Abstract
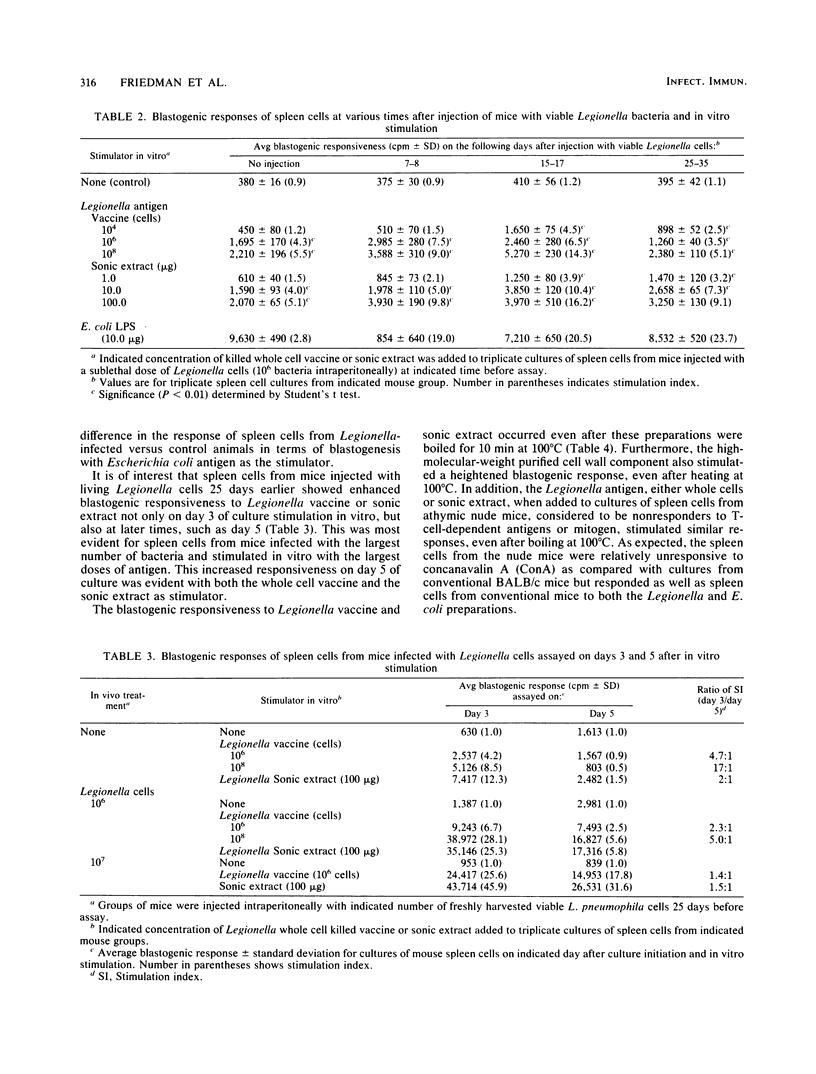
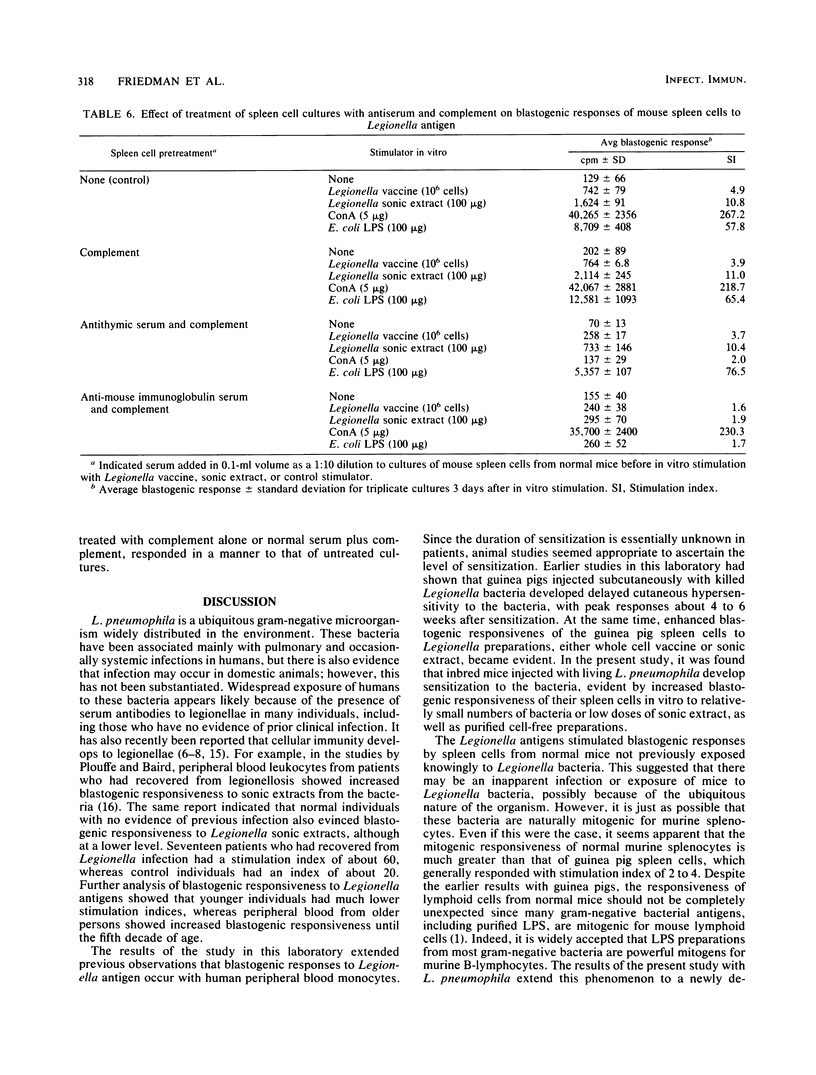
Legionella pneumophilia antigen preparations, either killed whole cell vaccine, a soluble sonic extract, or a purified large-molecular-weight somatic antigen, stimulated blastogenic responses by splenocytes from both normal and Legionella-sensitized mice. Graded amounts of the bacterial preparations, when added to cultures of normal spleen cells, resulted in increased uptake of thymidine into cellular DNA, indicating that the preparations were mitogenic for normal mouse splenocytes. Spleen cells from mice injected with graded numbers of living bacteria showed blastogenic responsiveness to Legionella preparations generally at a higher level than spleen cells from normal animals. The heightened blastogenic response was mainly evident with spleen cells obtained from mice injected with living bacteria 2 to 3 weeks earlier. Splenocytes from mice infected with legionella less than 1 to 2 weeks or for more than 4 to 5 weeks responded generally similar to those obtained from uninjected mice, indicating that sensitization with living organisms had a relatively short duration. Spleen cell suspensions responding to the L. pneumophila antigens appeared to be mainly B-lymphocytes since cell suspensions from athymic nude mice deficient in T-cells responded as well as cells from conventional mice. Furthermore, passage of splenocytes over nylon wool columns to obtain B-cell-enriched preparations resulted in cell populations capable of responding to Legionella antigen. The cell fractions rich in T-cells were much less capable of responding to the Legionella antigens. In addition, treatment of spleen cell populations with antitheta serum plus complement failed to inhibit the blastogenic response, whereas the same spleen cell preparations treated with anti-mouse immunoglobulin serum plus complement markedly diminished blastogenic responsiveness, again consistent with the likelihood that B-lymphocytes were the major cell class responding to the Legionella preparations.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elliott J. A., Johnson W., Helms C. M. Ultrastructural localization and protective activity of a high-molecular-weight antigen isolated from Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):822–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.822-824.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Orenstein W., Parkin W. E., Beecham H. J., Sharrar R. G., Harris J., Mallison G. F., Martin S. M., McDade J. E. Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1189–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman A. P., Katz S. M. The prevalence of serum antibodies to Legionella pneumophila in patients with chronic pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Feb;123(2):238–239. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund K. W., McGann V. G., Copeland D. S., Little S. F., Allen R. G. Immunologic protection against the Legionnaires' disease bacterium in the AKR/J mouse. