Abstract
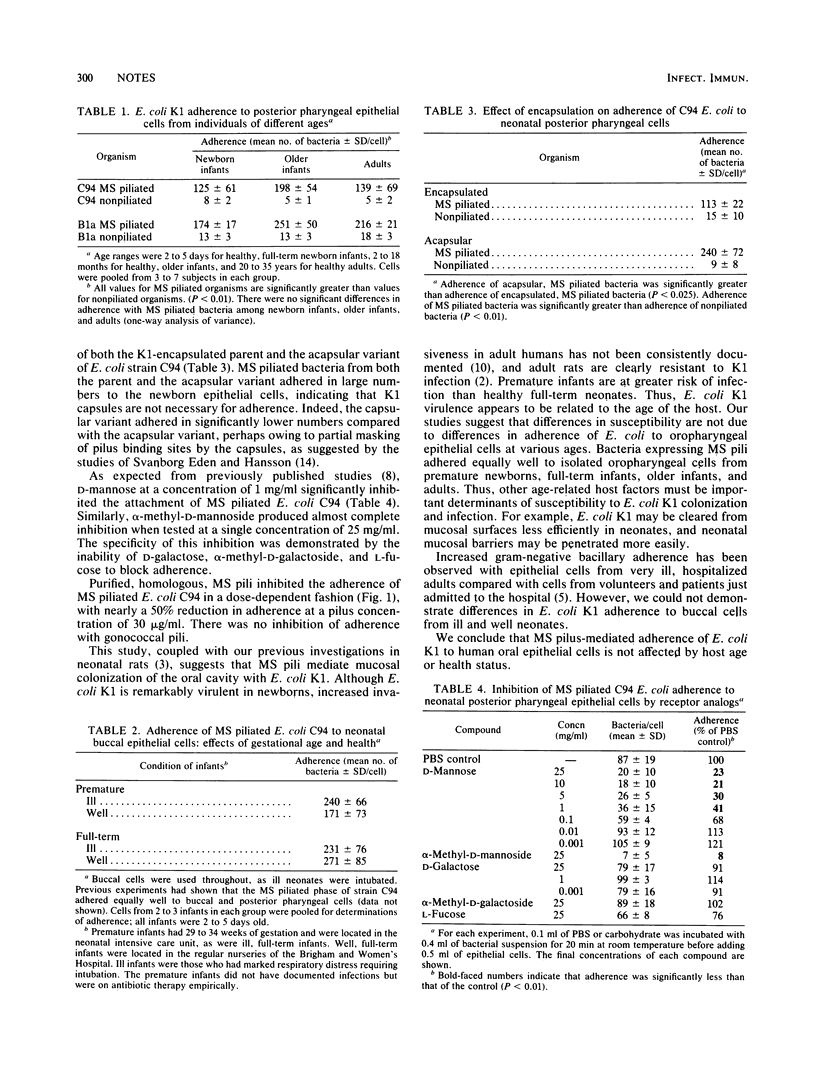
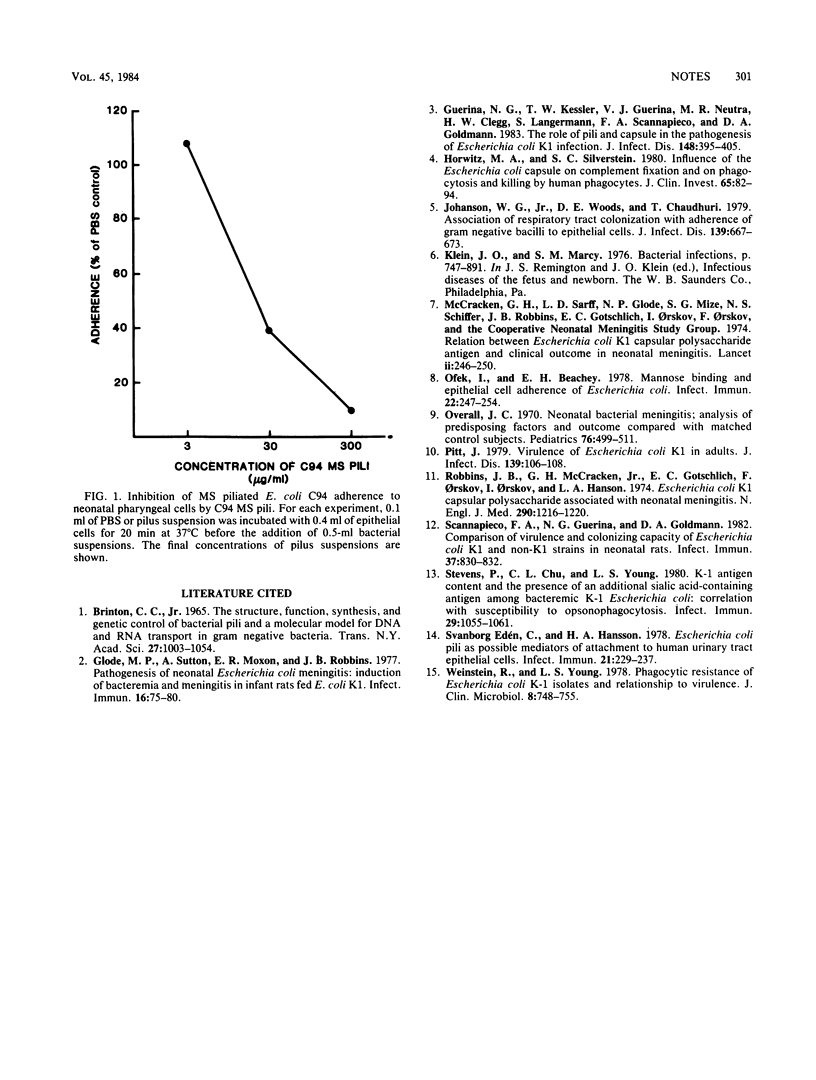
We examined the effect of host age and health status on the adherence of mannose-sensitive piliated Escherichia coli K1 to human oral epithelial cells. Mannose-sensitive piliated bacteria adhered in comparable numbers to newborn, older infant, and adult cells (125 +/- 61, 198 +/- 54, and 139 +/- 69 bacteria per cell, respectively). Prematurity and serious illness did not alter adherence in newborns. The increased susceptibility of premature newborns to E. coli K1 cannot be explained by enhanced epithelial cell adherence.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Hansson H. A. Escherichia coli pili as possible mediators of attachment to human urinary tract epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):229–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.229-237.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode M. P., Sutton A., Moxon E. R., Robbins J. B. Pathogenesis of neonatal Escherichia coli meningitis: induction of bacteremia and meningitis in infant rats fed E. coli K1. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.75-80.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Kessler T. W., Guerina V. J., Neutra M. R., Clegg H. W., Langermann S., Scannapieco F. A., Goldmann D. A. The role of pili and capsule in the pathogenesis of neonatal infection with Escherichia coli K1. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):395–405. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Influence of the Escherichia coli capsule on complement fixation and on phagocytosis and killing by human phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):82–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI109663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Jr, Woods D. E., Chaudhuri T. Association of respiratory tract colonization with adherence of gram-negative bacilli to epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):667–673. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Sarff L. D., Glode M. P., Mize S. G., Schiffer M. S., Robbins J. B., Gotschlich E. C., Orskov I., Orskov F. Relation between Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide antigen and clinical outcome in neonatal meningitis. Lancet. 1974 Aug 3;2(7875):246–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Mannose binding and epithelial cell adherence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):247–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.247-254.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall J. C., Jr Neonatal bacterial meningitis. Analysis of predisposing factors and outcome compared with matched control subjects. J Pediatr. 1970 Apr;76(4):499–511. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80399-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt J. Virulence of Escherichia coli K1 in adults. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):106–108. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scannapieco F. A., Guerina N. G., Goldmann D. A. Comparison of virulence and colonizing capacity of Escherichia coli K1 and non-K1 strains in neonatal rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):830–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.830-832.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Chu C. L., Young L. S. K-1 antigen content and the presence of an additional sialic acid-containing antigen among bacteremic K-1 Escherichia coli: correlation with susceptibility to opsonophagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1055–1061. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1055-1061.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R., Young L. S. Phagocytic resistance of Escherichia coli K-1 isolates and relationship to virulence. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):748–755. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.748-755.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


