Abstract
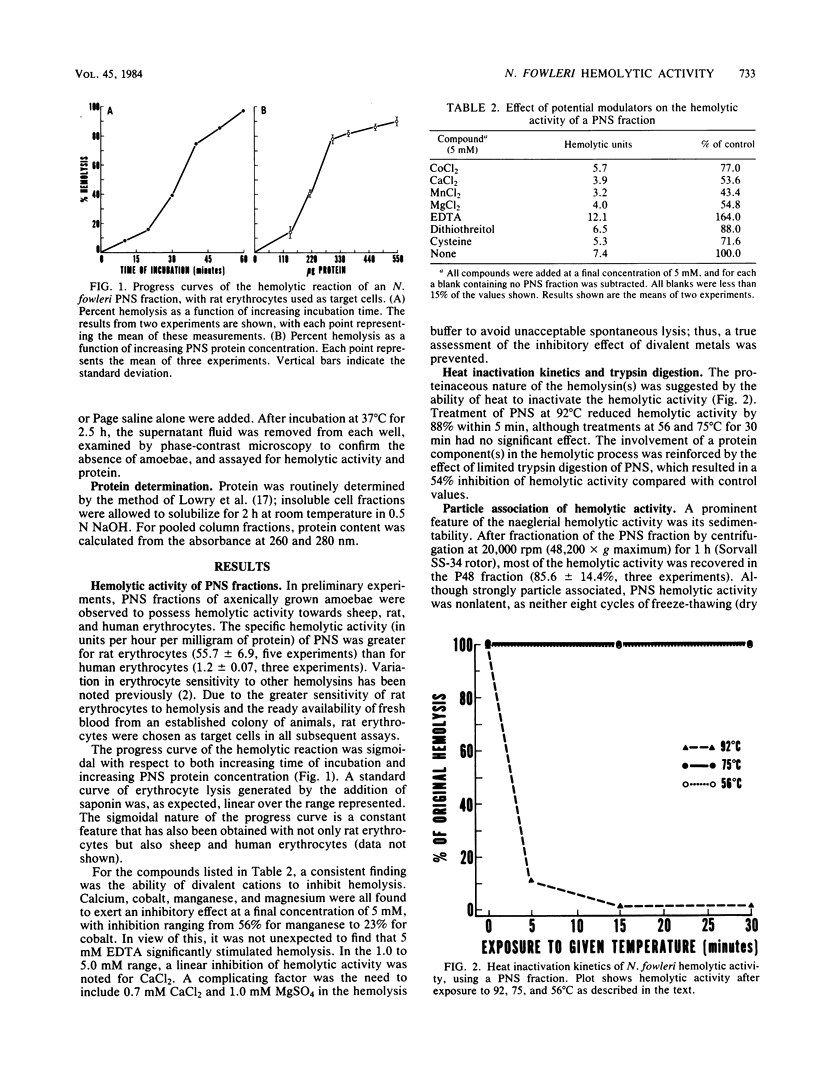
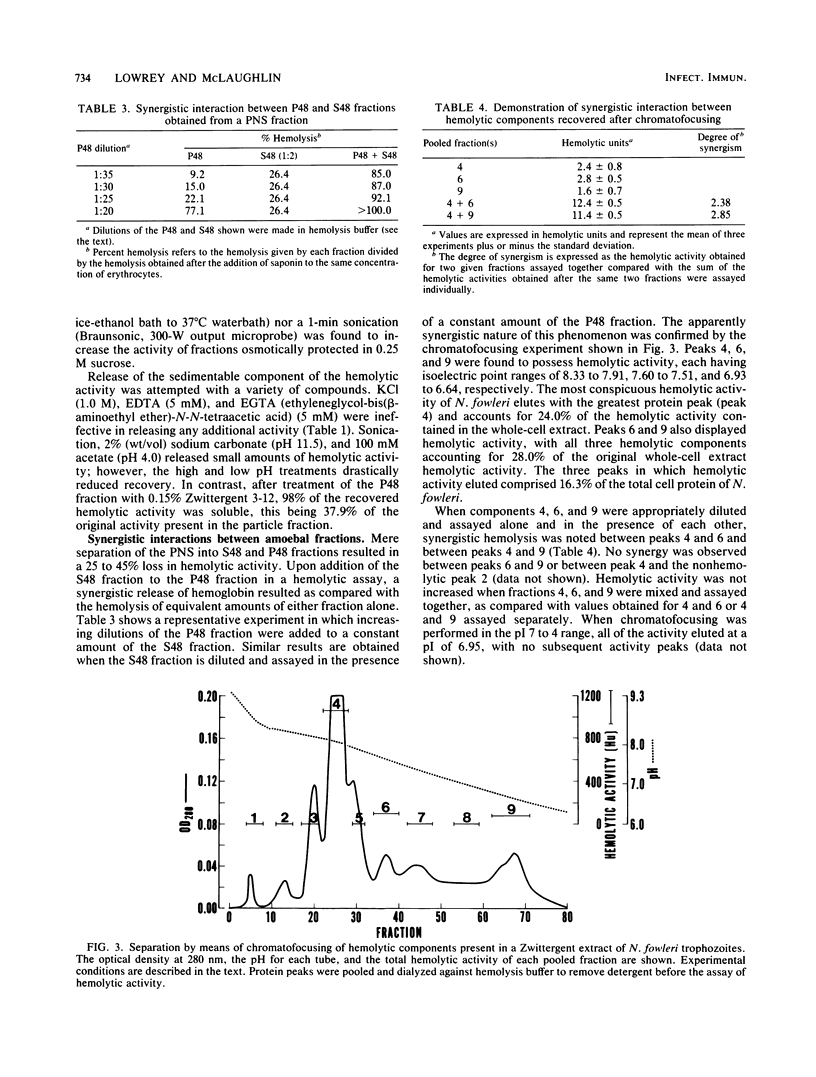
A hemolytic activity associated with postnuclear supernatant fractions of Naegleria fowleri has been partially characterized in an attempt to isolate cytolytic molecules that may participate in naeglerial cytopathogenicity. Hemolysis by naeglerial postnuclear supernatant fractions was sensitive to heat and trypsin hydrolysis, and was inhibited by divalent cations. The majority of the hemolytic activity was nonlatent and associated with a particle fraction sedimenting at 48,000 X g (maximum) for 1 h. This particle-associated hemolytic activity appears to be membrane associated, as high salt concentration, chelating agents, and pH extremes were ineffective in solubilizing the hemolytic activity, whereas treatment with 0.15% Zwittergent 3-12, a dipolar ionic detergent, results in 98% release of the sedimentable hemolysin. The sigmoidal nature of the progress curve of postnuclear supernatant hemolysis, as well as synergistic interactions between fractions of amoebal whole cell extracts, suggests that the hemolytic activity has a multicomponent nature, with at least two and possibly three components participating in the hemolytic event. The significance of these findings in the context of naeglerial cytopathogenicity is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown T. Inhibition by amoeba-specific antiserum and by cytochalasin B of the cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri in mouse embryo-cell cultures. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Aug;12(3):355–362. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. Observations by immunofluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy on the cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri in mouse embryo-cell cultures. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Aug;12(3):363–371. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. Observations by light microscopy on the cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri in mouse embryo-cell cultures. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Aug;11(3):249–259. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-3-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Wassom D. L., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., David J. R. Damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni induced directly by eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):221–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONDREA E., DEVRIES A., MAGER J. HEMOLYSIS AND SPLITTING OF HUMAN ERYTHROCYTE PHOSPHOLIPIDS BY SNAKE VENOMS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 24;84:60–73. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. L. Pathogenesis of pathogenic Naegleria amoeba. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1979;26(3):195–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. Differences in virulence of Naegleria fowleri. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1979 Oct;27(8):453–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnebacke T. H., Schuster F. L. The nature of a cytopathogenic material present in amebae of the genus Naegleria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 May;26(3):412–421. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J., Franson R. C., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Schneider A., Harris L. Separation and purification of a potent bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and a closely associated phospholipase A2 from rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Observations on their relationship. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11000–11009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Bee and wasp venoms. Science. 