6526(64)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Kane J. A. Characterization of the surface antigens of Staphylococcus aureus, strain K-93M. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1199–1208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Kane J. A. Immunochemical analysis of a Smith-like antigen isolated from two human strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):564–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Kane J. A., Smith M. R. Isolation of an acidic surface antigen from a conventional strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):511–518. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.511-518.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Young D. A. Immunochemical study of diverse surface antigens of a Staphylococcus aureus isolate from an osteomyelitis patient and their role in in vitro phagocytosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):399–408. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.399-408.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Young D. A. Immunological specificity of heat-stable opsonins in immune and nonimmune sera and their interaction with non-encapsulated and encapsulated strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):175–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.175-186.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Young D. A., Kane J. A. Structural analysis of the cellular constituents of a fresh clinical isolate of Staphylococcus aureus, and their role in the interaction between the organisms and polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the presence of serum factors. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):496–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.496-505.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Structural analysis of the surface polysaccharide of Staphylococcus aureus M. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):194–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.194-200.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau D. F., Melly M. A., Hash J. H. Surface polysaccharide from Staphylococcus aureus M that contains taurine, D-aminogalacturonic acid, and D-fucosamine. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):913–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.913-922.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE S. I. Isolation and properties of a surface antigen of Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med. 1962 Feb 1;115:295–311. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maverakis N. H., Wiley B. B. Evidence for a multiplicity of capsular types among Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):472–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.472-479.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S. V., Melly M. A., Harris T. M., Hellerqvist C. G., Hash J. H. The repeating sequence of the capsular polysaccharide of Staphylococcus aureus M. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Jun 16;117:113–123. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAHMIAS A., SAKURAI N., BLUMBERG R., DOE GE A., SULZER C. The Staphylococcus "80/81 complex: epidemiological and laboratory observations. J Infect Dis. 1961 Nov-Dec;109:211–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.3.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. M., DUBOS R. J. The behavior of virulent and avirulent staphylococci in the tissues of normal mice. J Exp Med. 1956 Jan 1;103(1):87–108. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandford P. A., Nafziger A. J., Jeanes A. Reaction of sodium hypochlorite with amines and amides. A new method for quantitating polysaccharides containing hexosamines. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90352-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandford P. A., Nafziger A. J., Jeanes A. Reaction of sodium hypochlorite with amines and amides: a new method for quantitating amino sugars in monomeric form. Anal Biochem. 1971 Aug;42(2):422–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Barrera O., Sutton A., Robbins J. B. Preparation, characterization, and immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-protein conjugates. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):361–376. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. C. A capsulate Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Aug;2(3):253–260. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-3-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellner K., Saito H., Hakomori S. I. Determination of aminosugar linkages in glycolipids by methylation. Aminosugar linkages of ceramide pentasaccharides of rabbit erythrocytes and of Forssman antigen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Apr;155(2):464–472. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann W. F., Jann K. Structure and serological specificity of the K13-antigenic polysaccharide (K13 antigen) of urinary tract-infective Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):85–92. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.85-92.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann W. F., Soderstrom T., Egan W., Tsui F. P., Schneerson R., Orskov I., Orskov F. Serological, chemical, and structural analyses of the Escherichia coli cross-reactive capsular polysaccharides K13, K20, and K23. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):623–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.623-629.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILEY B. B. A new virulence test for Staphylococcus aureus and its application to encapsulated strains. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Dec;7:933–943. doi: 10.1139/m61-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILEY B. B., WONNACOTT J. C. Isolation and partial characterization of a capsular material from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1169–1176. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1169-1176.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. Teichoic and teichuronic acids: biosynthesis, assembly, and location. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):211–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.211-243.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B. Capsule size, coagulase production, and egg virulence among certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jun;14(6):685–689. doi: 10.1139/m68-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Maverakis N. H. Virulent and avirulent encapsulated variants of Staphyococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):998–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.998-1002.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Park J. T. Chemical characterization of a new surface antigenic polysaccharide from a mutant of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):874–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.874-884.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]