Abstract
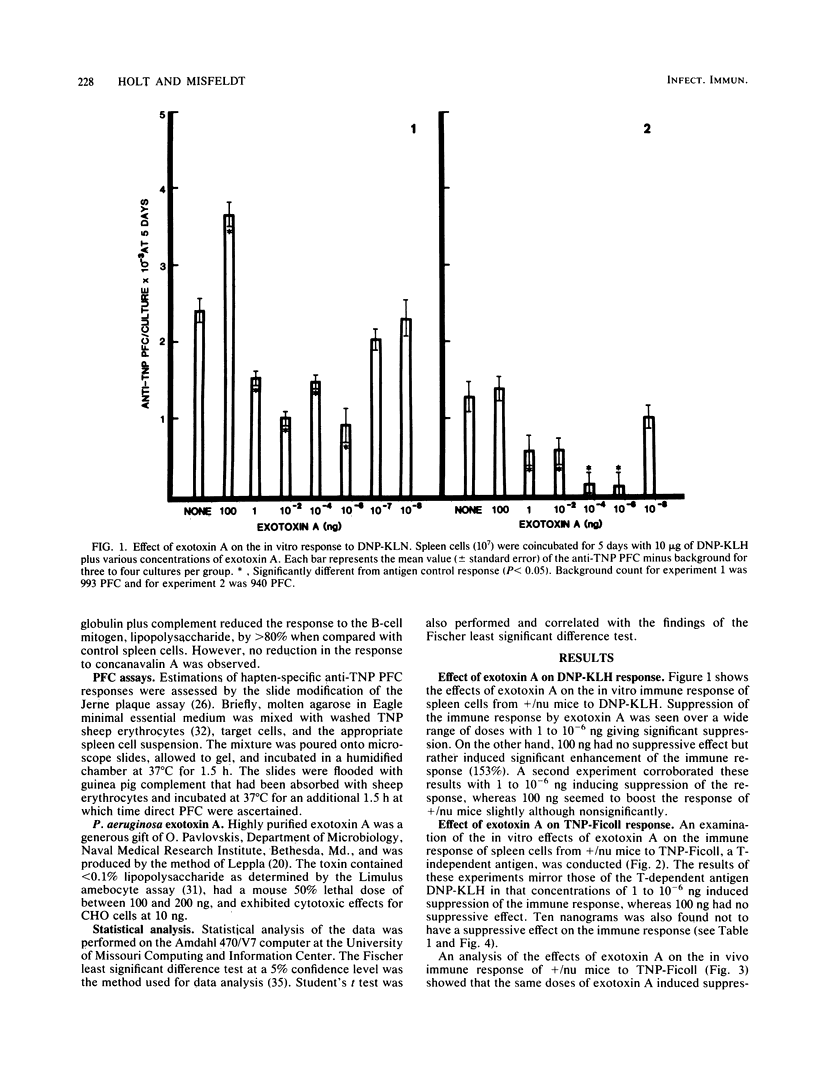
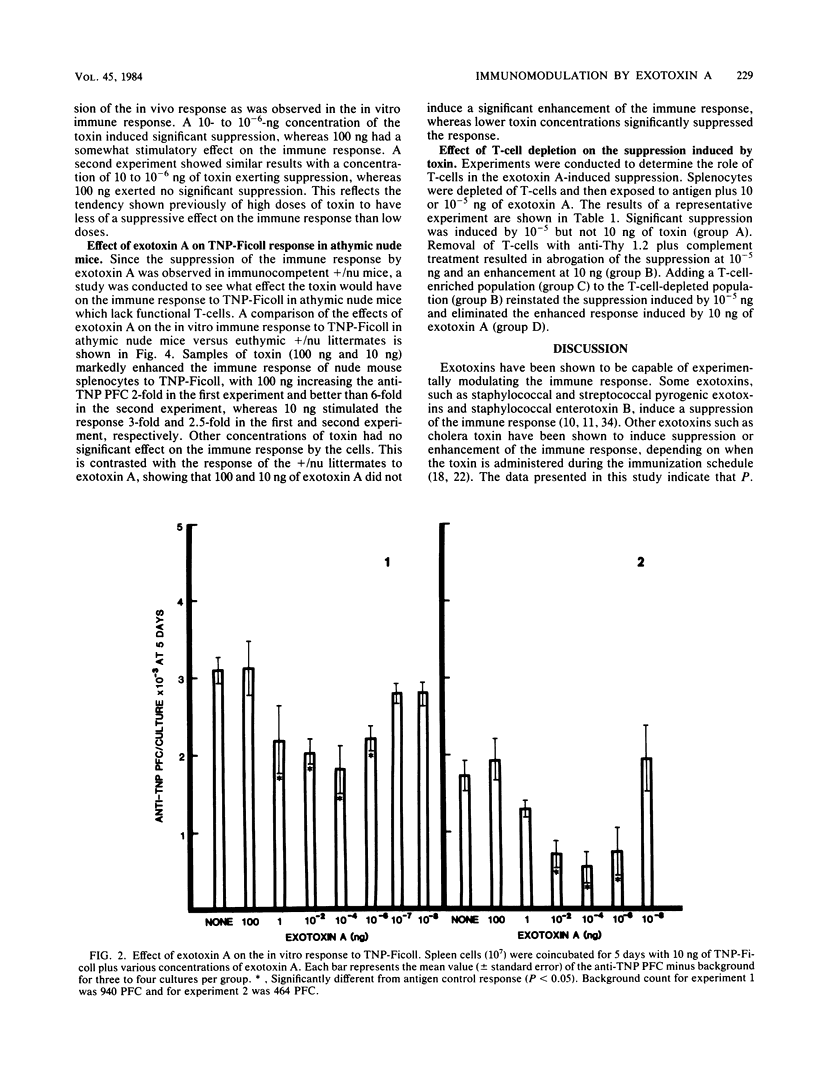
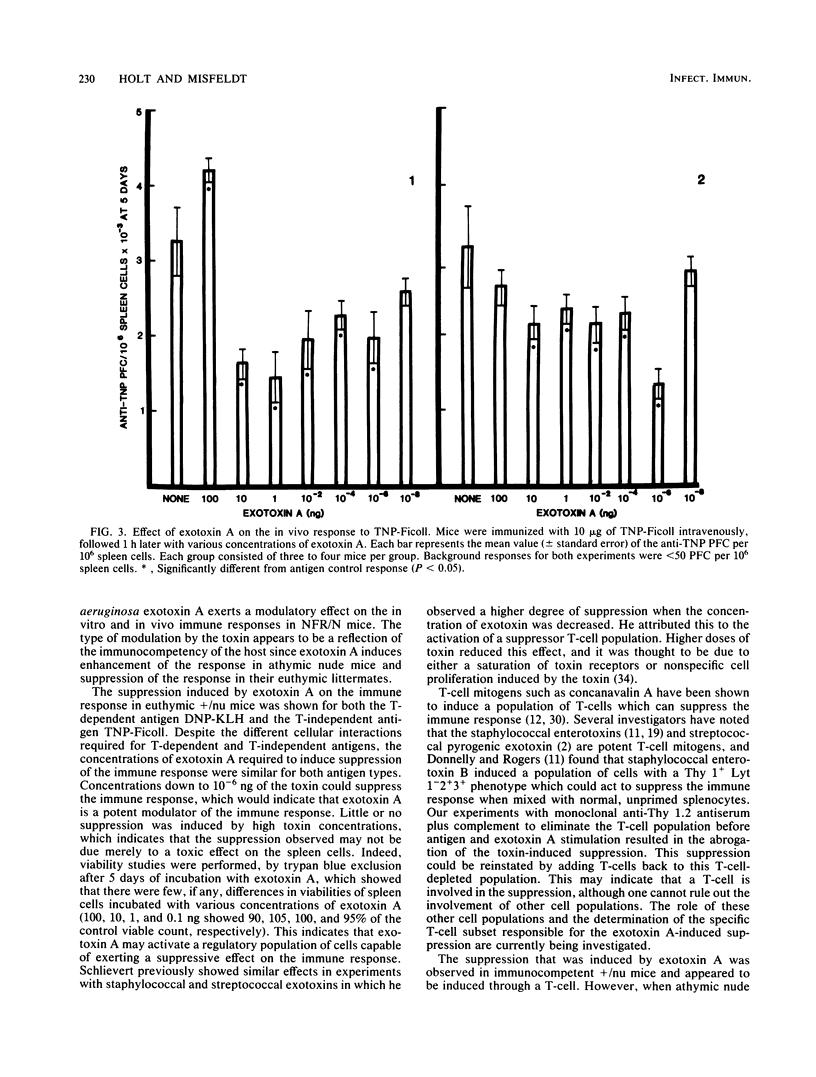
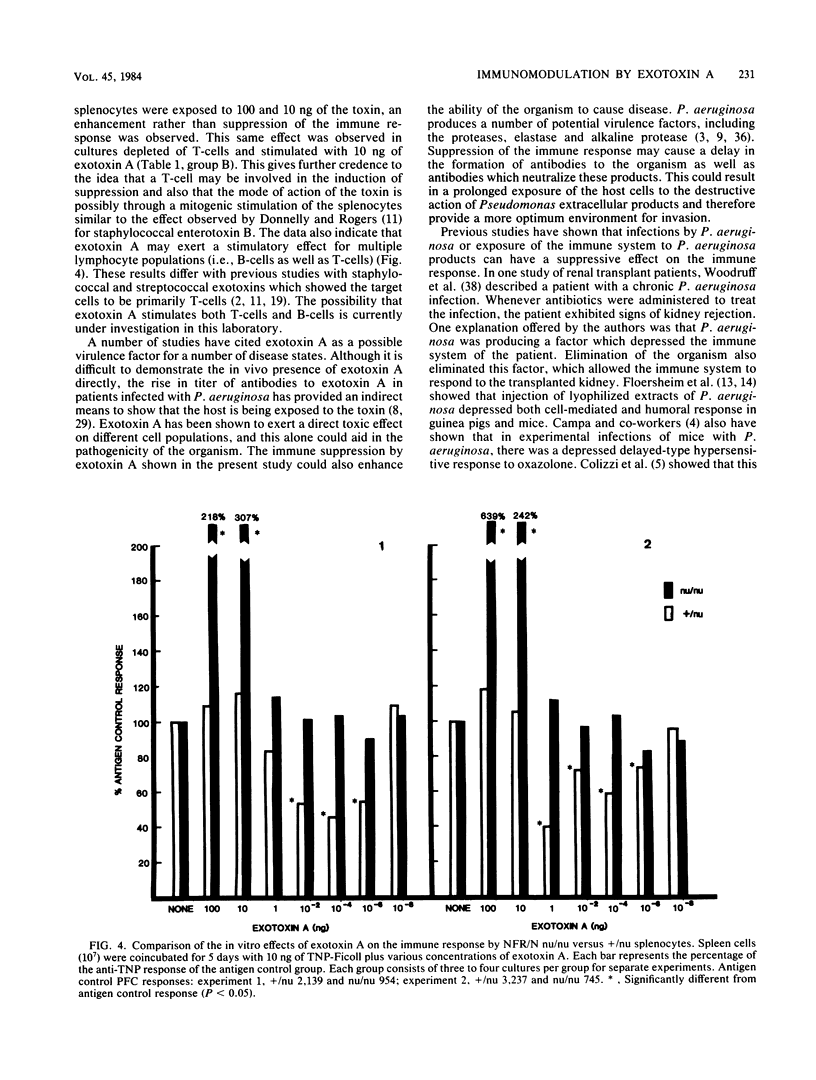
Pseudomonas exotoxin A has been implicated as a possible virulence factor in Pseudomonas infections. This toxin has a direct cytotoxic effect on a number of cell types, including macrophages and their precursors, and therefore may affect other cells of the immune system. NFR/N(H-2q) (+/nu or nu/nu) mice were immunized with either T-dependent or T-independent antigens along with various doses of exotoxin A. The immune response was then assayed by a modification of the Jerne plaque assay. Exotoxin A induced a dose-dependent suppression of the in vitro and in vivo immune responses to T-dependent and T-independent antigens in immunocompetent +/nu mice. However, in NFR/N nu/nu mice, suppression of the immune response to the T-independent antigen trinitrophenylated-Ficoll was not observed. Instead, a marked enhancement of the response was observed at doses of 100 and 10 ng of exotoxin A. Removal of T-cells with anti-Thy 1.2 antiserum plus complement before antigen and exotoxin A stimulation in +/nu mice results in abrogation of the suppression. These data suggest that Pseudomonas exotoxin A exerts an effect on both B- and T-lymphocyte populations to modulate the immune response and that this activity may be one facet of the pathogenic effects of this toxin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker N. R. Role of exotoxin A and proteases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in respiratory tract infections. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Feb;28(2):248–255. doi: 10.1139/m82-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsumian E. L., Schlievert P. M., Watson D. W. Nonspecific and specific immunological mitogenicity by group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):681–688. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.681-688.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood L. L., Stone R. M., Iglewski B. H., Pennington J. E. Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A and elastase as virulence factors in acute lung infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):198–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.198-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campa M., Garzelli C., Ferrannini E., Falcone G. Evidence for suppressor cell activity associated with depression of contact sensitivity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infected mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):355–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colizzi V., Campa M., Garzelli C., Falcone G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection depresses contact sensitivity to oxazolone by enhancing suppressor cell activity. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1979 Aug;167(3):181–188. doi: 10.1007/BF02121184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Effect of diphtheria toxin on protein synthesis: inactivation of one of the transfer factors. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):83–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H., Sokol P. A. Evidence for the role of toxin A in the pathogenesis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in humans. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):538–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in a murine burn wound sepsis model by passive transfer of antitoxin A, antielastase, and antilipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1072–1079. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1072-1079.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham C. M., Watson D. W. Suppression of antibody response by group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin and characterization of the cells involved. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):470–476. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.470-476.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly R. P., Rogers T. J. Immunosuppression induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 1;72(1):166–177. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton R. W. Inhibitory and stimulatory effects of concanavalin A on the response of mouse spleen cell suspensions to antigen. I. Characterization of the inhibitory cell activity. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1445–1460. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floersheim G. L., Borel J. F., Wiesinger D., Brundell J., Kis Z. Antiarthritic and immunosuppressive effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Agents Actions. 