Abstract
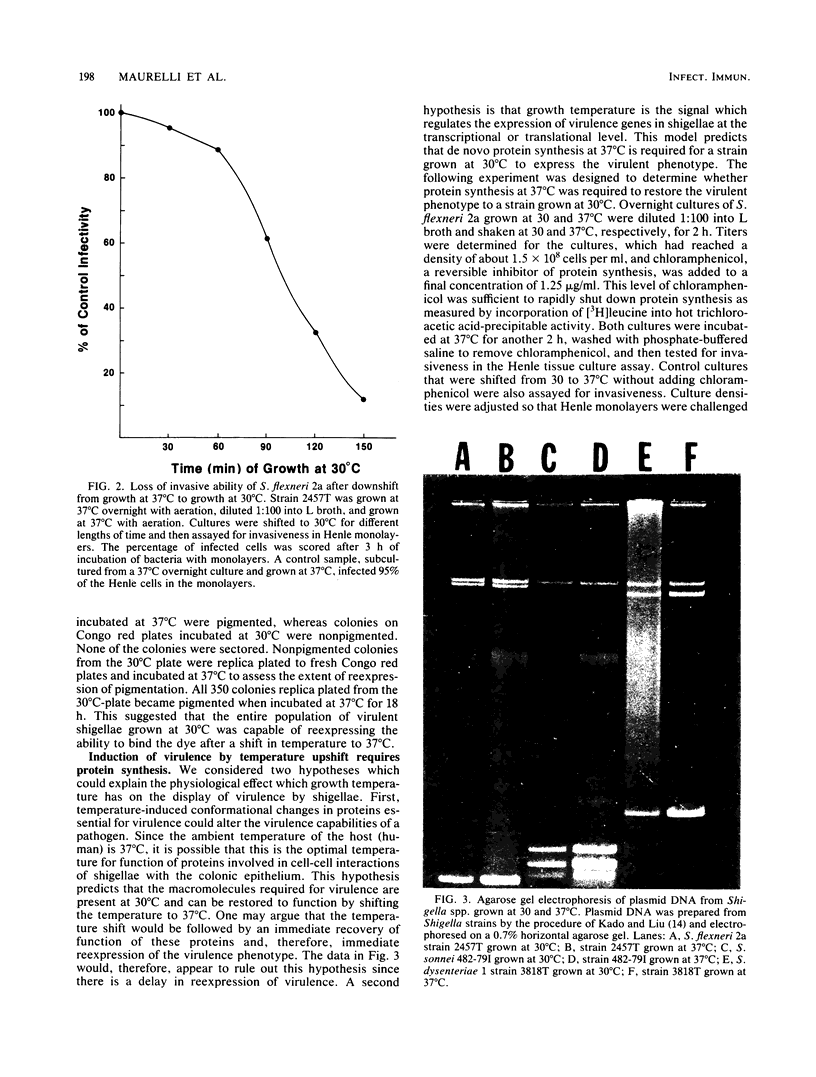
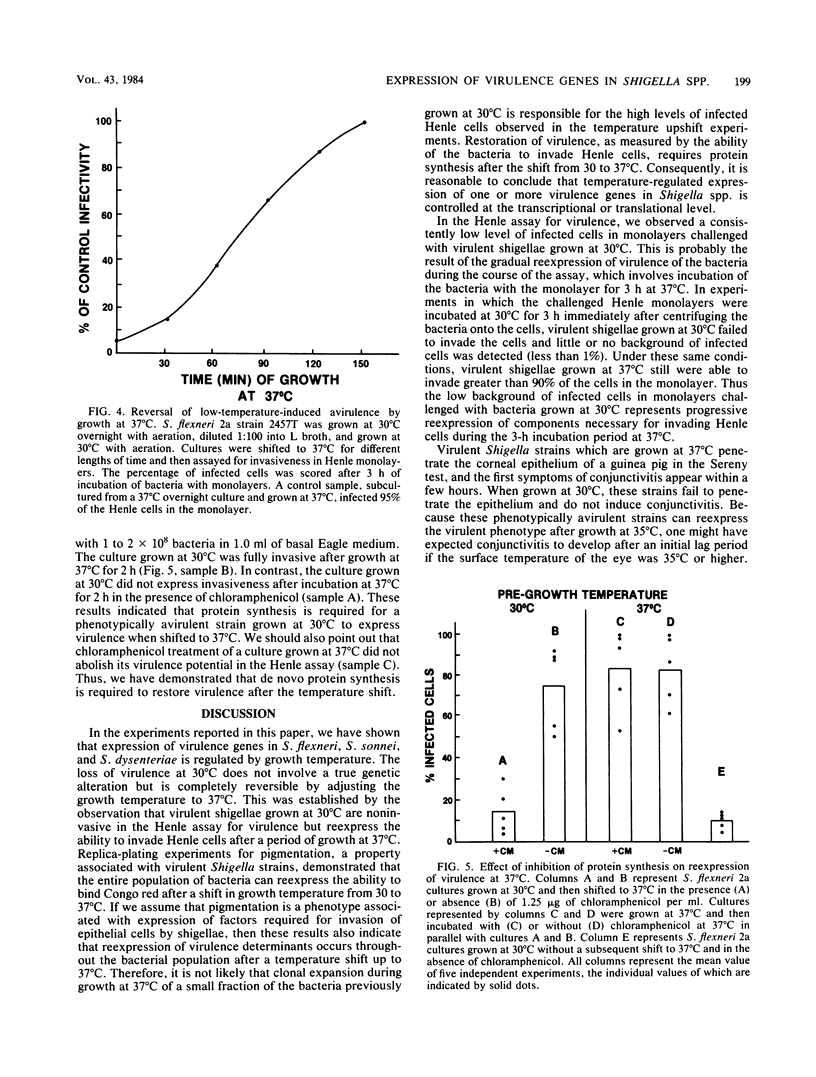
The pathogenicity of Shigella spp. involves the ability of the bacteria to penetrate and replicate within the epithelial cells of the large intestine. Model systems for examining the virulence of shigellae employ Henle intestinal epithelial cells in tissue culture and an in vivo assay for virulence in guinea pig eyes (Sereny test). Using these systems, we studied the genetic and physiological bases for the ability of shigellae to invade epithelial cells. We found that expression of virulence in Shigella spp. is dependent on the temperature at which the bacteria are grown. When grown at 37 degrees C, strains of Shigella flexneri 2a, Shigella sonnei, and Shigella dysenteriae 1 were fully virulent and invaded Henle cells. They also produced keratoconjunctivitis in guinea pigs. When grown at 30 degrees C, the bacteria neither penetrated Henle cells nor produced conjunctivitis in the Sereny test and were phenotypically avirulent. Strains grown at 33 degrees C were only partially invasive in the Henle assay, whereas strains grown at 35 degrees C were as invasive as strains grown at 37 degrees C. Using the Henle cell assay, we determined that the loss of ability to penetrate epithelial cells was completely reversed by shifting the growth temperature from 30 to 37 degrees C. The percentage of Henle cells invaded by bacteria increased with increasing time of growth at 37 degrees C. Restoration of invasiveness after growth at 30 degrees C required protein synthesis. When shigellae were grown at 30 degrees C and shifted to 37 degrees C for 2 h in the presence of chloramphenicol, the bacteria remained noninvasive. Similarly treated bacteria grown at 37 degrees C were still invasive. These results suggested that expression of one or more genes required for virulence of Shigella spp. are subject to regulation by growth temperature.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bortolussi R., Ferrieri P., Quie P. G. Influence of growth temperature of Escherichia coli on K1 capsular antigen production and resistance to opsonization. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1136–1141. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1136-1141.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows M. R., Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A. Haemagglutinating and adhesive properties associated with the K99 antigen of bovine strains of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):269–275. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., DAMMIN G. J., LABREC E. H., SCHNEIDER H. Experimental Shigella infections: characteristics of a fatal infection produced in guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):604–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.604-610.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Washington O., Formal S. B. Shigellosis due to Shigella dysenteriae. 1. Relative importance of mucosal invasion versus toxin production in pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):523–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENLE G., DEINHARDT F. The establishment of strains of human cells in tissue culture. J Immunol. 1957 Jul;79(1):54–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of Henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the bacterium. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):879–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.879-886.