Abstract
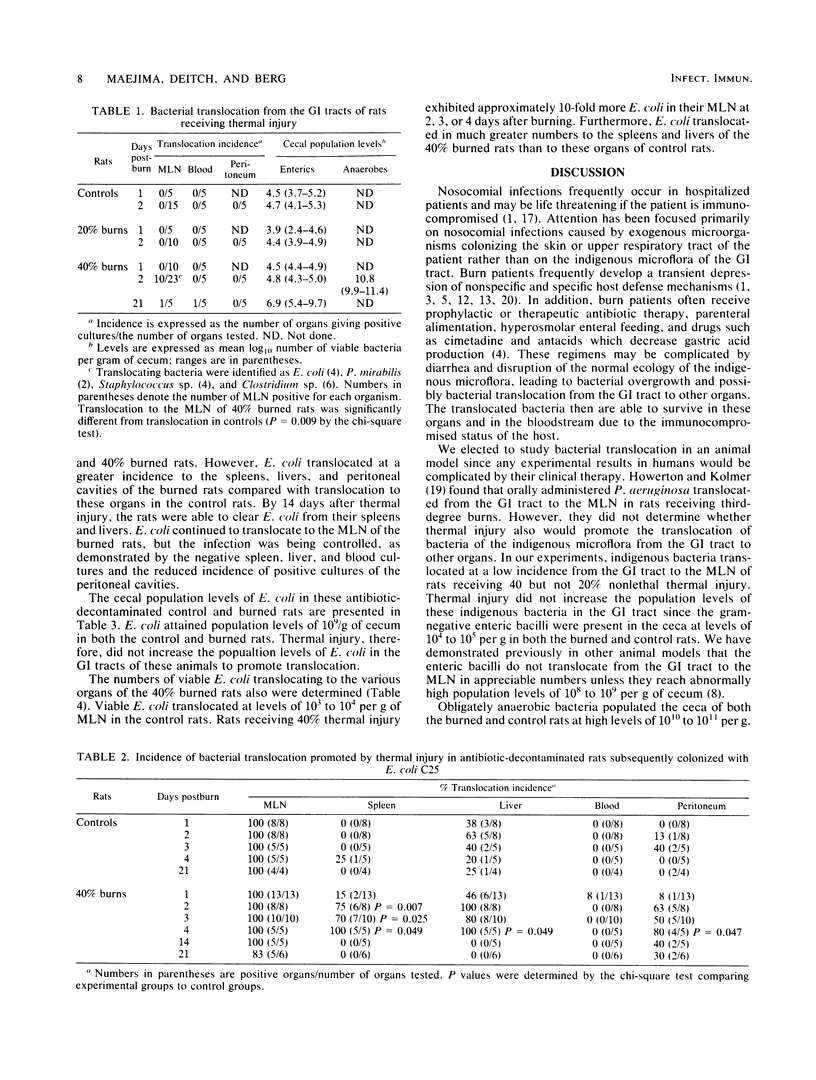
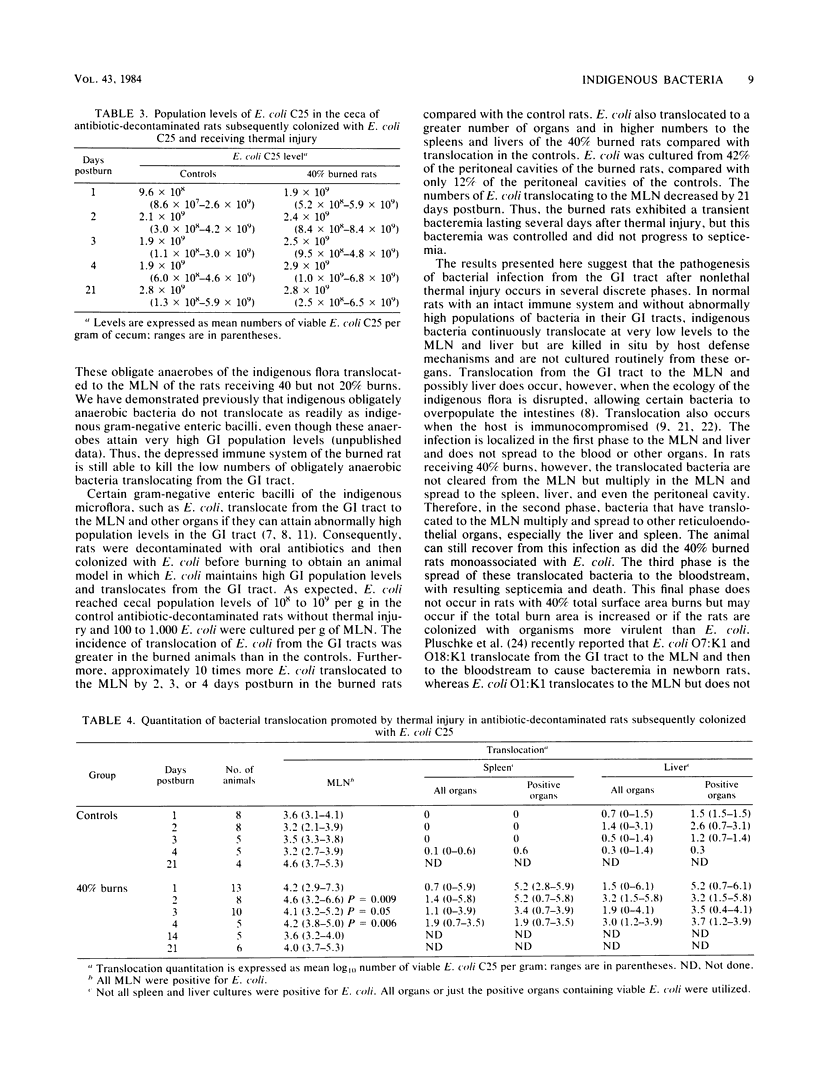
Rats receiving nonlethal thermal burns over 20 or 40% of their total body surface area were tested at various intervals for the translocation of indigenous bacteria from their gastrointestinal tracts to their mesenteric lymph nodes, peritoneal cavities, and bloodstreams. No indigenous bacteria were cultured from these organs of control rats or from rats receiving 20% burns. However, 44% of the rats receiving 40% burns exhibited viable Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Staphylococcus sp. and Clostridium sp. in their mesenteric lymph nodes 2 days after thermal injury. Bacterial translocation after burn stress also was tested in antibiotic-decontaminated rats monoassociated with E. coli. E. coli attained population levels in these animals of 10(8) to 10(9) per g cecum. E. coli translocated to 100% of the mesenteric lymph nodes of both the control and 40% burned rats. However, E. coli translocated at a greater incidence to the spleens, livers, and peritoneal cavities of the burned rats compared with translocation to these organs in control rats. The numbers of E. coli translocating to the mesenteric lymph nodes, spleens, and livers also were greater in the 40% burned rats than in control rats. By 14 days after thermal injury, the rats were able to clear E. coli from their spleens and livers, and the infection remained localized in the mesenteric lymph nodes. These results support the concept that the indigenous gastrointestinal flora or exogenous organisms colonizing the gastrointestinal tract are potential sources of septicemia after thermal injury.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W., Ogle C. K., Stinnett J. D., Macmillan B. G. A sequential, prospective analysis of immunologic abnormalities and infection following severe thermal injury. Ann Surg. 1978 Dec;188(6):809–816. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197812000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aranki A., Freter R. Use of anaerobic glove boxes for the cultivation of strictly anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1329–1334. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arturson G., Högman C. F., Johansson S. G., Killander J. Changes in immunoglobulin levels in severely burned patients. Lancet. 1969 Mar 15;1(7594):546–548. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91957-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Miller C. L., Trunkey D. D. Predicting fatal sepsis in burn patients. J Trauma. 1979 Sep;19(9):641–648. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197909000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D. Antagonism among the normal anaerobic bacteria of the mouse gastrointestinal tract determined by immunofluorescence. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1066–1073. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1066-1073.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Garlington A. W. Translocation of certain indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the mesenteric lymph nodes and other organs in a gnotobiotic mouse model. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):403–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.403-411.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D. Inhibition of Escherichia coli translocation from the gastrointestinal tract by normal cecal flora in gnotobiotic or antibiotic-decontaminated mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1073–1081. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1073-1081.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Owens W. E. Inhibition of translocation of viable Escherichia coli from the gastrointestinal tract of mice by bacterial antagonism. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):820–827. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.820-827.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D. Promotion of the translocation of enteric bacteria from the gastrointestinal tracts of mice by oral treatment with penicillin, clindamycin, or metronidazole. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):854–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.854-861.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson A. B., Altemeier W. A., Bjornson H. S. Changes in humoral components of host defense following burn trauma. Ann Surg. 1977 Jul;186(1):88–96. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197707000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Gelder F., McDonald J. C. Prognostic significance of abnormal neutrophil chemotaxis after thermal injury. J Trauma. 1982 Mar;22(3):199–204. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198203000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Gelder F., McDonald J. C. The relationship between CIG depletion and peripheral neutrophil function in rabbits and man. J Trauma. 1982 Jun;22(6):469–475. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198206000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R. In vivo and in vitro antagonism of intestinal bacteria against Shigellaflexneri. II. The inhibitory mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jan-Feb;110:38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R., Jayne-Williams D. J. Resistance of the fowl (Gallus domesticus) to invasion by its intestinal flora. II. Clearance of translocated intestinal bacteria. Res Vet Sci. 1970 Jul;11(4):368–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartford C. E. The bequests of Moncrief and Moyer: an appraisal of topical therapy of burns- 1981 American Burn Association Presidential Address. J Trauma. 1981 Oct;21(10):827–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howerton E. E., Kolmen S. N. The intestinal tract as a portal of entry of Pseudomonas in burned rats. J Trauma. 1972 Apr;12(4):335–340. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197204000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munster A. M., Winchurch R. A., Birmingham W. J., Keeling P. Longitudinal assay of lymphocyte responsiveness in patients with major burns. Ann Surg. 1980 Dec;192(6):772–775. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198012000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OZAWA A., FRETER R. ECOLOGICAL MECHANISM CONTROLLING GROWTH OF ESCHERICHIA COLI IN CONTINUOUS FLOW CULTURES AND IN THE MOUSE INTESTINE. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:235–242. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens W. E., Berg R. D. Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract of athymic (nu/nu) mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):461–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.461-467.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Mercer A., Kusećek B., Pohl A., Achtman M. Induction of bacteremia in newborn rats by Escherichia coli K1 is correlated with only certain O (lipopolysaccharide) antigen types. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):599–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.599-608.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER H. L., MASON A. D., Jr, RAULSTON G. L. SURFACE INFECTION WITH PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. Ann Surg. 1964 Aug;160:297–305. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196408000-00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolochow H., Hildebrand G. J., Lamanna C. Translocation of microorganisms across the intestinal wall of the rat: effect of microbial size and concentration. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):523–528. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