1972;2(5):231–235. doi: 10.1007/BF02087047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floersheim G. L., Hopff W. H., Gasser M., Bucher K. Impairment of cell-mediated immune responses by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Aug;9(2):241–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kateley J. R., Kasarov L., Friedman H. Modulation of in vivo antibody responses by cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Biological effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin A on human peripheral lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.62-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Extracellular toxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S94–S99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons S. F., Friedman H. Differential effects of cholera toxin pre-treatment on in vitro vs. in vivo immunocyte responses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Apr;157(4):631–635. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Fink P., Gridley T., Raulet D. H., Bevan M. J., Gefter M. L. Properties and applications of monoclonal antibodies directed against determinants of the Thy-1 locus. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2491–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1139/m77-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L., Hanna E. E. Deregulation of mouse antibody-forming cells by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin (SPE). IV. Fractionation of a T-cell subpopulation which generates SPE-induced deregulation of anti-TNP PFC responses. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jan 1;57(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Iglewski B. H., Pollack M. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A in experimental mouse infections: adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of elongation factor 2. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.29-33.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Anderson S. E., Jr Toxicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A for human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1092–1096. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1092-1096.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Young L. S. Protective activity of antibodies to exotoxin A and lipopolysaccharide at the onset of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):276–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich R. R., Pierce C. W. Biological expressions of lymphocyte activation. II. Generation of a population of thymus-derived suppressor lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):649–659. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg M. B., Pratt K. L. Antitrinitrophenyl (TNP) plaque assay. Primary response of Balb/c mice to soluble and particulate immunogen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):575–581. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saelinger C. B., Snell K., Holder I. A. Experimental studies on the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: direct evidence for toxin production during Pseudomonas infection of burned skin tissues. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):555–561. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Activation of murine T-suppressor lymphocytes by group A streptococcal and staphylococcal pyurogenic exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):876–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.876-880.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell K., Holder I. A., Leppla S. A., Saelinger C. B. Role of exotoxin and protease as possible virulence factors in experimental infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.839-845.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart R. K., Pollack M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A inhibits proliferation of human bone marrow progenitor cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):206–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.206-211.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., Nolan B., Robson J. S., MacDonald M. K. Renal transplantation in man. Experience in 35 cases. Lancet. 1969 Jan 4;1(7584):6–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90982-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. The role of exotoxins in the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):626–630. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


