Abstract
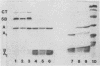
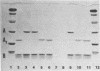
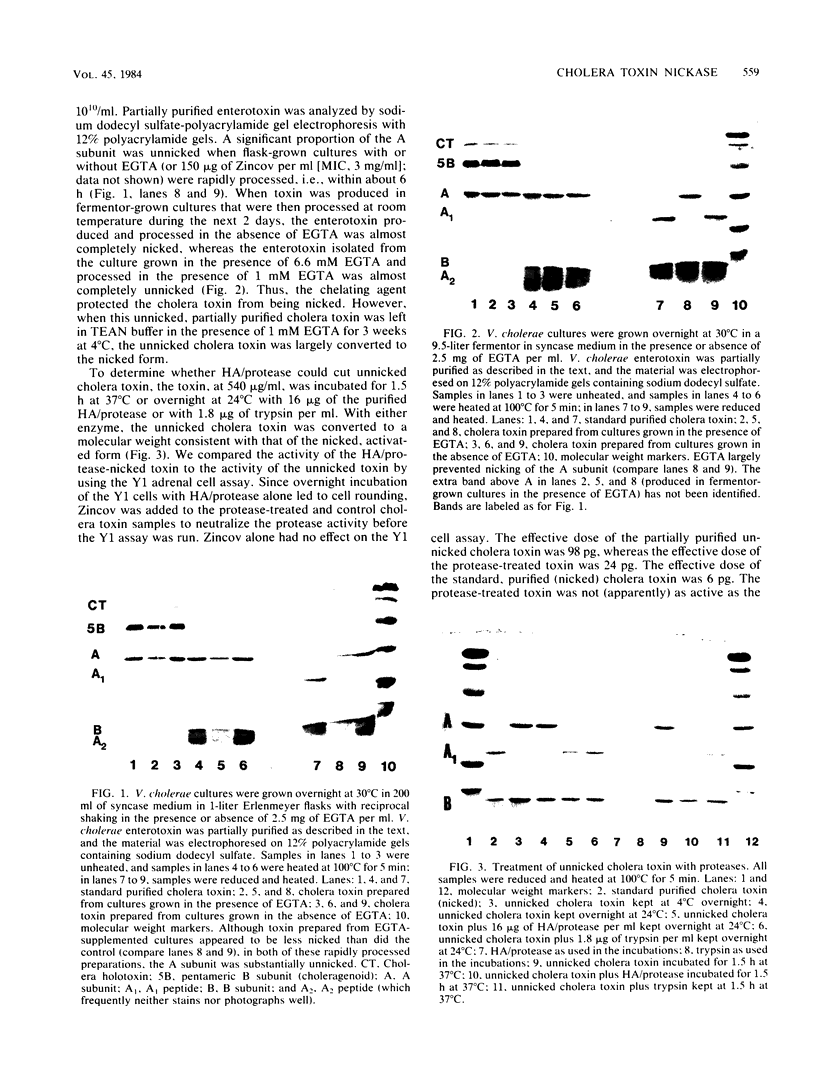
Unnicked cholera enterotoxin was isolated from culture supernatants of Vibrio cholerae 569B by either rapid processing of flask-grown cultures or by growing and processing fermentor cultures in the presence of ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetra acetic acid, an inhibitor of the previously described V. cholerae hemagglutinin/protease. When unnicked cholera enterotoxin was incubated with purified hemagglutinin/protease, the unnicked A subunit was converted to a molecular weight consistent with that of the A1 subunit as demonstrated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and its specific activity for Y1 adrenal cells increased.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth B. A., Boesman-Finkelstein M., Finkelstein R. A. Vibrio cholerae soluble hemagglutinin/protease is a metalloenzyme. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):639–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.639-644.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Boesman-Finkelstein M., Holt P. Vibrio cholerae hemagglutinin/lectin/protease hydrolyzes fibronectin and ovomucin: F.M. Burnet revisited. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1092–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Fujita K., LoSpalluto J. J. Procholeragenoid: an aggregated intermediate in the formation of choleragenoid. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1043–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Hanne L. F. Purification and characterization of the soluble hemagglutinin (cholera lectin)( produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1199–1208. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1199-1208.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera. Preparation and isolation of choleragen and choleragenoid. J Exp Med. 1969 Jul 1;130(1):185–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Monospecific equine antiserum against cholera exo-enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Dec;2(6):691–697. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.6.691-697.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Rappaport R. S. Origin of the enzymatically active A1 fragment of cholera toxin. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):674–680. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Finkelstein R. A., Capra J. D. Subunit structure and N-terminal amino acid sequence of the three chains of cholera enterotoxin. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jul;13(7):605–611. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Enzymic activity of cholera toxin. II. Relationships to proteolytic processing, disulfide bond reduction, and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5855–5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]