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):676–679. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1618–1635. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Interaction of the legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) with human phagocytes. II. Antibody promotes binding of L. pneumophila to monocytes but does not inhibit intracellular multiplication. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):398–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W., Elliott J. A., Helms C. M., Renner E. D. A high molecular weight antigen in Legionnaires' disease bacterium: isolation and partial characterization. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):638–641. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., Kastello M. D., White J. D., Shirey F. G., McGann V. G., Larson E. W., Hedlund K. W. In vitro interaction between normal cynolmolgus monkey alveolar macrophages and Legionnaires disease bacteria. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):761–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.761-763.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., White J. D., Shirey F. G., McGann V. G., Berendt R. F., Larson E. W., Hedlund K. W. In vitro responses of guinea pig peritoneal macrophages to Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1209–1213. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1209-1213.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. C., Jones W. L., Feeley J. C. Upper limit of normal titer for detection of antibodies to Legionella pneumophila by the microagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):754–755. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.754-755.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease. Annu Rev Med. 1980;31:219–232. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.31.020180.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., George J. R., Reeves M. W., Harrell W. K. Development of a chemically defined liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):615–626. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.615-626.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouffe J. F., Baird I. M. Lymphocyte transformation to Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1981 May;5(3):149–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Cruce D. D., Broome C. V. Validation of Legionella pneumophila indirect immunofluorescence assay with epidemic sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.139-146.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Glavin F. L., Perl D. P., Keller J. L., Andres T. L., Brown T. M., Coffin C. M., Sensecqua J. E., Roman L. N., Craighead J. E. The pathology of Legionnaires' disease. Fourteen fatal cases from the 1977 outbreak in Vermont. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Jul;102(7):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


