Abstract
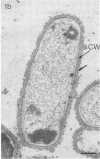
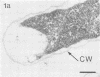
Effective serum-mediated killing of sensitive gram-negative bacteria requires all the complement components. In the preimmune phase the antibody-independent interaction of the first component of complement, C1, with the bacteria might be especially important. Electron microscopic studies showed that the C1 subcomponent C1q binds only to the serum-sensitive R form of Salmonella minnesota and not to the serum-resistant S form.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz S. J., Isliker H. Antibody-independent interactions between Escherichia coli J5 and human complement components. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1748–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Bullivant S., Gilula N. B., Karnovsky M. J., Moor H., Mühlethaler K., Northcote D. H., Packer L., Satir B., Satir P. Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):54–56. doi: 10.1126/science.1166299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Loos M. Antibody-independent binding of the first component of complement (C1) and its subcomponent C1q to the S and R forms of Salmonella minnesota. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1138–1144. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1138-1144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Loos M. Killing of the S and Re forms of Salmonella minnesota via the classical pathway of complement activation in guinea-pig and human sera. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):547–556. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golecki J. R., Oelze J. Differences in the architecture of cytoplasmic and intracytoplasmic membranes of three chemotrophically and phototrophically grown species of the Rhodospirillaceae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):781–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.781-788.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Bitter-Suermann D., Dierich M. Interaction of the first (C1), the second (C2) and the fourth (C4) component of complement with different preparations of bacterial lipopolysaccharides and with lipid A. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):935–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Wellek B., Thesen R., Opferkuch W. Antibody-independent interaction of the first component of complement with Gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):5–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.5-9.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Kline L. F. Activation of the classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]