Abstract
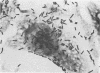
We showed that Escherichia coli strains attach to HeLa cells in two different patterns. In one, the bacteria cover the whole surface of the cell (diffuse adherence), and in the other, attachment is limited to one or a few sites of the cell surface (localized adherence). Among the enteropathogenic strains, serogroups O55, O86, O11ab, O119, O125, O128ab, and O142 usually showed localized adherence when tested in the presence of D-mannose. Localized adherence was not shown either by E. coli strains isolated from urine or by enteroinvasive and enterotoxigenic E. coli strains. Some of these strains showed diffuse adherence. Some strains of serogroups O55, O111, and O119 showed both localized and diffuse adherence in the same preparation. Mannose-resistant adherence was not related to colonization factor antigens.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bettelheim K. A., Reeve K. G. An outbreak of gastroenteritis due to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, which are also enterotoxigenic. N Z Med J. 1982 Apr 14;95(705):215–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C. R., Christie D. L. Chronic diarrhea in infants caused by adherent enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):358–361. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeish A. S., Turner P., Fleming J., Evans N. Mucosal adherence of human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1975 Nov 15;2(7942):946–948. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis M. H., Matos D. P., de Castro A. F., Toledo M. R., Trabulsi L. R. Relationship among enterotoxigenic phenotypes, serotypes, and sources of strains in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):24–27. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.24-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo M. R., Trabulsi L. R. Correlation between biochemical and serological characteristics of Escherichia coli and results of the Serény test. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):419–421. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.419-421.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H., Sedgwick M. I., Evans N., Turner P. J., George R. H., McNeish A. S. Adherence of an enteropathogenic strain of Escherichia coli to human intestinal mucosa is mediated by a colicinogenic conjugative plasmid. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):393–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.393-402.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]