Abstract
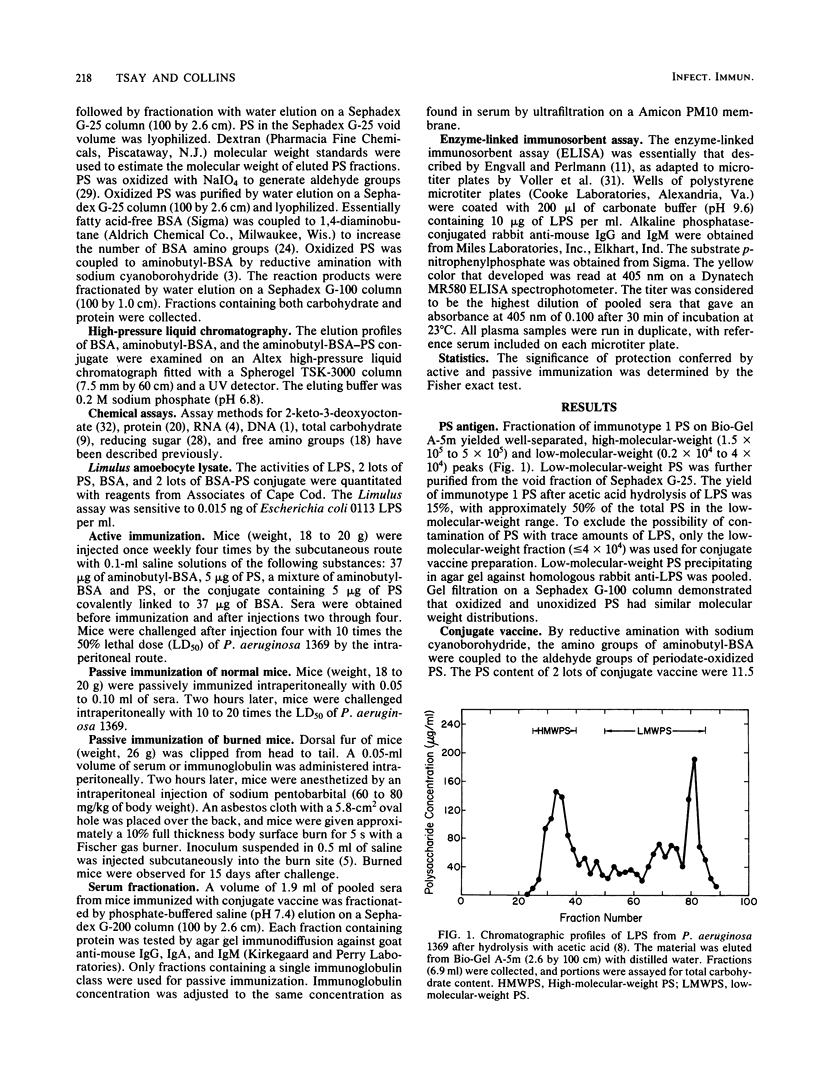
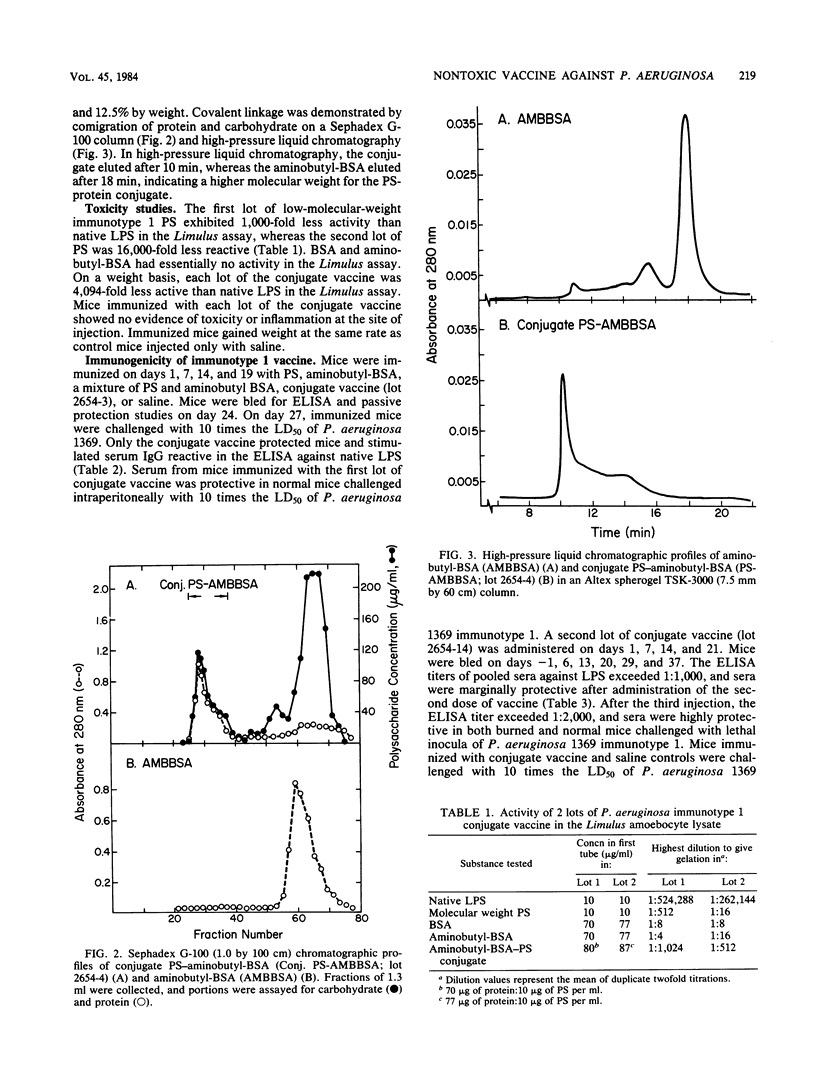
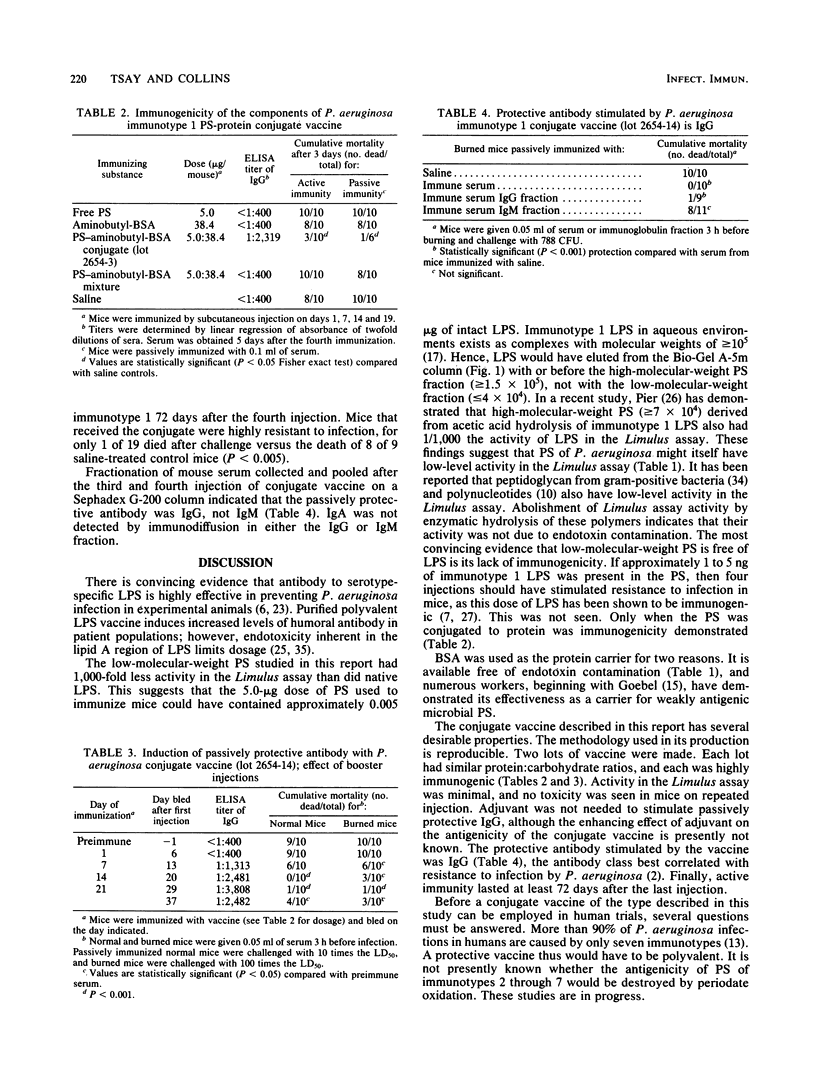
Acid treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype 1 lipopolysaccharide generated a low-molecular-weight polysaccharide fraction that was detectable in agar gel immunodiffusion but did not induce antibodies or resistance to infection in mice. The polysaccharide was treated with periodate to generate additional aldehyde groups. Oxidized polysaccharide was covalently coupled by reductive amination to 1,4-diaminobutyl-derivatized bovine serum albumin. Physical properties of the conjugate were characterized by gel filtration and high-pressure liquid chromatography. The gelation activity of the conjugate in the Limulus amoebocyte lysate assay was 4,000-fold less than native lipopolysaccharide by weight. Mice immunized with the conjugate resisted challenge with P. aeruginosa immunotype 1 that killed 90% of mice immunized with saline. Immunization with the conjugate vaccine induced humoral immunoglobulin G that passively protected normal and burned mice. These results indicate that conjugation of nonimmunogenic polysaccharide antigen of P. aeruginosa restores immunogenicity similar to that of native lipopolysaccharide without restoring endotoxicity inherent in lipopolysaccharide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G. N., Scaletta C., Vaughan J. H. Modified diphenylamine reaction for increased sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):547–549. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson A. B., Michael J. G. Contribution of humoral and cellular factors to the resistance to experimental infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. I. Interaction between immunoglobulins, heat-labile serum factors, and phagocytic cells in the killing of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):462–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.462-467.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. S., Roby R. E. Anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa activity of an intravenous human IgG preparation in burned mice. J Trauma. 1983 Jun;23(6):530–534. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198306000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in a murine burn wound sepsis model by passive transfer of antitoxin A, antielastase, and antilipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1072–1079. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1072-1079.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Protection against fatal Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn wound sepsis by immunization with lipopolysaccharide and high-molecular-weight polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):795–799. