BIOPHYSICS Correction for “Direct demonstration of the cross-bridge recovery stroke in muscle thick filaments in aqueous solution by using the hydration chamber,” by Haruo Sugi, Hiroki Minoda, Yuhri Inayoshi, Fumiaki Yumoto, Takuya Miyakawa, Yumiko Miyauchi, Masaru Tanokura, Tsuyoshi Akimoto, Takakazu Kobayashi, Shigeru Chaen, and Seiryo Sugiura, which appeared in issue 45, November 11, 2008, of Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (105:17396–17401; first published November 5, 2008; 10.1073/pnas.0809581105).
The authors note that due to a printer's error, the locants were transposed in Fig. 1 C and D. The panels are intended to be viewed clockwise from A. The corrected figure and its legend appear below.
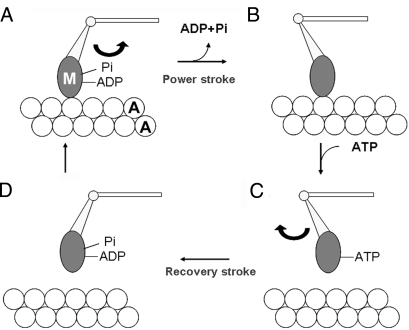
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of attachment–detachment cycle between the cross-bridge (M) extending from the thick filament and actin (A) in the thin filament. M in the form of M·ADP·Pi attaches to actin to exert a power stroke, associated with release of Pi and ADP (from A to B). After the end of the power stroke, M remains attached to A, taking its postpower stroke configuration (B). Upon binding with ATP, M detaches from A to exert a recovery stroke, associated with reaction M·ATP → M·ADP·Pi (from C to D). M·ADP·Pi again attaches to A to again exert a power stroke (from D to A). M is assumed to attach rigidly to A, whereas its power and recovery strokes are assumed to result from swinging of the lever arm around the hinge.