1972 Jul 28;177(4046):314–322. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4046.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hysmith R. M., Franson R. C. Degradation of human myelin phospholipids by phospholipase-enriched culture media of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 14;712(3):698–701. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hysmith R. M., Franson R. C. Elevated levels of cellular and extracellular phospholipases from pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 15;711(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John D. T. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis and the biology of Naegleria fowleri. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:101–123. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Poisson M. A., Rein M. F. Beta-hemolytic activity of Trichomonas vaginalis correlates with virulence. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1291–1295. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1291-1295.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch E. C., Rosenberg I. M., Gitler C. An ion-channel forming protein produced by Entamoeba histolytica. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):801–804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F. M., Patterson M., John D. T., Bradley S. G. Cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria gruberi for established mammalian cell cultures. J Parasitol. 1982 Dec;68(6):1110–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F., John D. T. Cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri for rat neuroblastoma cell cultures: scanning electron microscopy study. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1214–1217. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1214-1217.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. Secretion of acid hydrolases and its intracellular source in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Cell Biol. 1972 Feb;52(2):478–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.2.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Antibacterial activity of cationic proteins from human granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1118–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page F. C. Taxonomic criteria for limax amoebae, with descriptions of 3 new species of Hartmannella and 3 of Vahlkampfia. J Protozool. 1967 Aug;14(3):499–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1967.tb02036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said-Fernández S., López-Revilla R. Subcellular distribution and stability of the major hemolytic activity of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Z Parasitenkd. 1982;67(3):249–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00927659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnyder J., Baggiolini M. Role of phagocytosis in the activation of macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1449–1457. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weik R. R., John D. T. Agitated mass cultivation of Naegleria fowleri. J Parasitol. 1977 Oct;63(5):868–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. M., Karr S. L., Jr, Chow C. K. Changes in the virulence of Naegleria fowleri maintained in vitro. J Parasitol. 1977 Oct;63(5):872–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Young T. M., Lu L. P., Unkeless J. C., Cohn Z. A. Characterization of a membrane pore-forming protein from Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1677–1690. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman N., Cafmeyer N., Hudson R. A. Use of erythrocyte hemolysis kinetics in the purification of complex cardiotoxin mixtures. Toxicon. 1982;20(2):517–520. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