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.795-799.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewry D. T., Symes K. C., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. Studies of polysaccharide fractions from the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa N.C.T.C. 1999. Biochem J. 1975 Jul;149(1):93–106. doi: 10.1042/bj1490093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Nonspecificity of the limulus amebocyte lysate test: positive reactions with polynucleotides and proteins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):349–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. W. A polyvalent human gamma-globulin immune to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: passive protection of mice against lethal infection. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S181–S185. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. W., Devlin H. B., Gnabasik F. J. New immunotype schema for Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on protective antigens. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):835–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.835-836.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick M. R., Cluff L. E. Pseudomonas bacteremia. Review of 108 cases. Am J Med. 1976 Apr;60(4):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90716-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer G. G., Milazzo F. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide: an uncoupler of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jun;21(6):877–883. doi: 10.1139/m75-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton D., Riley D. A. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):727–733. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E., Colescott R. L., Bossinger C. D., Cook P. I. Color test for detection of free terminal amino groups in the solid-phase synthesis of peptides. Anal Biochem. 1970 Apr;34(2):595–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler R., White A. Detection of IgG antibodies to type-specific Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharides by solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):112–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus W. F., Goodwin C. W., Mason A. D., Jr, Pruitt B. A., Jr Burn wound infection. J Trauma. 1981 Sep;21(9):753–756. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198109000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. R., Kessel R. W., Young V. M., Fiset P. Role of nonagglutinating antibody in the protracted immunity of vaccinated mice to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):905–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.905-913.