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Protein synthesis in HeLa or Henle 407 cells infected with Shigella dysenteriae 1, Shigella flexneri 2a, or Salmonella typhimurium W118. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.137-144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Smith M. G. The chromosome of bacteriophage T5. I. Analysis of the single-stranded DNA fragments by agarose gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Richardson L. A. The attachment to, and invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: the contribution of mannose-sensitive and mannose-resistant haemagglutinating activities. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):361–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A., Thorns C. J., Scott A. C., Sojka W. J. Adhesive properties associated with the Vir plasmid: a transmissible pathogenic characteristic associated with strains of invasive Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2097–2103. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAYLOR H. B., FUKUI G. M., McDUFF C. R. Effect of temperature on growth and virulence of Pasteurella pestis. Physical and nutritional requirements for restoration of virulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:649–655. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.649-655.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Smith H. W., Sojka W. J. The establishment of K99, a thermolabile, transmissible escherichia coli K antigen, previously called "Kco", possessed by calf and lamb enteropathogenic strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Feb;83(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Detection and differentiation of iron-responsive avirulent mutants on Congo red agar. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.94-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluth R. F., Fatt I. Temperature measurements in the eye. Exp Eye Res. 1977 Oct;25(4):325–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(77)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental keratoconjunctivitis shigellosa. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1957;4(4):367–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Shigella sonnei plasmids: evidence that a large plasmid is necessary for virulence. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.75-83.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P., David M., Toucas M. Corrélation entre la perte d'ADN plasmidique et le passage de la phase I virulente à la phase II avirulente chez Shigella sonnei. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1980 Mar 31;290(13):879–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Further observations on Escherichia coli enterotoxins with particular regard to those produced by atypical piglet strains and by calf and lamb strains: the transmissible nature of these enterotoxins and of a K antigen possessed by calf and lamb strains. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):243–250. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Localization in Yersinia pestis of peptides associated with virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):129–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.129-135.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Wientjes F. B., Klaasen-Boor P. Production of K99 antigen by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains of antigen groups o8, o9, o20, and o101 grown at different conditions. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):216–221. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.216-221.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]