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance F. C., Hines J. L., Fulton R. E., Bornside G. H. Treatment of experimental burn wound sepsis by postburn immunization with polyvalent Pseudomonas antigen. Surgery. 1970 Jul;68(1):248–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Reynolds H. Y., Wood R. E., Robinson R. A., Levine A. S. Use of a Pseudomonas Aeruginosa vaccine in pateints with acute leukemia and cystic fibrosis. Am J Med. 1975 May;58(5):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90498-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B. Safety and immunogenicity of high molecular weight polysaccharide vaccine from immunotype 1 Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):303–308. doi: 10.1172/JCI110453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Sidberry H. F., Sadoff J. C. Protective immunity induced in mice by immunization with high-molecular-weight polysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):919–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.919-925.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porro M., Viti S., Antoni G., Neri P. Modifications of the Park-Johnson ferricyanide submicromethod for the assay of reducing groups in carbohydrates. Anal Biochem. 1981 Dec;118(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90586-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Wilson D. V. A simple method for coupling proteins to insoluble polysaccharides. Immunology. 1971 Jun;20(6):1061–1065. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C., Greene W. H., Young V. M., Wiernik P. H. Significance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the patient with leukemia or lymphoma. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S24–S31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D., Huldt G., Engvall E. A microplate method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and its application to malaria. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51(2):209–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARAVDEKAR V. S., SASLAW L. D. A sensitive colorimetric method for the estimation of 2-deoxy sugars with the use of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1945–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildfeuer A., Heymer B., Schleifer K. H., Haferkamp O. Investigations on the specificity of the Limulus test for the detection of endotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):867–871. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.867-871.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Meyer R. D., Armstrong D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in cancer patients. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Oct;79(4):518–527. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-4-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


